LIO-SAM跑KITTI数据集和自己数据集代码修改
一、编译并运行LIO-SAM二、代码修改1、cloud_info.msg2、imageProjection.cpp 三、KITTI数据集准备四、自己数据集准备五、修改配置文件params.yaml六、GPS信息的添加七、效果图八、轨迹保存九、点云地图保存(PCD)1、注意到save_map.srv文件2、进入到mapOptmization.cpp3、最后在配置文件params.yaml修改参数4、PCD效果展示 全文参考文献
一、编译并运行LIO-SAM
参考我的另一篇文章:
Ubuntu20.04下的编译与运行LIO-SAM【问题解决】
二、代码修改
因为liosam 要求输入的点云每个点都有ring 信息和相对时间time信息,目前的雷达驱动基本具备这些信息,但是早期的KITTI数据集不具备,所以代码要自己计算一下 ring和time。方法可以参考lego-loam中这部分内容,具体修改如下。
1、cloud_info.msg
添加# 用于改写ring和time相关float32 startOrientationfloat32 endOrientationfloat32 orientationDiff2、imageProjection.cpp
ring部分:
1、把ring通道强制关闭2、添加计算ring代码if (false){rowIdn = laserCloudIn->points[i].ring;} else {verticalAngle = atan2(thisPoint.z, sqrt(thisPoint.x * thisPoint.x + thisPoint.y * thisPoint.y)) * 180 / M_PI;// 拿16、32、64线激光雷达为例if(N_SCAN == 16) {rowIdn = int((verticalAngle + 15) / 2 + 0.5);if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN){continue;} else if(rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0) {continue;}} else if (N_SCAN == 32) { rowIdn = int((verticalAngle + 92.0 / 3.0) * 3.0 / 4.0); if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN) { continue; } else if(rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0) { continue; } } else if (N_SCAN == 64) { if (verticalAngle >= -8.83) { rowIdn = int((2 - verticalAngle) * 3.0 + 0.5); } else { rowIdn = N_SCAN / 2 + int((-8.83 - verticalAngle) * 2.0 + 0.5); } // use [0 50] > 50 remove outlies if (verticalAngle > 2 || verticalAngle < -24.33 || rowIdn > 50 || rowIdn < 0) { continue; } else if(rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0) { continue; } } else { printf("wrong scan number\n"); ROS_BREAK(); }}time部分:
1、把time通道强制关闭2、计算time并赋值bool halfPassed = false;int cloudNum = laserCloudIn->points.size();// start and end orientation of this cloudcloudInfo.startOrientation = -atan2(laserCloudIn->points[0].y, laserCloudIn->points[0].x);cloudInfo.endOrientation = -atan2(laserCloudIn->points[laserCloudIn->points.size() - 1].y, laserCloudIn->points[laserCloudIn->points.size() - 1].x) + 2 * M_PI;if (cloudInfo.endOrientation - cloudInfo.startOrientation > 3 * M_PI) { cloudInfo.endOrientation -= 2 * M_PI;} else if (cloudInfo.endOrientation - cloudInfo.startOrientation < M_PI) { cloudInfo.endOrientation += 2 * M_PI;}cloudInfo.orientationDiff = cloudInfo.endOrientation - cloudInfo.startOrientation;PointType point;for (int i = 0; i < cloudNum; ++i){ point.