用红黑树封装map、set
1. 红黑树1.1 模板参数的控制1.1.1 Value1.1.2 KeyOfValue 1.2 正向迭代器1.2.1 构造函数1.2.2 begin()+end()1.2.3 operator++()1.2.4 operator--()1.2.5 operator*()1.2.6 operator->()1.2.7 operator==()1.2.8 operator!=()1.2.9 总代码 1.3 反向迭代器1.3.1 rbegin()+rend()1.3.2 总代码 1.4 find()1.5 insert() 2. Map2.1 operator[] 3. typename作用4. 完整代码4.1 Map.h4.2 Set.h4.3 RBTree.h
1. 红黑树
set是K模型,map是KV模型,二者底层都是使用红黑树来实现的,所以我们可以将红黑树设置为模板,即:set、map复用同一个类模板的红黑树。1.1 模板参数的控制
1.1.1 Value
Value决定你是k模型的set、还是KV模型的map。
enum Color { //枚举,一一列举出事物具有的所有可能Red, //枚举常量,给枚举变量进行赋值Black,};template<class T>//红黑树的节点struct RBTreeNode {typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//三叉链-》优点:便于查找孩子、父亲节点Node* _left; //该节点的左孩子Node* _right; //该节点的右孩子Node* _parent; //该节点的父亲,便于向上更新T _data;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data, Color col = Red) //构造函数:_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _col(col) //默认新插入节点的颜色为红色{ }};//Value决定你是k模型的set、还是KV模型的maptemplate<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBTree { public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;};template<class K>class set{ //K模型public: private: //set中的key不允许被修改RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t; //红黑树对象};}template<class K, class V>class map { //KV模型 public:private: //map中的key不允许被修改RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t; //红黑树对象};};
1.1.2 KeyOfValue
KeyOfT : 取出Value对象中的key。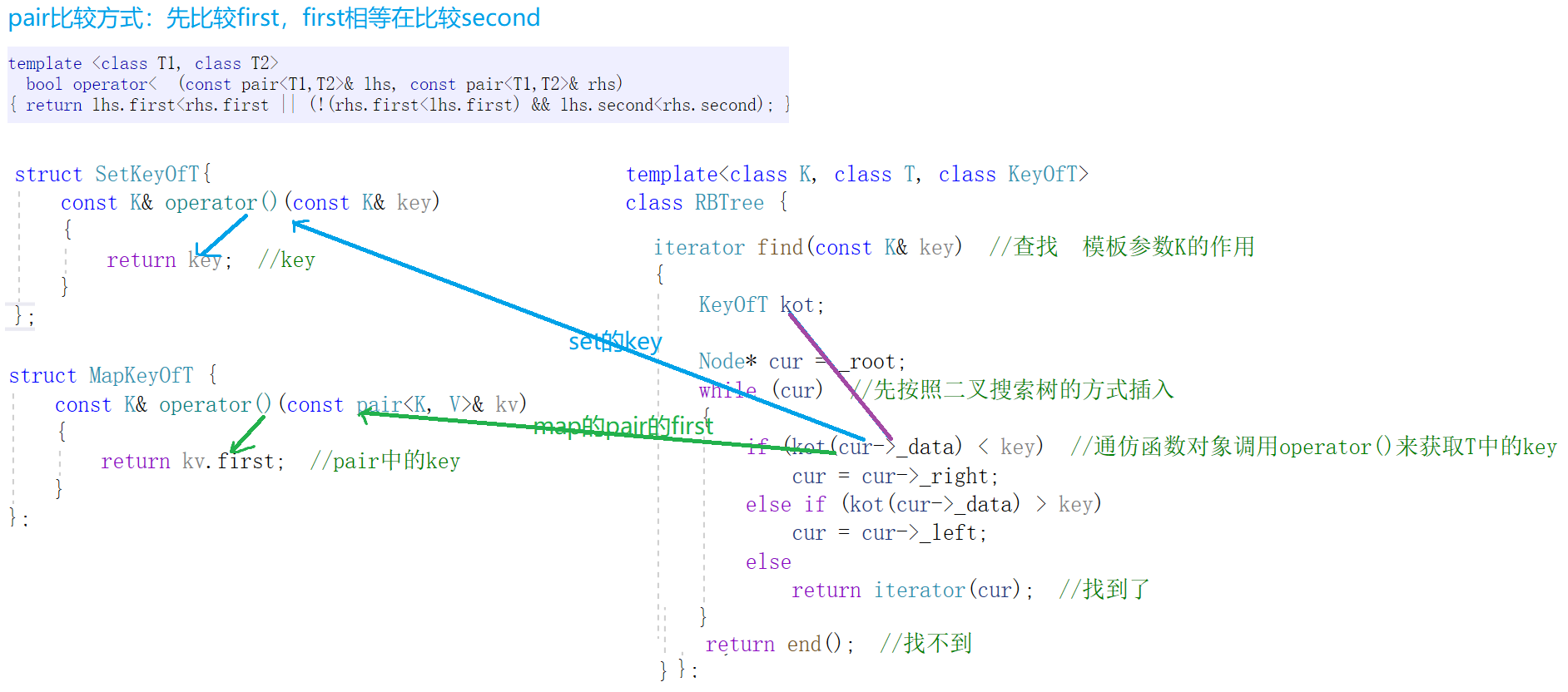
// KeyOfT : 取出Value对象中的keytemplate<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBTree { };struct SetKeyOfT{ const K& operator()(const K& key){return key; //key}};struct MapKeyOfT {const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first; //pair中的key}};
1.2 正向迭代器
1.2.1 构造函数
?RBTreeIterator(Node* node) ;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node) //构造函数,单参数构造函数支持隐式类型转化:_node(node){ }1.2.2 begin()+end()
?iterator begin( ) ;
功能:返回红黑树中最左节点(左孩子必为空)的迭代器。Tips:set、map对象为非const对象,就调用begin()、end()。iterator begin() //红黑树最左节点{ Node* subLeft = _root; while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)subLeft = subLeft->_left;return iterator(subLeft);}?iterator end( ) ;
功能:返回最后一个元素的下一个的迭代器(空指针)。iterator end() //空指针 左闭右开[begin,end){return iterator(nullptr);}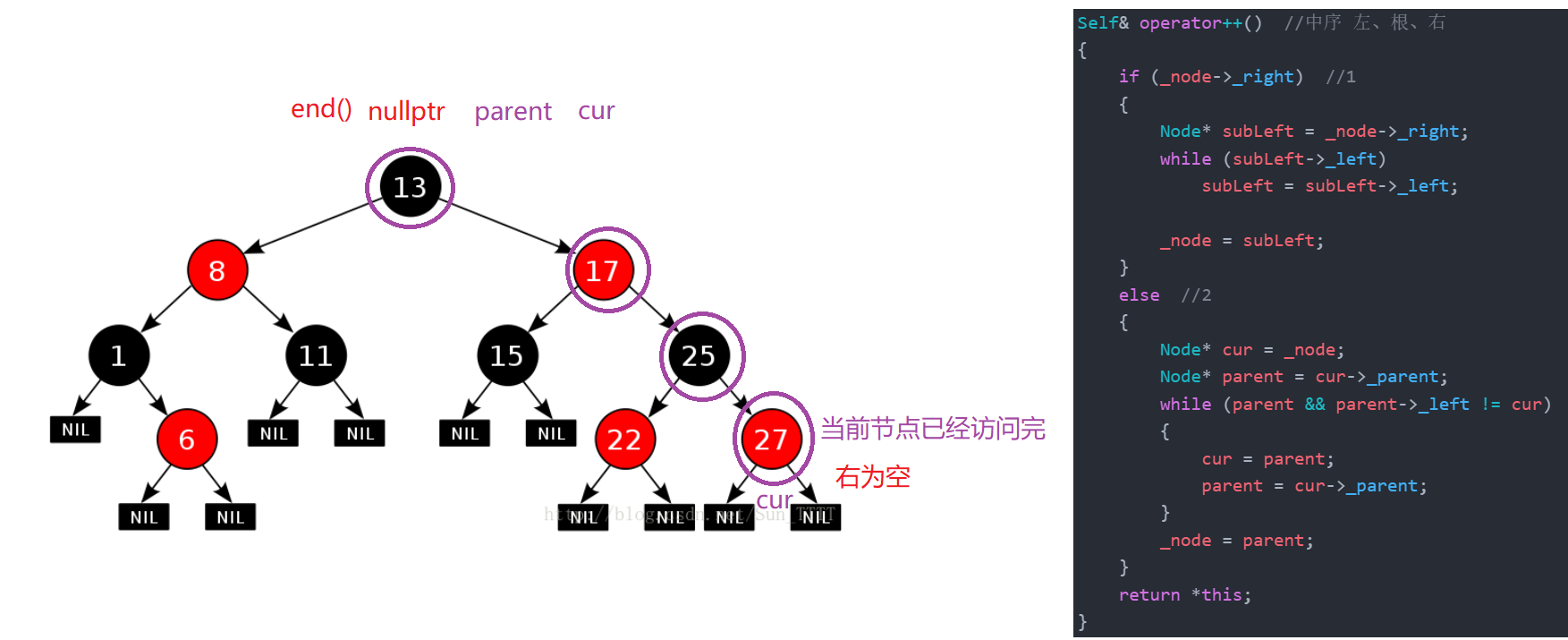
1.2.3 operator++()
/*1.右不为空,下一个为该节点右子树的最左节点 ;* 2.右为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的右,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,* 直到该节点为父亲的左,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲左*/Self& operator++() //中序 左、根、右{if (_node->_right) //1{Node* subLeft = _node->_right;while (subLeft->_left)subLeft = subLeft->_left;_node = subLeft;}else //2{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left != cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}情况一:右不为空,下一个为该节点右子树的最左节点 ;
