目录
1、手写一个简单的本地缓存1.1、封装缓存实体类1.2、创建缓存工具类1.3、测试 2、Guava Cache2.1、Guava Cache 简介2.2、入门案例2.2.1、引入 POM 依赖2.2.2、创建 LoadingCache 缓存 2.3、Guava Cache 的优劣势和适用场景 3、Caffeine3.1、Caffeine 简介3.2、对比 Guava Cache 的性能主要优化项3.3、入门案例3.3.1、引入 POM 依赖3.3.2、开启缓存功能3.3.3、配置缓存管理器3.3.4、编写 User 实体类3.3.5、编写 UserServceImpl 4、Ehcache4.1、Ehcache 简介4.2、入门案例【Ehcache3.x 】4.2.1、引入 POM4.2.2、开启缓存功能4.2.3、配置缓存管理器4.2.4、编写 UserServceImpl4.2.5、编写 TestController 5、JetCache5.1、JetCache 简介5.2、JetCache 核心概念5.3、入门案例5.3.1、引入依赖5.3.2、修改配置文件5.3.3、添加配置扫描注解5.3.4、使用 JetCache5.3.4.1、添加 `UserServiceImpl`: 5.3.4.2、添加 `TestController`:5.3.5、JetCache 中常用的注解5.3.5.1、`@Cached` 注解5.3.5.1.1、cacheType 属性 5.3.5.2、`@CacheUpdate` 注解5.3.5..3、`@CacheInvalidate` 注解
1、手写一个简单的本地缓存
1.1、封装缓存实体类
封装一个缓存实体类,包括:缓存键、缓存值、过期时间。如下:
@Datapublic class CacheEntity { // 缓存键 private String key; // 缓存键 private Object value; // 过期时间 private Long expireTime; }1.2、创建缓存工具类
缓存工具类:
使用 Map 结构存储数据添加缓存:将数据添加到 Map 结构中删除缓存:从 Map 结构中删除数据查询缓存:从 Map 结构中获取数据清除缓存:有定时任务定期扫描 Map,并删除过期的数据public class CacheUtil { // 存缓存数据 private final static Map<String, CacheEntity> CACHE_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); // 定时器线程池,用于清理过期缓存 private static ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); static { // 注册一个定时任务,服务启动 1000 毫秒后,每隔 500 毫秒执行一次 Runnable task = CacheUtil::clear; executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, 1000L, 500L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); }// 添加缓存 public static void put(String key, Object value) { put(key, value, 0L); }// 添加缓存 public static void put(String key, Object value, Long expire) { CacheEntity cacheEntity = new CacheEntity(); cacheEntity.setKey(key); cacheEntity.setValue(value); if (expire > 0) { // 计算过期时间 Long expireTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + Duration.ofSeconds(expire).toMillis(); cacheEntity.setExpireTime(expireTime); } CACHE_MAP.put(key, cacheEntity); }// 获取 public static Object get(String key) { if (CACHE_MAP.containsKey(key)) { return CACHE_MAP.get(key); } return null; }// 删除 public static void remove(String key) { CACHE_MAP.remove(key); }// 清除过期缓存 public static void clear() { if (CACHE_MAP.isEmpty()) { return; } CACHE_MAP.entrySet().removeIf(entityEntry -> entityEntry.getValue().getExpireTime() != null && entityEntry.getValue().getExpireTime() > System.currentTimeMillis()); }}实现思路:采用 ConcurrentHashMap 作为缓存数据存储服务,然后开启一个定时调度,每隔 500 毫秒检查一下过期的缓存数据并清除
1.3、测试
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CacheUtil.put("name", "zzc", 10L); System.out.println("第一次查询结果:" + CacheUtil.get("name")); Thread.sleep(2000L); System.out.println("第二次查询结果:" + CacheUtil.get("name")); }}2、Guava Cache
2.1、Guava Cache 简介