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x; point.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y; point.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z; float ori = -atan2(point.y, point.x); if (!halfPassed) { if (ori < cloudInfo.startOrientation - M_PI / 2) { ori += 2 * M_PI; } else if (ori > cloudInfo.startOrientation + M_PI * 3 / 2) { ori -= 2 * M_PI; } if (ori - cloudInfo.startOrientation > M_PI) { halfPassed = true; } } else { ori += 2 * M_PI; if (ori < cloudInfo.endOrientation - M_PI * 3 / 2) { ori += 2 * M_PI; } else if (ori > cloudInfo.endOrientation + M_PI / 2) { ori -= 2 * M_PI; } } float relTime = (ori - cloudInfo.startOrientation) / cloudInfo.orientationDiff; // 激光雷达10Hz,周期0.1 laserCloudIn->points[i].time = 0.1 * relTime;}需要修改好的,可以查看我的。
三、KITTI数据集准备
关于KITTI数据集,已有公开的kitti2bag工具,使用方法:参见我的另一个博客在Ubuntu20.04系统上将KITTI原始数据集转化为.bag形式。但是输出的bag文件liosam是不能正常跑的,位姿Z型突变,仔细了解一下发现这个bag的imu频率跟雷达一样,也就是很低频,无法满足代码需求。liosam作者提供了一个2011_09_30_drive_0028.bag在google drive,但可能无法快速下载。
如果想自己制作bag,作者自己改了kitti2bag就在源码的文件夹下,你需要准备如下文件(文件位置需对应):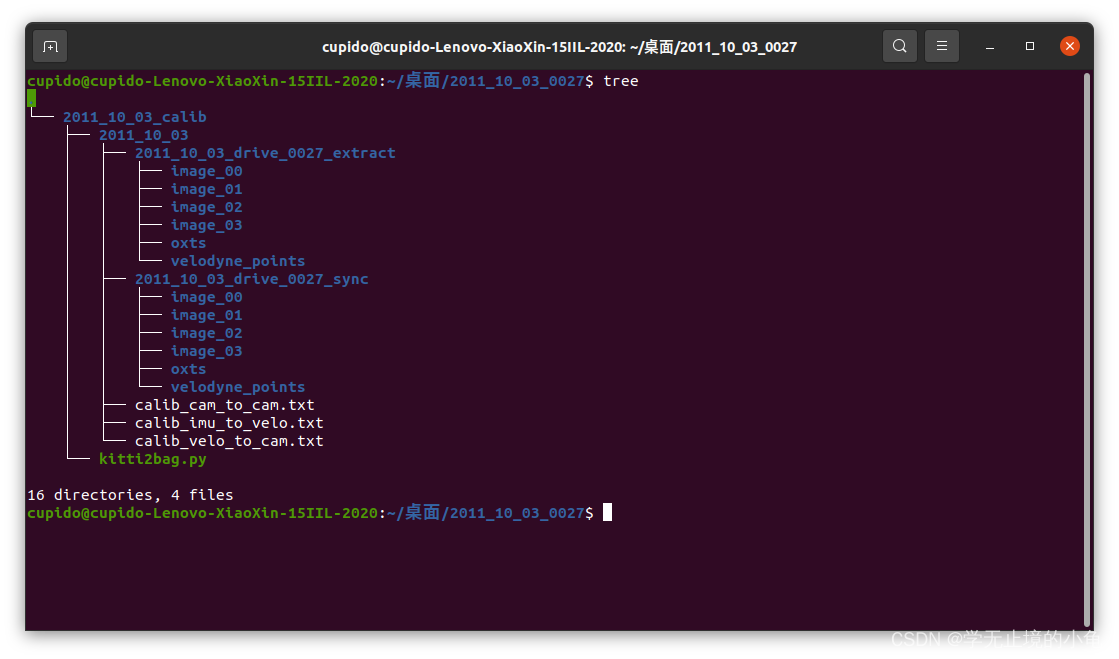
首先,在终端输入以下指令:
pip3 install tqdm效果:
然后,在"2011_10_03"文件夹的上一级目录(即:此处的2011_10_03_calib文件下),打开终端,输入:
python3 kitti2bag.py -t 2011_10_03 -r 0027 raw_synced注意自己的文件的文件名
效果如下: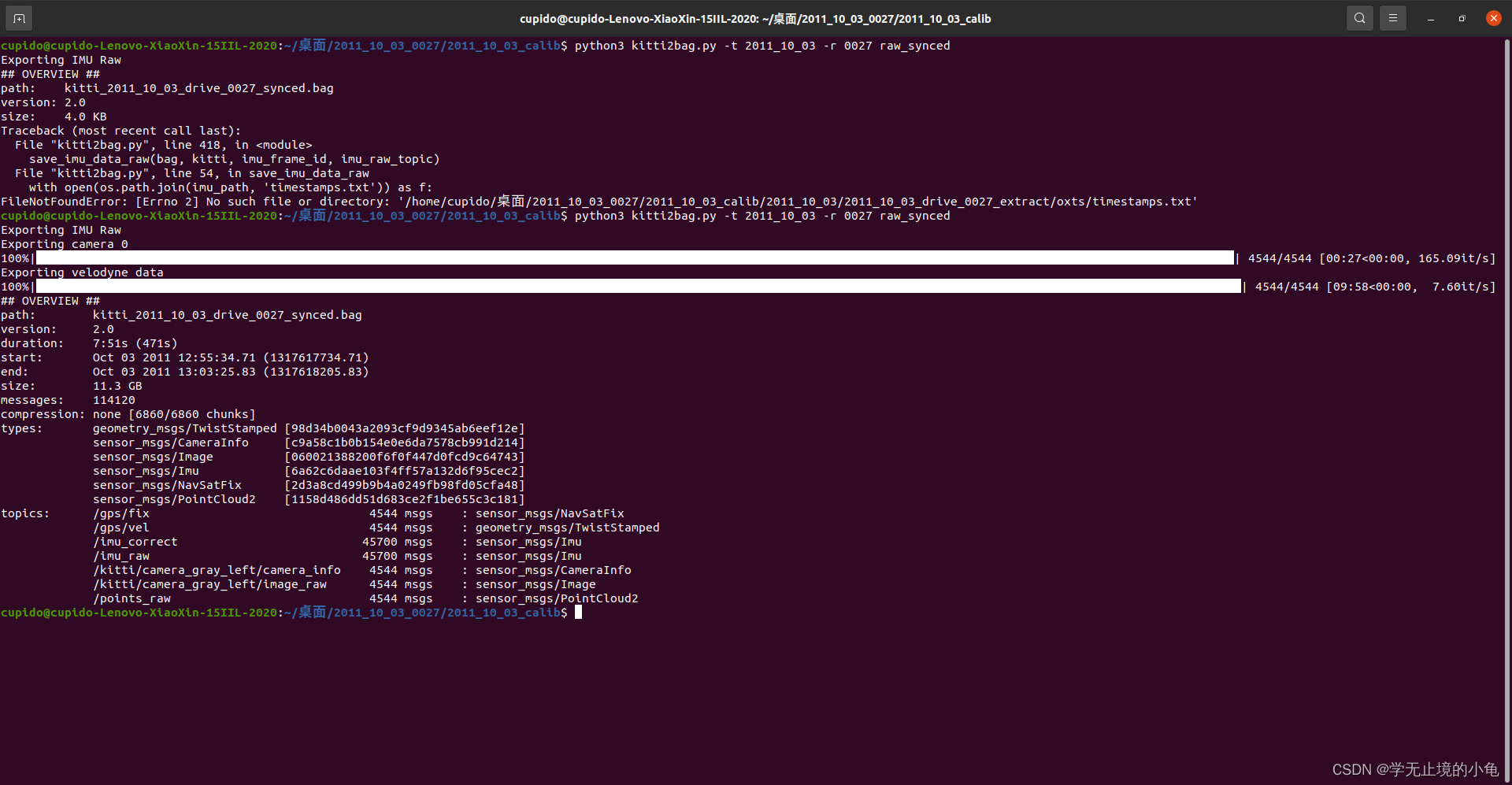
我第一次文件位置不对,导致无法生成bag文件
四、自己数据集准备
具体采集步骤在后续更新…
五、修改配置文件params.yaml
1、话题名修改
# Topics pointCloudTopic: "points_raw" # Point cloud data imuTopic: "imu_raw" # IMU data2、根据KITTI采集数据的实际传感器修改对应参数
# KITTI sensor: velodyne # lidar sensor type, either 'velodyne' or 'ouster' N_SCAN: 64 # number of lidar channel (i.e., 16, 32, 64, 128) Horizon_SCAN: 2083 # lidar horizontal resolution (Velodyne:1800, Ouster:512,1024,2048) downsampleRate: 1 # default: 1. Downsample your data if too many points. i.e., 16 = 64 / 4, 16 = 16 / 1 lidarMinRange: 1.0 # default: 1.0, minimum lidar range to be used lidarMaxRange: 1000.0 # default: 1000.0, maximum lidar range to be used对照我的另一个博客:LeGO-LOAM跑KITTI数据集评估方法【代码改】
3、外参的修改