情况二:右为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的右,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,直到该节点为父亲的左,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲左。
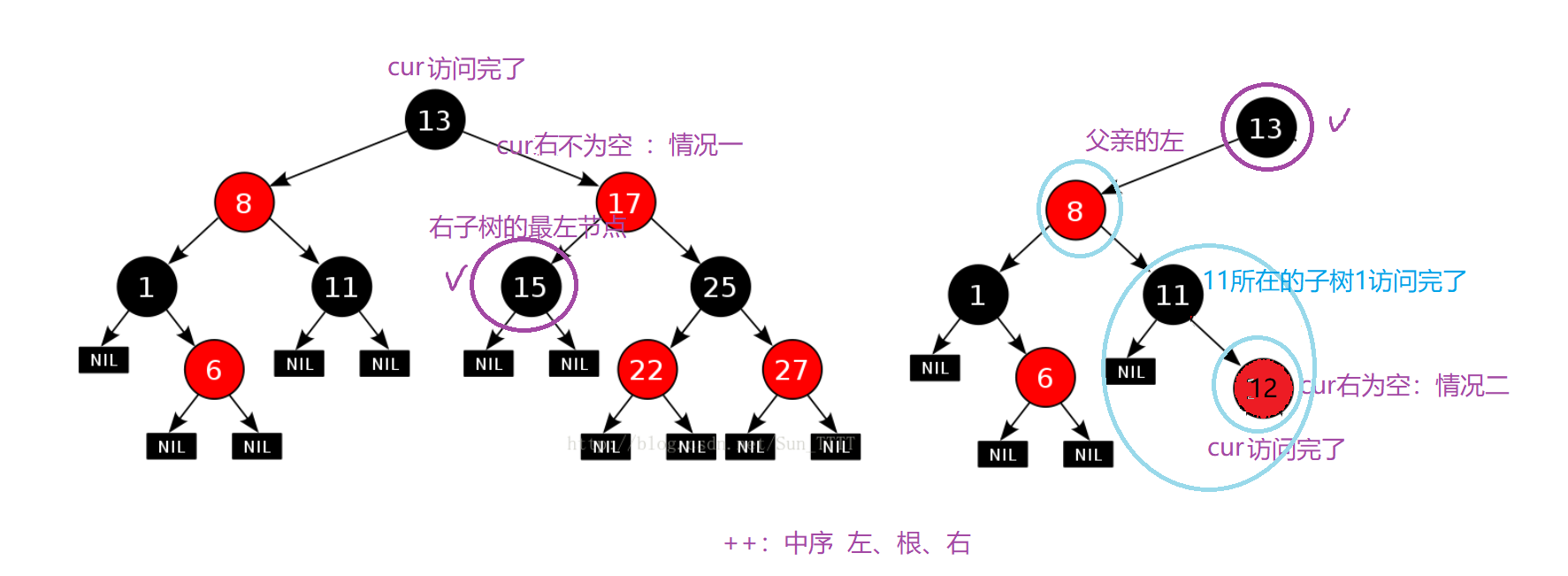
1.2.4 operator–()
/*1.左不为空,下一个为该节点左子树的最右节点 ;* 2.左为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的左,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,* 直到该节点为父亲的右,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲右*/Self& operator--() //中序 左、根、右 --与++逻辑相反{if (_node->_left) //1{Node* subRight = _node->_left;while (subRight->_right)subRight = subRight->_right;_node = subRight;}else //2{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_right != cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}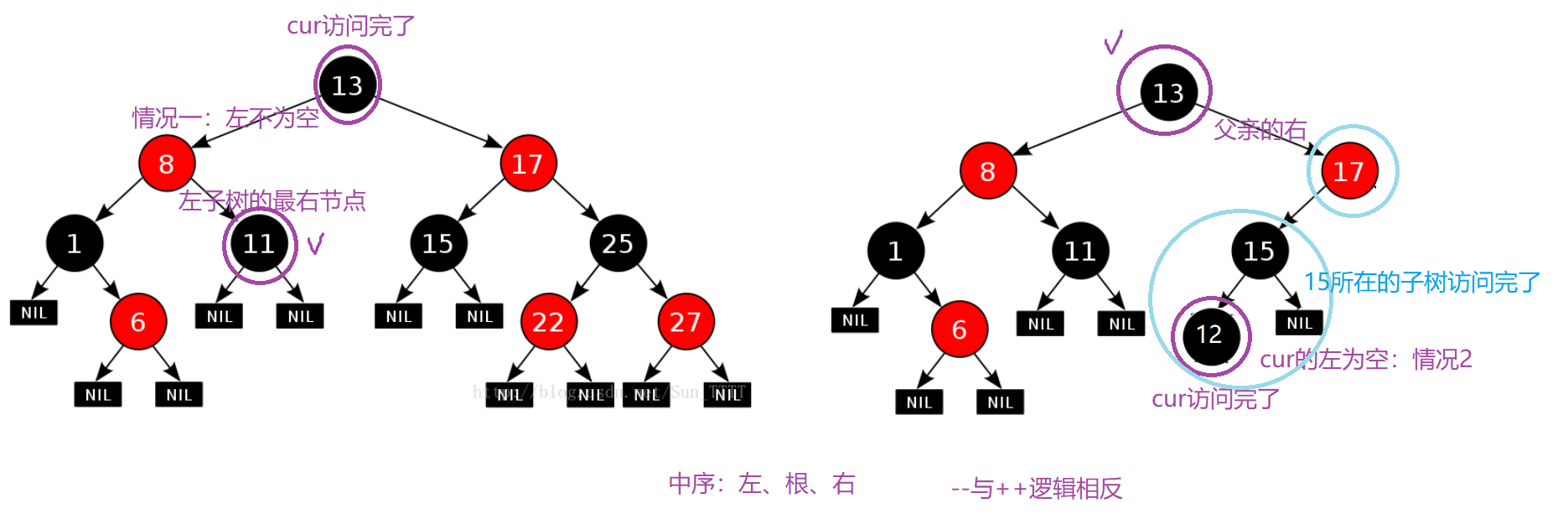
1.2.5 operator*()
Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}
1.2.6 operator->()
Ptr operator->() //结构体指针,data为结构体{return &_node->_data;}
1.2.7 operator==()
bool operator==(const Self& rb){return _node == rb._node;}
1.2.8 operator!=()
bool operator!=(const Self& rb){return _node != rb._node;}
1.2.9 总代码
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct RBTreeIterator //红黑树的正向迭代器{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;RBTreeIterator(Node* node) //构造函数,单参数构造函数支持隐式类型转化:_node(node){ }Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->() //结构体指针,data为结构体{return &_node->_data;}/*1.右不为空,下一个为该节点右子树的最左节点 ;* 2.右为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的右,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,* 直到该节点为父亲的左,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲左*/Self& operator++() //中序 左、根、右{if (_node->_right) //1{Node* subLeft = _node->_right;while (subLeft->_left)subLeft = subLeft->_left;_node = subLeft;}else //2{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left != cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}/*1.左不为空,下一个为该节点左子树的最右节点 ;* 2.左为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的左,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,* 直到该节点为父亲的右,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲右*/Self& operator--() //中序 左、根、右 --与++逻辑相反{if (_node->_left) //1{Node* subRight = _node->_left;while (subRight->_right)subRight = subRight->_right;_node = subRight;}else //2{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_right != cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& rb){return _node != rb._node;}bool operator==(const Self& rb){return _node == rb._node;}};