Guava Cache 是 Google 开发的 Guava 工具包中一套完善的 JVM 本地缓存框架,底层实现的数据结构类似于 ConcurrentHashMap,但是进行了更多的能力拓展,包括:缓存过期时间设置、缓存容量设置、多种淘汰策略、缓存监控等。
Guava Cache 是一个支持高并发的线程安全的本地缓存。多线程情况下也可以安全的访问或者更新 Cache,这些都是借鉴了 ConcurrentHashMap 的结果
它的特点:
支持最大容量限制支持两种过期删除策略(插入时间和读取时间)支持简单的统计功能基于 LRU 算法实现2.2、入门案例
SpringBoot 整合 Guava Cache 实现本地缓存
2.2.1、引入 POM 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>32.0.0-jre</version></dependency>2.2.2、创建 LoadingCache 缓存
Guava Cache 使用时主要分二种模式:
LoadingCache 创建时需要有合理的默认方法来加载或计算与键关联的值CallableCache 创建时无需关联固定的 CacheLoader 使用起来更加灵活 这里以 创建 LoadingCache 缓存 为例:
在创建 LoadingCache 时,需要指定 CacheLoader【理解为一个固定的加载器】,然后简单地重写 V load(K key) throws Exception 方法,就可以达到当检索不存在的时候自动加载数据的效果
代码如下:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException { LoadingCache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() //设置并发级别为 8,并发级别是指可以同时写缓存的线程数 .concurrencyLevel(8) // 初始化缓存容量 .initialCapacity(10) // 最大缓存容量,超出就淘汰 —— 基于容量进行回收 .maximumSize(100L) // 是否需要统计缓存情况,该操作消耗一定的性能,生产环境应该去除 .recordStats() // 设置缓存过期时间【写入缓存后多久过期】,超过这个时间就淘汰 —— 基于时间进行回收 .expireAfterWrite(10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 设置缓存刷新时间【写入缓存后多久刷新缓存】,超过这个时间就刷新缓存,并调用refresh方法,默认是异步刷新 .refreshAfterWrite(5L, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // key 使用弱引用 WeakReference .weakKeys() // 当 Entry 被移除时的监听器 .removalListener(notification -> System.out.println("notification=" + notification)) // 创建一个 CacheLoader,重写 load() 方法,以实现"当 get() 时缓存不存在,则调用 load() 方法,放到缓存并返回"的效果 .build(new CacheLoader<String, String>() { // 自动写缓存数据的方法 @Override public String load(String key) throws Exception { System.out.println("调用 load() 方法, key 为:" + key); return "zzc"; } // 异步刷新缓存 @Override public ListenableFuture<String> reload(String key, String oldValue) throws Exception { return super.reload(key, oldValue); } }); cache.put("name", "zzc"); // key 为 name 时,不会调用 load() 方法,直接从缓存中获取【因为先执行了 put() 方法】 String nameValue = cache.get("name"); // key 为 age 时,会调用 load() 方法 String ageValue = cache.get("age"); // key 为 age 时,不会调用 load() 方法, 直接返回 Callable#call() 方法结果 String sexValue = cache.get("sex", () -> "key 不存在"); }}在调用 CacheBuilder#build() 方法时,必须传递一个 CacheLoader 类型的参数,CacheLoader#load() 方法需要我们提供实现:当调用 LoadingCache#get() 方法时,如果缓存不存在对应 key 的记录,则CacheLoader#load() 方法会被自动调用从外存加载数据,load() 方法的返回值会作为 key 对应的 value存储到 LoadingCache 中,并从 get() 方法返回。
2.3、Guava Cache 的优劣势和适用场景
优劣势:Guava Cache 通过内存处理数据,具有减少 IO 请求,读写性能快的优势,但是受内存容量限制,只能处理少量数据的读写,还有可能对本机内存造成压力,并且在分布式部署中,会存在不同机器节点数据不一致的情况,即缓存漂移适用场景:读多写少,对数据一致性要求不高的场景 3、Caffeine
3.1、Caffeine 简介
Caffeine 官网
Caffeine 是基于Java 1.8 的高性能本地缓存库,同样是 Google 开发的,由 Guava 改进而来,底层设计思路、功能和使用方式与 Guava 非常类似,但是各方面的性能都要远远超过前者,可以看做是 Guava Cache 的升级版。而且在 Spring5 开始的默认缓存实现就将 Caffeine 代替原来的 Google Guava,官方说明指出,其缓存命中率已经接近最优值