# kitti外参 extrinsicTrans: [-8.086759e-01, 3.195559e-01, -7.997231e-01] extrinsicRot: [9.999976e-01, 7.553071e-04, -2.035826e-03, -7.854027e-04, 9.998898e-01, -1.482298e-02, 2.024406e-03, 1.482454e-02, 9.998881e-01] extrinsicRPY: [9.999976e-01, 7.553071e-04, -2.035826e-03, -7.854027e-04, 9.998898e-01, -1.482298e-02, 2.024406e-03, 1.482454e-02, 9.998881e-01]注意点:
1、配置文件(params.yaml)内的参数通过参数服务器传送进源程序,会覆盖掉头文件内(utility.h)的对应参数。
2、其中extrinsicRot表示imu -> lidar的坐标变换,用于旋转imu坐标系下的角速度和线加速度到lidar坐标系下,extrinsicRPY则用于旋转imu坐标系下的欧拉角(姿态信息)到lidar坐标下,由于lio-sam作者使用的imu的欧拉角旋转指向与lidar坐标系不一致,因此使用了两个不同的旋转矩阵,但是大部分的设备两个旋转应该是设置为相同的。
六、GPS信息的添加
待更新…
七、效果图
KITTI: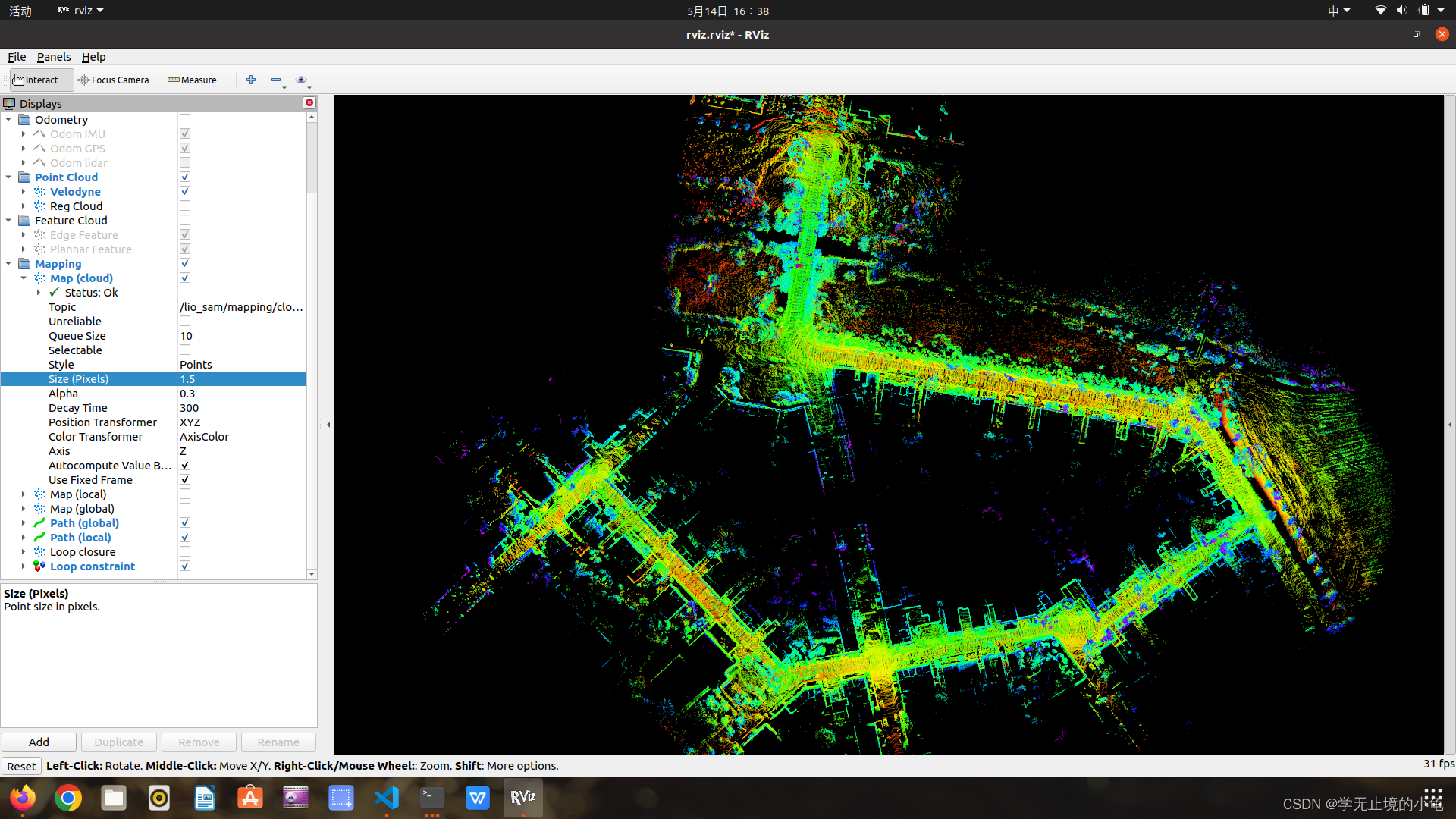
00的可能会飞,05以后的应该没问题
八、轨迹保存
找到输出位姿信息,通过以下代码,输出位姿信息(KITTI格式):
// 位姿输出到txt文档std::ofstream pose1("/home/cupido/output-data/lio-sam/pose.txt", std::ios::app);pose1.setf(std::ios::scientific, std::ios::floatfield);// pose1.precision(15);//save final trajectory in the left camera coordinate system.Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;rotation_matrix = Eigen::AngleAxisd(pose_in.yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) * Eigen::AngleAxisd(pose_in.pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) * Eigen::AngleAxisd(pose_in.roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> mylio_pose;mylio_pose.topLeftCorner(3,3) = rotation_matrix;mylio_pose(0,3) = pose_in.x;mylio_pose(1,3) = pose_in.y;mylio_pose(2,3) = pose_in.z;Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> cali_paremeter;/*cali_paremeter << 4.276802385584e-04, -9.999672484946e-01, -8.084491683471e-03, -1.198459927713e-02, //00-02 -7.210626507497e-03, 8.081198471645e-03, -9.999413164504e-01, -5.403984729748e-02, 9.999738645903e-01, 4.859485810390e-04, -7.206933692422e-03, -2.921968648686e-01, 0, 0, 0, 1;*//*cali_paremeter << -1.857739385241e-03,-9.999659513510e-01, -8.039975204516e-03, -4.784029760483e-03, -6.481465826011e-03, 8.051860151134e-03, -9.999466081774e-01, -7.337429464231e-02, 9.999773098287e-01, -1.805528627661e-03, -6.496203536139e-03, -3.339968064433e-01, //04-10 