1.3 反向迭代器
1.3.1 rbegin()+rend()
?reverse_iterator rbegin( ) ;
功能:返回红黑树中最右节点(右孩子必为空)的迭代器。reverse_iterator rbegin() //红黑树最右节点,因为此处反向迭代器*,是直接调用正向迭代器* [rbegin,erend){Node* subRight = _root;while (subRight && subRight->_right)subRight = subRight->_right;return reverse_iterator(subRight);}?reverse_iterator rend( ) ;
功能:返回第一个元素的前一个的迭代器(空指针)。reverse_iterator rend() {return reverse_iterator(nullptr);}
1.3.2 总代码
template<class iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ReverseIterator //红黑树的反向迭代器——适配器 begin = rend、end = rbegin{typedef ReverseIterator<iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self; iterator _it; //适配器ReverseIterator(iterator it):_it(it){ }Ref operator*(){return *_it;}Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*()); //}Self& operator++(){--_it;return *this;}Self& operator--(){++_it;return *this;}bool operator==(const Self& rb){return _it == rb._it;}bool operator!=(const Self& rb){return _it != rb._it;}};
1.4 find()
?iterator find(const K& key) ;
功能:查找。若key在红黑树中,则返回树中与key值相等元素的迭代器,否则,就返回end( )。iterator find(const K& key) //查找 模板参数K的作用{KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur) //先按照二叉搜索树的方式插入{if (kot(cur->_data) < key) //通仿函数对象调用operator()来获取T中的keycur = cur->_right;else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)cur = cur->_left;elsereturn iterator(cur); //找到了}return end(); //找不到}
1.5 insert()
?pair<iterator,bool> insert(const T& data) ;
功能:向红黑树中插入data。
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data) //插入 { //不能使用引用放回,因为返回值作用域为栈区,传值返回KeyOfT kot; //仿函数类创建的对象,对象去调用operator()Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur) //先按照二叉搜索树的方式插入 { if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) //通仿函数对象调用operator()来获取T中的key值 { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return make_pair(iterator(cur), false); //插入节点已存在,插入失败,返回在树中与该节点值相同的迭代器 } } cur = new Node(data); //注意 insertNode* newnode = cur; //非空树,插入成功,因为要做旋转处理,会导致cur值发生改变,需提前将新节点的位置存储起来if (parent == nullptr) //空树{_root = cur;_root->_col = Black; //跟节点为黑return make_pair(iterator(_root), true); //空树,插入成功,返回新插入节点在树中的迭代器}if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(cur->_data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent; //记录当前节点的父亲//更新颜色//插入结束:1.插入节点的父亲是黑色,因为插入前该树就为红黑树 2.