可以通过下图观测到,在下面缓存组件中 Caffeine 性能是其中最好的:
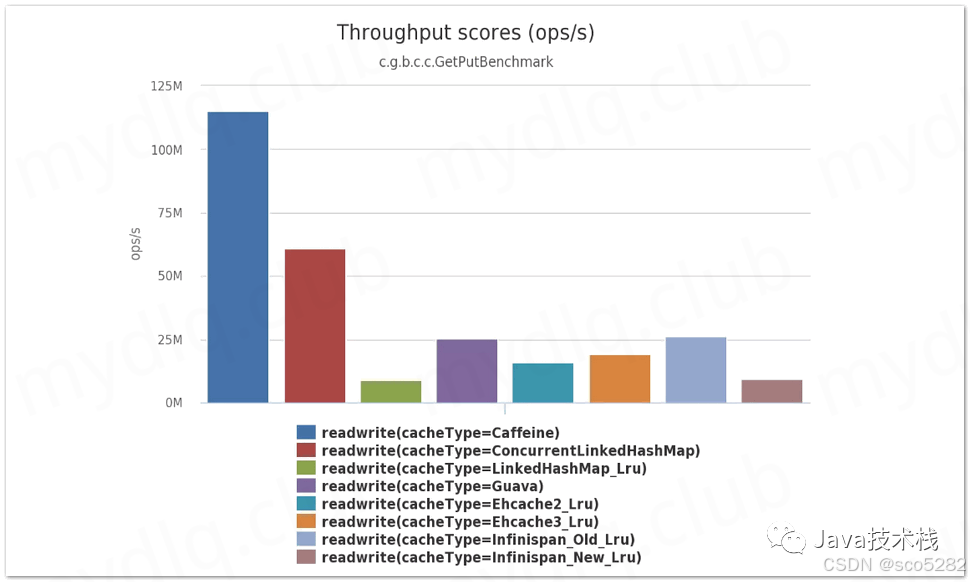
3.2、对比 Guava Cache 的性能主要优化项
Caffeine 底层又做了哪些优化,才能让其性能高于 Guava Cache 呢?主要包含以下三点:
异步策略:Guava Cache 在读操作中可能会触发淘汰数据的清理操作,虽然自身也做了一些优化来减少读的时候的清理操作,但是一旦触发,就会降低查询效率,对缓存性能产生影响。而Caffeine 支持异步操作,采用异步处理的策略,查询请求在触发淘汰数据的清理操作后,会将清理数据的任务添加到独立的线程池中进行异步操作,不会阻塞查询请求,提高了查询性能ConcurrentHashMap 优化:Caffeine 底层都是通过ConcurrentHashMap 来进行数据的存储,因此随着 Java8 中对 ConcurrentHashMap 的调整,数组 + 链表的结构升级为数组 + 链表 + 红黑树的结构以及分段锁升级为 syschronized + CAS,降低了锁的粒度,减少了锁的竞争,这两个优化显著提高了 Caffeine 在读多写少场景下的查询性能新型淘汰算法 W-TinyLFU:传统的淘汰算法,如 LRU、LFU、FIFO,在实际的缓存场景中都存在一些弊端。因此,Caffeine 引入了 W-TinyLFU 算法,由窗口缓存、过滤器、主缓存组成。缓存数据刚进入时会停留在窗口缓存中,这个部分只占总缓存的 1%,当被挤出窗口缓存时,会在过滤器汇总和主缓存中淘汰的数据进行比较,如果频率更高,则进入主缓存,否则就被淘汰,主缓存被分为淘汰段和保护段,两段都是 LRU 算法,第一次被访问的元素会进入淘汰段,第二次被访问会进入保护段,保护段中被淘汰的元素会进入淘汰段,这种算法实现了高命中率和低内存占用 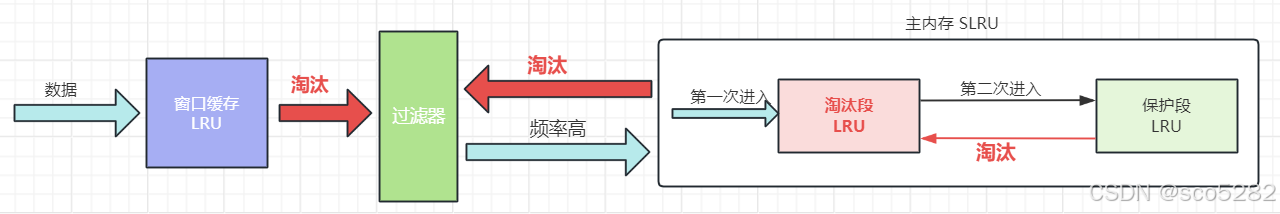
3.3、入门案例
SpringBoot 整合 Caffeine 实现本地缓存
在 SpringBoot 中,有两种使用 Caffeine 作为缓存的方式:
直接引入Caffeine 依赖,然后使用 Caffeine 方法实现缓存引入 Caffeine 和 Spring Cache 依赖,使用 SpringCache 注解方法实现缓存 这里就以第二种为例
3.3.1、引入 POM 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId> <artifactId>caffeine</artifactId> <version>2.6.2</version></dependency>3.3.2、开启缓存功能
开启缓存功能,需要先添加使能注解 @EnableCaching,通常习惯在启动类配置,否则缓存注解@Cacheable 等不起作用
@EnableCaching@SpringBootApplicationpublic class TestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args); }}3.3.3、配置缓存管理器
缓存管理器可以配置缓存的属性,如:
设置最大大小设置过期时间设置刷新策略Spring Cache 只是提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的 cache 实现。具体就是通过 CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术:
EhCacheCacheManager:使用 EhCache 作为缓存技术GuavaCacheManager:使用 Google 的 Guava Cache 作为缓存技术RedisCacheManager:使用 Redis 作为缓存技术CaffeineCacheManager:使用 Caffeine 作为缓存技术 如果不配置缓存管理器,则默认使用 ConcurrentMapCacheManager 缓存管理器;当然,也可以同时配置多个缓存管理器【Caffeine、Ehcache、Redis】,并给每个缓存管理器指定不同的 Bean 名称,就可以精确控制哪个缓存管理器被使用
这里,我以 CaffeineCacheManager 为例:
@Configurationpublic class CacheConfig { @Bean("caffeineCacheManager") public CacheManager cacheManager() { CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager(); cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder() .initialCapacity(100) .maximumSize(500) .expireAfterWrite(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); return cacheManager; }}3.3.4、编写 User 实体类
@Datapublic class User { private Integer id; private String name;}3.3.5、编写 UserServceImpl