0 0, 0, 1;*/cali_paremeter << 2.347736981471e-04, -9.999441545438e-01, -1.056347781105e-02, -2.796816941295e-03, 1.044940741659e-02, 1.056535364138e-02, -9.998895741176e-01, -7.510879138296e-02, 9.999453885620e-01, 1.243653783865e-04, 1.045130299567e-02, -2.721327964059e-01, 0, 0, 0, 1; Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> myloam_pose_f;myloam_pose_f = cali_paremeter * mylio_pose * cali_paremeter.inverse();pose1 << myloam_pose_f(0,0) << " " << myloam_pose_f(0,1) << " " << myloam_pose_f(0,2) << " " << myloam_pose_f(0,3) << " " << myloam_pose_f(1,0) << " " << myloam_pose_f(1,1) << " " << myloam_pose_f(1,2) << " " << myloam_pose_f(1,3) << " " << myloam_pose_f(2,0) << " " << myloam_pose_f(2,1) << " " << myloam_pose_f(2,2) << " " << myloam_pose_f(2,3) << std::endl;pose1.close();欧拉角到四元素的转换除了用eigen,还可以参考大佬:四元数与欧拉角(Yaw、Pitch、Roll)的转换
补充tum格式的轨迹输出(拿ALOAM举例,LIO-SAM修改相关参数即可)
// 位姿输出到txt文档std::ofstream pose1("/home/cupido/output-data/kitti/sequences/07/aloam.txt", std::ios::app);pose1.setf(std::ios::scientific, std::ios::floatfield);pose1.precision(15);//save final trajectory in the left camera coordinate system.Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;rotation_matrix = q_w_curr.toRotationMatrix();Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> myaloam_pose;myaloam_pose.topLeftCorner(3,3) = rotation_matrix;myaloam_pose(0,3) = t_w_curr.x();myaloam_pose(1,3) = t_w_curr.y();myaloam_pose(2,3) = t_w_curr.z();Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> cali_paremeter;// cali_paremeter << 4.276802385584e-04, -9.999672484946e-01, -8.084491683471e-03, -1.198459927713e-02, //00-02// -7.210626507497e-03, 8.081198471645e-03, -9.999413164504e-01, -5.403984729748e-02, // 9.999738645903e-01, 4.859485810390e-04, -7.206933692422e-03, -2.921968648686e-01,// 0, 0, 0, 1;cali_paremeter << -1.857739385241e-03,-9.999659513510e-01, -8.039975204516e-03, -4.784029760483e-03, //04-10 -6.481465826011e-03, 8.051860151134e-03, -9.999466081774e-01, -7.337429464231e-02, 9.999773098287e-01, -1.805528627661e-03, -6.496203536139e-03, -3.339968064433e-01, 0, 0, 0, 1;/*cali_paremeter << 