情况一处理完后,cur为根节点,且为黑色while (parent && parent->_col == Red){ //爷爷一定存在,因为c为红,p为红,所以p一定不是根节点,且一定有父节点Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left) //旋转需要确定方向{Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red) //情况一:叔叔存在且为红->无方向(p、u为g的任意边,c为p的任一边){ //cur可能为新增节点,也可能一开始为黑色,cur的子树(下一层为红,下一层为新插入节点)在调整过程中将cur由黑变为红parent->_col = uncle->_col = Black; //p、u变为黑,g变为红grandfather->_col = Red;//g可能为根节点(更新结束),也可能为子树(继续向上更新)cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //情况二:叔叔不存在 或者 叔叔存在且为黑{ //叔叔不存在,cur为新增节点 或 cur原来为黑,经子树调整由黑变红if (parent->_left == cur) //左左——右单旋{RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black; //p变为黑,g变为红grandfather->_col = Red;}else //左右——左右单旋 {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black; //c变黑,g变红grandfather->_col = Red;}break; //更新结束:3.旋转+颜色处理后就是红黑树了}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){parent->_col = uncle->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur) //右右——左单旋{RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else //右左——右左单旋{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black; //g为根,颜色变为黑,更新结束return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true); //情况一,插入节点的父亲为黑,插入结束}
2. Map
2.1 operator[]
?V& operator[ ](const K& key) ;
功能:访问与key相对应的value值。即可读又可写。原理:operator[ ]底层是通过调用insert( )将键值队插入到map中。如果key存在,插入失败,insert返回与map中key值相同元素的迭代器。如果key不存在,插入成功,insert返回在map中新插入元素的迭代器。operator[ ]最后返回与key值相对应的value值的引用。operator[ ] 具有插入、查找、插入+修改、查找+修改功能。V& operator[](const K& key) //功能:查找+修改、插入+修改{pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}
3. typename作用
使用域作用限定符(: : )的两种情况:静态变量、类中typedef的类型。使用typename表示: :后面为类型,不是静态成员//使用::两种情况:静态变量、类中typedef的类型 typename表示::前面为类型,不是静态成员typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
4. 完整代码
4.1 Map.h
#pragma once#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"RBTree.h"#include<string>namespace zzx {template<class K, class V>class map { //KV模型 public:struct MapKeyOfT {const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first; //pair中的key}};//使用::两种情况:静态变量、类中typedef的类型 typename表示::前面为类型,不是静态成员typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator; //正向迭代器typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator; //反向迭代器iterator begin() {return _t.begin();}iterator end() {return _t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return _t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend(){return _t.rend();}iterator find(const K& key) //查找{return _t.find(key);}pair<iterator, bool> insert(pair<const K, V>& kv) //插入{return _t.insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key) //功能:查找+修改、插入+修改{pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}private: //map中的key不允许被修改RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t; //红黑树对象};};
4.2 Set.h