@Slf4j@Service@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "caffeineCacheManager")public class UserServiceImpl3 { // 模拟数据库数据 private Map<Integer, User> userMap = new HashMap<>(); @CachePut(key = "#user.id") public User add(User user) { log.info("add"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user; } @Cacheable(key = "#id", unless = "#result == null") public User get(Integer id) { log.info("get"); return userMap.get(id); } @CachePut(key = "#user.id") public User update(User user) { log.info("update"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user; } @CacheEvict(key = "#id") public void delete(Integer id) { log.info("delete"); userMap.remove(id); } @Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name") @GetMapping("/list") public List<User> list(User user) { LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq(user.getId() != null, User::getId, user.getId()); queryWrapper.eq(user.getName() != null, User::getName, user.getName()); List<User> list = userService.list(queryWrapper); return list; }}①:add() 方法注解 @CachePut
add() 方法是用来保存用户信息的,希望在该用户信息保存到数据库的同时,也往缓存中缓存一份数据,可以在 add() 方法上加上注解 @CachePut
key 的写法如下:
#user.id : #user 指的是方法形参的名称, id 指的是 user 的 id 属性 , 也就是使用 user 的 id 属性作为 key ;#user.name: #user 指的是方法形参的名称, name 指的是 user 的 name 属性 ,也就是使用 user 的 name 属性作为 key ;#result.id : #result 代表方法返回值,该表达式代表以返回对象的 id 属性作为 key ;#result.name : #result 代表方法返回值,该表达式 代表以返回对象的 name 属性作为 key 数据最终是缓存在 JVM 内存中,那么当我们的服务器重启之后,缓存中的数据就会丢失【使用 Redis 缓存就可避免】
②:get() 方法注解 @Cacheable
在 get() 方法执行前,Spring 先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值【返回值不为 NULL】放到缓存中
注意:此处,我们使用的时候只能够使用 unless, 因为在 condition 中,我们是无法获取到结果 #result 的
③:update() 方法注解 @CachePut
update() 方法是修改用户信息,也希望同时修改缓存数据,就在 update() 方法上添加 @CachePut。
当然,我们也可以删掉缓存:
//@CacheEvict(key = "#p0.id") //第一个参数的id属性//@CacheEvict(key = "#user.id") //参数名为user参数的id属性//@CacheEvict(key = "#root.args[0].id") //第一个参数的id属性@CacheEvict(key = "#result.id") //返回值的id属性public User update(User user) { log.info("update"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user;}④:delete() 方法注解 @CacheEvict
我们在删除数据库 user 表的数据的时候,需要删除缓存中对应的数据,此时就可以使用 @CacheEvict 注解
@CacheEvict(key = "#id")//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#p0") //#p0 代表第一个参数//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0]") //#root.args[0] 代表第一个参数public void delete(Integer id) { log.info("delete"); userMap.remove(id);}⑤:list() 方法注解 @Cacheable
在 list() 方法中进行查询时,有两个查询条件,如果传递了 id,根据 id 查询;如果传递了 name, 根据 name 查询,那么我们缓存的 key 在设计的时候,就需要既包含 id,又包含 name
4、Ehcache
4.1、Ehcache 简介
EhCache 是一种广泛使用的开源 Java 分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存、Java EE 和轻量级容器,可以和大部分 Java 项目无缝整合。
Ehcache 虽然也支持分布式模式,但是分布式方案不是很好,建议只将其作为单机的进程内缓存使用
特点:
直接在 JVM 虚拟机中缓存,速度快,效率高支持多种缓存策略:LRU、LFU、FIFO 淘汰算法支持内存和磁盘存储,默认存储在内存中,如内存不够时把缓存数据同步到磁盘中;支持多缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域支持基于 Filter 的 Cache 实现,也支持 Gzip 压缩算法EhCache 可以单独使用,一般在第三方库中被用到的比较多【mybatis、shiro】;EhCache 对分布式支持不够好,多个节点通过组播方式同步,效率不高,通常和 Redis 一块使用【通过 RMI 或者 Jgroup 多播方式进行广播缓存通知更新,缓存共享复杂,维护不方便;简单的共享可以,但是涉及到缓存恢复,大数据缓存,则不合适】 4.2、入门案例【Ehcache3.x 】