2.347736981471e-04, -9.999441545438e-01, -1.056347781105e-02, -2.796816941295e-03, // 03 1.044940741659e-02, 1.056535364138e-02, -9.998895741176e-01, -7.510879138296e-02, 9.999453885620e-01, 1.243653783865e-04, 1.045130299567e-02, -2.721327964059e-01, 0, 0, 0, 1;*/ Eigen::Matrix<double, 4, 4> myloam_pose_f;myloam_pose_f = cali_paremeter * myaloam_pose * cali_paremeter.inverse();Eigen::Matrix3d temp;temp = myloam_pose_f.topLeftCorner(3,3);Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion(temp);// 获取当前更新的时间 这样与ground turth对比才更准确static double timeStart = odometryBuf.front()-> header.stamp.toSec();// 相当于是第一帧的时间auto T1 = ros::Time().fromSec(timeStart);pose1 << odomAftMapped.header.stamp - T1 << " " << myloam_pose_f(0,3) << " " << myloam_pose_f(1,3) << " " << myloam_pose_f(2,3) << " " << quaternion.x() << " " << quaternion.y() << " " << quaternion.z() << " " << quaternion.w() << std::endl;pose1.close();注意点:
1、输出路径注意修改
2、评估轨迹精度的时候,输出轨迹若发现未和真值完全对齐(这里指的是,不考虑自己算法精度,单纯两轨迹对齐),可以在终端输入以下指令:
//(注意是-a,不是--align_origin)evo_ape tum groundtruth.txt xxx.txt -a -p九、点云地图保存(PCD)
追根溯源:
1、注意到save_map.srv文件
float32 resolutionstring destination---bool success2、进入到mapOptmization.cpp
相关代码:
// 订阅一个保存地图功能的服务srvSaveMap = nh.advertiseService("lio_sam/save_map", &mapOptimization::saveMapService, this);/** * 保存全局关键帧特征点集合 */bool saveMapService(lio_sam::save_mapRequest& req, lio_sam::save_mapResponse& res){ string saveMapDirectory; cout << "****************************************************" << endl; cout << "Saving map to pcd files ..." << endl; // 如果是空,说明是程序结束后的自动保存,否则是中途调用ros的service发布的保存指令 if(req.destination.empty()) saveMapDirectory = std::getenv("HOME") + savePCDDirectory; else saveMapDirectory = std::getenv("HOME") + req.destination; cout << "Save destination: " << saveMapDirectory << endl; // create directory and remove old files; // 删掉之前有可能保存过的地图 int unused = system((std::string("exec rm -r ") + saveMapDirectory).c_str()); unused = system((std::string("mkdir -p ") + saveMapDirectory).c_str()); // save key frame transformations // 首先保存历史关键帧轨迹 pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/trajectory.pcd", *cloudKeyPoses3D); pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/transformations.pcd", *cloudKeyPoses6D); // extract