#pragma once#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"RBTree.h"namespace zzx{template<class K>class set{ //K模型public: //仿函数类:比较对象大小,获取对象中的元素—自己手动传递比较逻辑struct SetKeyOfT{ const K& operator()(const K& key){return key; //key}};//使用::两种情况:静态变量、类中typedef的类型 typename表示::后面为类型,不是静态成员typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator; //正向迭代器typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator; //反向迭代器iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return _t.rbegin();}reverse_iterator rend(){return _t.rend();}iterator find(const K& key) //查找{return _t.find(key);}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key) //插入{return _t.insert(key);}private: //set中的key不允许被修改RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t; //红黑树对象};}4.3 RBTree.h
#pragma once#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include<iostream>using namespace std;enum Color { //枚举,一一列举出事物具有的所有可能Red, //枚举常量,给枚举变量进行赋值Black,};template<class T>//红黑树的节点struct RBTreeNode {typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//三叉链-》优点:便于查找孩子、父亲节点Node* _left; //该节点的左孩子Node* _right; //该节点的右孩子Node* _parent; //该节点的父亲,便于向上更新T _data;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data, Color col = Red) //构造函数:_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _col(col) //默认新插入节点的颜色为红色{ }};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct RBTreeIterator //红黑树的正向迭代器{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;RBTreeIterator(Node* node) //构造函数,单参数构造函数支持隐式类型转化:_node(node){ }Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->() //结构体指针,data为结构体{return &_node->_data;}/*1.右不为空,下一个为该节点右子树的最左节点 ;* 2.右为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的右,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,* 直到该节点为父亲的左,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲左*/Self& operator++() //中序 左、根、右{if (_node->_right) //1{Node* subLeft = _node->_right;while (subLeft->_left)subLeft = subLeft->_left;_node = subLeft;}else //2{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left != cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}/*1.左不为空,下一个为该节点左子树的最右节点 ;* 2.左为空,说明该节点所在的子树已经访问完了,若该节点为父亲的左,说明该父亲所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,* 直到该节点为父亲的右,则要访问的下一个节点是它的父亲,即:找祖先里面的孩纸 = 父亲右*/Self& operator--() //中序 左、根、右 --与++逻辑相反{if (_node->_left) //1{Node* subRight = _node->_left;while (subRight->_right)subRight = subRight->_right;_node = subRight;}else //2{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_right != cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& rb){return _node != rb._node;}bool operator==(const Self& rb){return _node == rb._node;}};template<class iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ReverseIterator //红黑树的反向迭代器——适配器 begin = rend、end = rbegin{typedef ReverseIterator<iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self; iterator _it; //适配器ReverseIterator(iterator it):_it(it){ }Ref operator*(){return *_it;}Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*()); //}Self& operator++(){--_it;return *this;}Self& operator--(){++_it;return *this;}bool operator==(const Self& rb){return _it == rb._it;}bool operator!=(const Self& rb){return _it != rb._it;}};//红黑树的模板参数:T决定你是k模型的set、还是KV模型的map ; KeyOfT:取出T对象中的key ; pair比较:先比较first,在比较secondtemplate<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBTree { public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//正向迭代器typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; //普通迭代器typedef RBTreeIterator<T,const T&, const T*> const_iterator; //const迭代器//反向迭代器typedef ReverseIterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;iterator begin() //红黑树最左节点{ Node* subLeft = _root; while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)subLeft = subLeft->_left;return iterator(subLeft);}iterator end() //空指针 左闭右开[begin,end){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin()const {Node* subLeft = _root;while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)subLeft = subLeft->_left;return const_iterator(subLeft);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}reverse_iterator rbegin() //红黑树最右节点,因为此处反向迭代器*,是直接调用正向迭代器* [rbegin,erend){Node* subRight = _root;while (subRight && subRight->_right)subRight = subRight->_right;return reverse_iterator(subRight);}reverse_iterator rend() {return reverse_iterator(nullptr);}const_reverse_iterator rbegin()const{Node* subRight = _root;while (subRight && subRight->_right)subRight = subRight->_right;return const_reverse_iterator(subRight);}const_reverse_iterator rend()const{return const_reverse_iterator(nullptr);}iterator find(const K& key) //查找 模板参数K的作用{KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur) //先按照二叉搜索树的方式插入{if (kot(cur->_data) < key) //通仿函数对象调用operator()来获取T中的keycur = cur->_right;else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)cur = cur->_left;elsereturn iterator(cur); //找到了}return end(); //找不到}void RotateL(Node* parent) //右右—左单旋{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;Node* pphead = parent->_parent;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pphead->_left == parent)pphead->_left = subR;elsepphead->_right = subR;subR->_parent = pphead;}}void RotateR(Node* parent) //左左—右单旋{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;Node* pphead = parent->_parent;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pphead->_left == parent)pphead->_left = subL;elsepphead->_right = subL;subL->_parent = pphead;}}void RotateRL(Node* parent) //右左—先右旋再左旋{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;RotateR(subR);RotateL(parent);}void RotateLR(Node* parent) //左右—先左旋再右旋{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;RotateL(subL);RotateR(parent);}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data) //插入 { //不能使用引用放回,因为返回值作用域为栈区,传值返回KeyOfT kot; //仿函数类创建的对象,对象去调用operator()Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur) //先按照二叉搜索树的方式插入{if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) //通仿函数对象调用operator()来获取T中的key值{parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(iterator(cur), false); //插入节点已存在,插入失败,返回在树中与该节点值相同的迭代器}}cur = new Node(data); //注意 insertNode* newnode = cur; //非空树,插入成功,因为要做旋转处理,会导致cur值发生改变,需提前将新节点的位置存储起来if (parent == nullptr) //空树{_root = cur;_root->_col = Black; //跟节点为黑return make_pair(iterator(_root), true); //空树,插入成功,返回新插入节点在树中的迭代器}if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(cur->_data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent; //记录当前节点的父亲//更新颜色//插入结束:1.插入节点的父亲是黑色,因为插入前该树就为红黑树 2.情况一处理完后,cur为根节点,且为黑色while (parent && parent->_col == Red){ //爷爷一定存在,因为c为红,p为红,所以p一定不是根节点,且一定有父节点Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left) //旋转需要确定方向{Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red) //情况一:叔叔存在且为红->无方向(p、u为g的任意边,c为p的任一边){ //cur可能为新增节点,也可能一开始为黑色,cur的子树(下一层为红,下一层为新插入节点)在调整过程中将cur由黑变为红parent->_col = uncle->_col = Black; //p、u变为黑,g变为红grandfather->_col = Red;//g可能为根节点(更新结束),也可能为子树(继续向上更新)cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //情况二:叔叔不存在 或者 叔叔存在且为黑{ //叔叔不存在,cur为新增节点 或 cur原来为黑,经子树调整由黑变红if (parent->_left == cur) //左左——右单旋{RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = Black; //p变为黑,g变为红grandfather->_col = Red;}else //左右——左右单旋 {RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = Black; //c变黑,g变红grandfather->_col = Red;}break; //更新结束:3.旋转+颜色处理后就是红黑树了}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red){parent->_col = uncle->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (parent->_right == cur) //右右——左单旋{RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}else //右左——右左单旋{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = Black;grandfather->_col = Red;}break;}}}_root->_col = Black; //g为根,颜色变为黑,更新结束return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true); //情况一,插入节点的父亲为黑,插入结束}private:Node* _root = nullptr;};