4.2.1、引入 POM
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.ehcache</groupId> <artifactId>ehcache</artifactId> <version>3.9.3</version></dependency>4.2.2、开启缓存功能
开启缓存功能,需要先添加使能注解 @EnableCaching,通常习惯在启动类配置,否则缓存注解@Cacheable 等不起作用
@EnableCaching@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Test2Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Test2Application.class, args); }}4.2.3、配置缓存管理器
@Configurationpublic class EhCacheConfig { @Autowired private EhCacheProperty ehCacheProperty; @Bean(name = "ehCacheManager") public CacheManager cacheManager() { // ①:设置内存存储位置和数量大小 ResourcePools resourcePools = ResourcePoolsBuilder.newResourcePoolsBuilder() // 堆内存 .heap(ehCacheProperty.getHeap()) // 堆外内存 .offheap(ehCacheProperty.getOffheap(), MemoryUnit.MB) // 磁盘 .disk(ehCacheProperty.getDisk(),MemoryUnit.MB, true) .build(); // ②:设置生存时间 ExpiryPolicy userExpiry = ExpiryPolicyBuilder.noExpiration(); ExpiryPolicy itemExpiry = ExpiryPolicyBuilder.timeToIdleExpiration(Duration.ofMillis(1000)); // ③:设置 CacheConfiguration CacheConfiguration userCache = CacheConfigurationBuilder .newCacheConfigurationBuilder(Integer.class, String.class, resourcePools) .withExpiry(userExpiry) .build(); CacheConfiguration itemCache = CacheConfigurationBuilder .newCacheConfigurationBuilder(Integer.class, String.class, resourcePools) .withExpiry(itemExpiry) .build(); // ④:设置磁盘存储的位置 CacheManagerBuilder<PersistentCacheManager> cacheManagerBuilder = CacheManagerBuilder.newCacheManagerBuilder().with(CacheManagerBuilder.persistence(ehCacheProperty.getDiskDir())); // ⑤:设置缓存名称 Set<String> cacheNames = ehCacheProperty.getCacheNames(); Map<String, CacheConfiguration> cacheMap = new HashMap<>(2); cacheMap.put("userCache", userCache); cacheMap.put("itemCache", itemCache); for (String cacheName : cacheNames) { cacheManagerBuilder = cacheManagerBuilder.withCache(cacheName, cacheMap.get(cacheName)); } // 初始化 CacheManager return cacheManagerBuilder.build(true); }}4.2.4、编写 UserServceImpl
@Slf4j@Service@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "userCache")public class UserServiceImpl { // 模拟数据库数据 private Map<Integer, User> userMap = new HashMap<>(); @CachePut(key = "#user.id") public User add(User user) { log.info("add"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user; } @Cacheable(key = "#id", unless = "#result == null") public User get(Integer id) { log.info("get"); return userMap.get(id); } @CachePut(key = "#user.id") public User update(User user) { log.info("update"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user; } @CacheEvict(key = "#id") public void delete(Integer id) { log.info("delete"); userMap.remove(id); }}4.2.5、编写 TestController