global point cloud map(提取历史关键帧角点、平面点集合) pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr globalCornerCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>()); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr globalCornerCloudDS(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>()); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr globalSurfCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>()); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr globalSurfCloudDS(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>()); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr globalMapCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>()); // 遍历所有关键帧,将点云全部转移到世界坐标系下去 for (int i = 0; i < (int)cloudKeyPoses3D->size(); i++) { *globalCornerCloud += *transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[i], &cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i]); *globalSurfCloud += *transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[i], &cloudKeyPoses6D->points[i]); // 类似进度条的功能 cout << "\r" << std::flush << "Processing feature cloud " << i << " of " << cloudKeyPoses6D->size() << " ..."; } // 如果没有指定分辨率,就是直接保存 if(req.resolution != 0) { cout << "\n\nSave resolution: " << req.resolution << endl; // down-sample and save corner cloud // 使用指定分辨率降采样,分别保存角点地图和面点地图 downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(globalCornerCloud); downSizeFilterCorner.setLeafSize(req.resolution, req.resolution, req.resolution); downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*globalCornerCloudDS); pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/CornerMap.pcd", *globalCornerCloudDS); // down-sample and save surf cloud downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(globalSurfCloud); downSizeFilterSurf.setLeafSize(req.resolution, req.resolution, req.resolution); downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*globalSurfCloudDS); pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/SurfMap.pcd", *globalSurfCloudDS); } else { // save corner cloud pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/CornerMap.pcd", *globalCornerCloud); // save surf cloud pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/SurfMap.pcd", *globalSurfCloud); } // save global point cloud map(保存到一起,全局关键帧特征点集合) *globalMapCloud += *globalCornerCloud; *globalMapCloud += *globalSurfCloud; // 保存全局地图 int ret = pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(saveMapDirectory + "/GlobalMap.pcd", *globalMapCloud); res.success = ret == 0; downSizeFilterCorner.setLeafSize(mappingCornerLeafSize, mappingCornerLeafSize, mappingCornerLeafSize); downSizeFilterSurf.setLeafSize(mappingSurfLeafSize, mappingSurfLeafSize, mappingSurfLeafSize); cout << "****************************************************" << endl; cout << "Saving map to pcd files completed\n" << endl; return true;}std::thread visualizeMapThread(&mapOptimization::visualizeGlobalMapThread, &MO); // 可视化的线程(负责rviz相关可视化接口的发布)visualizeMapThread.join();/** * 展示线程 * 1、发布局部关键帧map的特征点云 * 2、保存全局关键帧特征点集合 */ // 全局可视化线程 void visualizeGlobalMapThread() { // 更新频率设置为0.2hz ros::Rate rate(0.2); while (ros::ok()){ rate.sleep(); // 发布局部关键帧map的特征点云 publishGlobalMap(); } // 当ros被杀死之后,执行保存地图功能 if (savePCD == false) return; lio_sam::save_mapRequest req; lio_sam::save_mapResponse res; // 保存全局关键帧特征点集合 if(!saveMapService(req, res)){ cout << "Fail to save map" << endl; } }这里注意到 if (savePCD == false)判断条件,转至配置文件params.yaml
3、最后在配置文件params.yaml修改参数
打开开关:
savePCD: true # https://github.com/TixiaoShan/LIO-SAM/issues/3更改路径:
savePCDDirectory: "/output-data/lio-sam/PCD/" # in your home folder, starts and ends with "/". Warning: the code deletes "LOAM" folder then recreates it. See "mapOptimization" for implementation对应路径和自身电脑的全局路径的关系如下: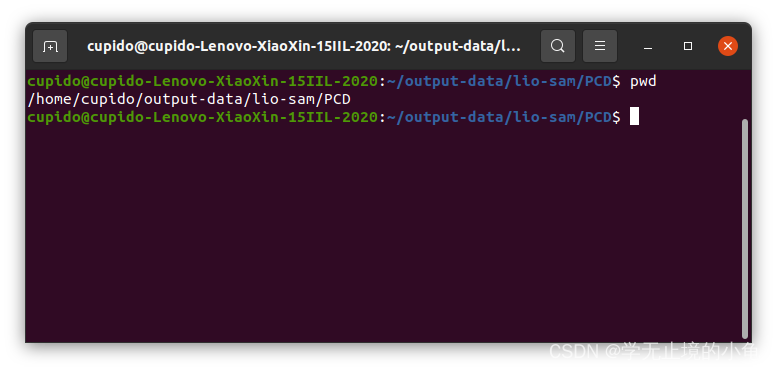
4、PCD效果展示
1、指令:
pcl_viewer xxx.pcd2、效果图:
此节参考大佬:
1、lio-sam中点云地图保存
2、复现lio_sam激光slam算法创建点云地图
3、PCL保存LIO-SAM地图时报错[pcl::PCDWriter::writeBinary]
全文参考文献
1、ubuntu18运行编译LIO-SAM并用官网和自己的数据建图(修改汇总)
2、LIO-SAM运行自己数据包遇到的问题解决–SLAM不学无数术小问题
3、使用开源激光SLAM方案LIO-SAM运行KITTI数据集,如有用,请评论雷锋
4、LIO-SAM:配置环境、安装测试、适配⾃⼰采集数据集
5、SLAM学习笔记(十九)开源3D激光SLAM总结大全——Cartographer3D,LOAM,Lego-LOAM,LIO-SAM,LVI-SAM,Livox-LOAM的原理解析及区别
6、多传感器融合定位 第六章 惯性导航结算及误差模型