@RestControllerpublic class TeController { @Autowired private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl; @PostMapping public String add(@RequestBody User user) { userServiceImpl.add(user); return "add"; } @GetMapping("/{id}") public User get(@PathVariable Integer id) { User user = userServiceImpl.get(id); return user; } @PutMapping public String update(@RequestBody User user) { userServiceImpl.update(user); return "update"; } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) { userServiceImpl.delete(id); return "delete"; }}5、JetCache
5.1、JetCache 简介
官网地址
官方文档
JetCache 是由阿里巴巴开源的一款基于 Spring 和 Redis 的分布式缓存框架 ,提供统一的 API 和注解来简化缓存的使用。
JetCache 提供了比 Spring Cache更加强大的注解,可以原生的支持 TTL、两级缓存、分布式自动刷新,还提供了 Cache 接口用于手工缓存操作。 当前有四个实现,RedisCache、TairCache(此部分未在 github 开源)、CaffeineCache(in memory) 和一个简易的 LinkedHashMapCache (in memory),要添加新的实现也是非常简单的
它的特性:
通过统一的 API 访问 Cache 系统通过注解实现声明式的方法缓存,支持 TTL 和两级缓存通过注解创建并配置 Cache 实例针对所有 Cache 实例和方法缓存的自动统计Key 的生成策略和 Value 的序列化策略是可以配置的分布式缓存自动刷新,分布式锁 (2.2+)异步 Cache API (2.2+,使用 Redis 的 lettuce 客户端时)5.2、JetCache 核心概念
缓存抽象:JetCache-Alibaba 提供了一个统一的缓存抽象层,这意味着你不需要直接和具体的缓存实现打交道。它为你封装好了底层的细节,你只需要通过它提供的 API 来操作缓存即可。这样一来,你更换缓存实现的时候,就不需要改动大量的代码了分布式缓存: 在分布式系统中,应用可能部署在多台机器上。这时候,如果每台机器都有自己的本地缓存,那数据就不一致了。JetCache-Alibaba 支持分布式缓存,它能确保多台机器上的缓存数据是一致的。这样,无论你的应用部署在哪里,都能读到正确的缓存数据缓存一致性: 缓存里的数据和数据库里的数据得保持一致。JetCache-Alibaba 提供了多种策略来确保缓存的一致性,比如缓存失效、缓存更新等。根据自己的业务场景来选择合适的策略降级策略: 有时候,缓存可能会失效或者出点什么问题。这时候,应用可不能直接崩溃。JetCache-Alibaba 提供了降级策略,当缓存不可用时,它会自动切换到数据库或者其他备份数据源,确保你的应用依然能够正常运行 5.3、入门案例
5.3.1、引入依赖
https://github.com/alibaba/jetcache/blob/master/docs/CN/GettingStarted.md
<dependency> <groupId>com.alicp.jetcache</groupId> <artifactId>jetcache-starter-redis</artifactId> <version>2.7.3</version></dependency><!-- jedis --><dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>4.3.0</version></dependency>这里使用了 Jedis 客户端连接 Redis
注意,如果启动出现 NoClassDefFoundError: redis/clients/util/Pool 或 NoClassDefFoundError: redis/clients/jedis/UnifiedJedis 报错,说明 springboot 与 jetcache 版本不一致。如果使用的是jetcache2.7.x 版本,因为该版本中有 jedis 包的依赖,需要额外添加如下依赖,或者将 jetcache 版本将至 2.6.5 以下
5.3.2、修改配置文件
更详细的参数配置可参考官网说明:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/je/jetcache/blob/master/docs/CN/Config.md
jetcache: # 统计间隔 0 表示不统计 statIntervalMinutes: 15 # 是否在缓存名称中包含 area。 # jetcache-anno 把 cacheName 作为远程缓存 key 前缀,2.4.3 以前的版本总是把 areaName 加在 cacheName 中,因此 areaName 也出现在 key 前缀中。 # 2.4.4以后可以配置,为了保持远程 key 兼容默认值为 true,但是新项目的话 false 更合理些,2.7 默认值已改为 false。 areaInCacheName: false # 缓存类型。local 本地缓存;remote 远程缓存;local+remote 本地+远程缓存 # 本地缓存:caffeine、linkedhashmap # 远程缓存:redis、tair local: # area:默认缓存配置。对应 @Cached 和 @CreateCache 的 area 属性 default: # 本地缓存类型 type: caffeine # key 转换器:fastjson、fastjson2、jackson # 仅当使用 @CreateCache 且缓存类型为 local 时可以指定为 none,此时通过 equals 方法来识别 key。方法缓存必须指定 keyConvertor keyConvertor: JACKSON # 每个缓存实例的最大元素的全局配置,仅 local 类型的缓存需要指定 limit: 100 # 缓存过期时间,单位毫秒 expireAfterWriteInMillis: 100000 # 指定多长时间没有访问,就让缓存失效,当前只有本地缓存支持 以毫秒为单位;0 表示不使用这个功能 expireAfterAccessInMillis: 100000 # 远程缓存配置 remote: default: # 远程缓存类型 type: redis keyConvertor: JACKSON # 配置远程缓存的广播通道,通常用于分布式环境中实现缓存同步 #broadcastChannel: myBroadcastChannel # 2.7+可选java/kryo/kryo5;2.6-可选java/kryo valueEncoder: java # 2.7+可选java/kryo/kryo5;2.6-可选java/kryo valueDecoder: java # redis 线程池 poolConfig: minIdle: 5 maxIdle: 20 maxTotal: 50 host: 127.0.0.1 port: 63795.3.3、添加配置扫描注解
启动类添加注解 @EnableCreateCacheAnnotation,开启缓存;添加@EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "com.zzc") 注解,配置缓存方法扫描路径
@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation@EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "com.zzc")@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Test2Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Test2Application.class, args); }}5.3.4、使用 JetCache
基于注解实现缓存:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/je/jetcache/blob/master/docs/CN/MethodCache.md
JetCache 方法缓存和 Spring Cache比较类似,它原生提供了 TTL 支持,以保证最终一致,并且支持二级缓存。JetCache2.4 以后支持基于注解的缓存更新和删除。
在 Spring 环境下,使用 @Cached 注解可以为一个方法添加缓存,@CacheUpdate 用于更新缓存,@CacheInvalidate用于移除缓存元素。注解可以加在接口上也可以加在类上,加注解的类必须是一个Spring Bean。
5.3.4.1、添加 UserServiceImpl:
@Slf4j@Servicepublic class UserServiceImpl { // 模拟数据库数据 private Map<Integer, User> userMap = new HashMap<>(); @Cached(name = "userCache:", key = "#user.id", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL) public User add(User user) { log.info("add"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user; } @Cached(name = "userCache:", key = "#id", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL) public User get(Integer id) { log.info("get"); return userMap.get(id); } @CacheUpdate(name = "userCache:", key = "#user.id", value = "#user") public User update(User user) { log.info("update"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user; } @CacheInvalidate(name = "userCache:", key = "#id") public void delete(Integer id) { log.info("delete"); userMap.remove(id); }}5.3.4.2、添加 TestController:
@RestControllerpublic class TestController { @Autowired private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl; @PostMapping public String add(@RequestBody User user) { userServiceImpl.add(user); return "add"; } @GetMapping("/{id}") public User get(@PathVariable Integer id) { User user = userServiceImpl.get(id); return user; } @PutMapping public String update(@RequestBody User user) { userServiceImpl.update(user); return "update"; } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) { userServiceImpl.delete(id); return "delete"; }}@CacheUpdate和 @CacheInvalidate 的 name 和 area 属性必须和 @Cached` 相同,name 属性还会用做 cache 的 key 前缀
5.3.5、JetCache 中常用的注解
5.3.5.1、@Cached 注解
@Cached 注解的属性如下:
| 属性 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| area | “default” | 如果在配置中配置了多个缓存 area,在这里指定使用哪个 area |
| name | 指定缓存的唯一名称,不是必须的,如果没有指定,会使用类名+方法名。name 会被用于远程缓存的 key 前缀。另外在统计中,一个简短有意义的名字会提高可读性。 | |
| key | 使用 SpEL 指定 key,如果没有指定会根据所有参数自动生成 | |
| expire | 超时时间。如果注解上没有定义,会使用全局配置,如果此时全局配置也没有定义,则为无穷大 | |
| timeUnit | TimeUnit.SECONDS | 指定 expire 的单位 |
| cacheType | CacheType.REMOTE | 缓存的类型,包括 CacheType.REMOTE、CacheType.LOCAL、CacheType.BOTH。如果定义为 BOTH,会使用 LOCAL 和 REMOTE 组合成两级缓存 |
| localLimit | 如果 cacheType 为 LOCAL 或 BOTH,这个参数指定本地缓存的最大元素数量,以控制内存占用。如果注解上没有定义,会使用全局配置,如果此时全局配置也没有定义,则为 100 | |
| localExpire | 仅当 cacheType 为 BOTH 时适用,为内存中的 Cache 指定一个不一样的超时时间,通常应该小于 expire | |
| serialPolicy | 指定远程缓存的序列化方式。可选值为 SerialPolicy.JAVA 和 SerialPolicy.KRYO。如果注解上没有定义,会使用全局配置,如果此时全局配置也没有定义,则为 SerialPolicy.JAVA | |
| keyConvertor | 指定 KEY 的转换方式,用于将复杂的 KEY 类型转换为缓存实现可以接受的类型,当前支持KeyConvertor.FASTJSON 和 KeyConvertor.NONE。NONE 表示不转换,FASTJSON 可以将复杂对象 KEY 转换成 String。如果注解上没有定义,会使用全局配置 | |
| enabled | true | 是否激活缓存。例如某个 dao 方法上加缓存注解,由于某些调用场景下不能有缓存,所以可以设置 enabled 为 false,正常调用不会使用缓存,在需要的地方可使用 CacheContext.enableCache 在回调中激活缓存,缓存激活的标记在 ThreadLocal 上,该标记被设置后,所有 enable=false 的缓存都被激活 |
| cacheNullValue | false | 当方法返回值为null的时候是否要缓存 |
| condition | 使用 SpEL 指定条件,如果表达式返回 true 的时候才去缓存中查询 | |
| postCondition | 使用 SpEL 指定条件,如果表达式返回 true 的时候才更新缓存,该评估在方法执行后进行,因此可以访问到 #result |
5.3.5.1.1、cacheType 属性
可以指定本地缓存、远程缓存、本地缓存 + 远程缓存。
@Cached(name = "userCache:", key = "#user.id", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.REMOTE)public User add(User user) { log.info("add"); userMap.put(user.getId(), user); return user;}此时,User 需要实现 Serializable 接口
多级缓存的形式,会先从本地缓存获取数据,本地获取不到会从远程缓存获取;
5.3.5.2、@CacheUpdate 注解
@CacheUpdate 注解的属性如下:
| 属性 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| area | “default” | 如果在配置中配置了多个缓存 area,在这里指定使用哪个 area |
| name | 指定缓存的唯一名称,不是必须的,如果没有指定,会使用类名+方法名。name 会被用于远程缓存的 key 前缀。另外在统计中,一个简短有意义的名字会提高可读性。 | |
| key | 使用 SpEL 指定 key,如果没有指定会根据所有参数自动生成 | |
| value | 使用 SpEL 指定 value | |
| condition | 使用 SpEL 指定条件,如果表达式返回 true 的时候才去缓存中查询 |
5.3.5…3、@CacheInvalidate 注解
@CacheInvalidate 注解的属性如下:
| 属性 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| area | “default” | 如果在配置中配置了多个缓存 area,在这里指定使用哪个 area |
| name | 指定缓存的唯一名称,不是必须的,如果没有指定,会使用类名+方法名。name 会被用于远程缓存的 key 前缀。另外在统计中,一个简短有意义的名字会提高可读性。 | |
| key | 使用 SpEL 指定 key,如果没有指定会根据所有参数自动生成 | |
| condition | 使用 SpEL 指定条件,如果表达式返回 true 的时候才去缓存中查询 |
使用 @CacheUpdate 和 @CacheInvalidate 的时候,相关的缓存操作可能会失败(比如网络 IO 错误),所以指定缓存的超时时间是非常重要的