看下面内容前,建议大家先看一些这篇的封装手法 -> 【C++】用红黑树封装set和map ,set/map和unordered_set/unordered_map的底层结构确实是不一样的,但是它们的封装手法确是极其相似的,接下来,我会用哈希表来封装unordered_set/unordered_map,封装前的代码如下:
#pragma once#include <iostream>#include <vector>using namespace std;enum State{EXIST,EMPTY,DELETE};template<class K>struct HashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}};template<>struct HashFunc<string>{size_t operator()(const string& s){size_t hash = 0;for (auto ch : s)hash += ch, hash *= 131;return hash;}};inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n){static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] ={53, 97, 193, 389, 769,1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291};const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list + __stl_num_primes;const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;}//链地址法实现哈希桶namespace hash_bucket{template<class K, class V>struct HashNode{pair<K, V> _kv;HashNode<K, V>* _next; //单链表HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _next(nullptr){}};template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;public:HashTable():_tables(__stl_next_prime(0), nullptr), _n(0){}HashTable(const HashTable& ht): _tables(ht._tables.size(), nullptr), _n(ht._n){for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); ++i){Node* cur = ht._tables[i];while (cur){Node* newnode = new Node(cur->_kv);newnode->_next = _tables[i];_tables[i] = newnode;cur = cur->_next;}}}HashTable& operator=(HashTable tmp){_tables.swap(tmp._tables);std::swap(_n, tmp._n);return *this;}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){//不允许插入两个相同的元素if (Find(kv.first))return false;Hash hash;if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){vector<Node* > newtable(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size() + 1));for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;//头插到新表size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newtable.size();cur->_next = newtable[hashi];newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();//头插,时间复杂度O(1)Node* newnode = new Node(kv);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return true;}Node* Find(const K& key){Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key)return cur;cur = cur->_next;}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* prev = nullptr;Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){//删除逻辑if (prev == nullptr) //头结点_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;else //中间结点prev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;--_n;return true;}elseprev = cur, cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n;};}下面我将在上述代码的基础上进行封装,大家如果看不懂上述代码,可以先看一下这篇文章 -> 【C++】哈希
一、共用一个哈希表
unordered_set是key搜索场景的结构,unordered_map是key/value搜索场景的结构。所以要用哈希表封装它们两个就需要2个哈希,这两个哈希表整体逻辑差不多一样,只是结点中的元素数据类型不一样,一个是K类型,一个是pair<K,V>类型。两棵极为相似的树,只是一点不同,如果实现两个会显得冗余,那么我们就可以考虑使用模板来将结点中的数据类型泛型化,使unordered_set和unordered_map底层共用一个哈希表。
我们上述代码中结点中的数据类型是pair,这样我们就把这个结点的数据类型写"死"了,unordered_set容器底层就不能用这个哈希表,我们要实现set和map共用一个哈希表,所以就需要把结点的数据类型泛型化(根据传来的类型来确定具体的类型):
修改一:

修改二:

修改三:
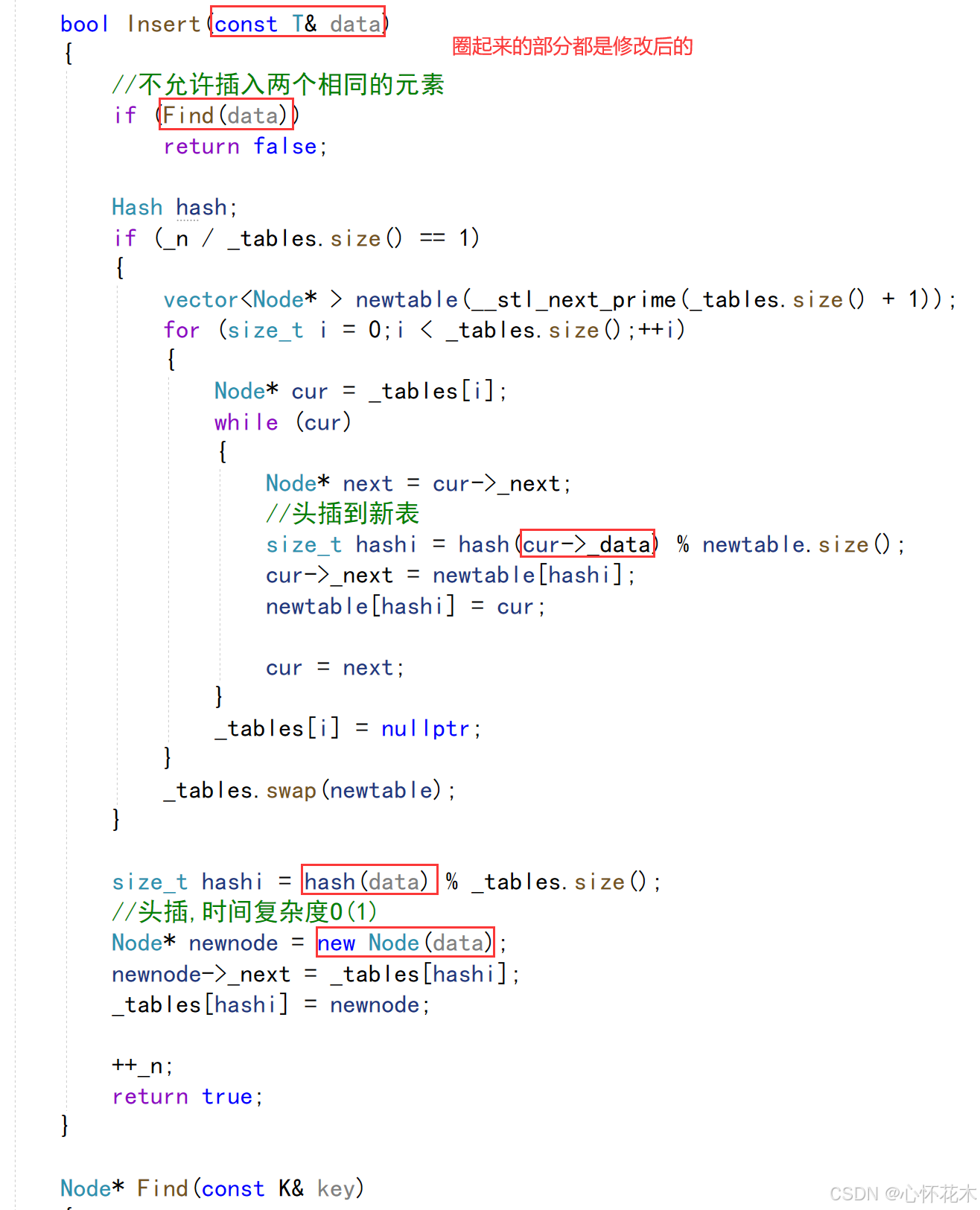
修改四:
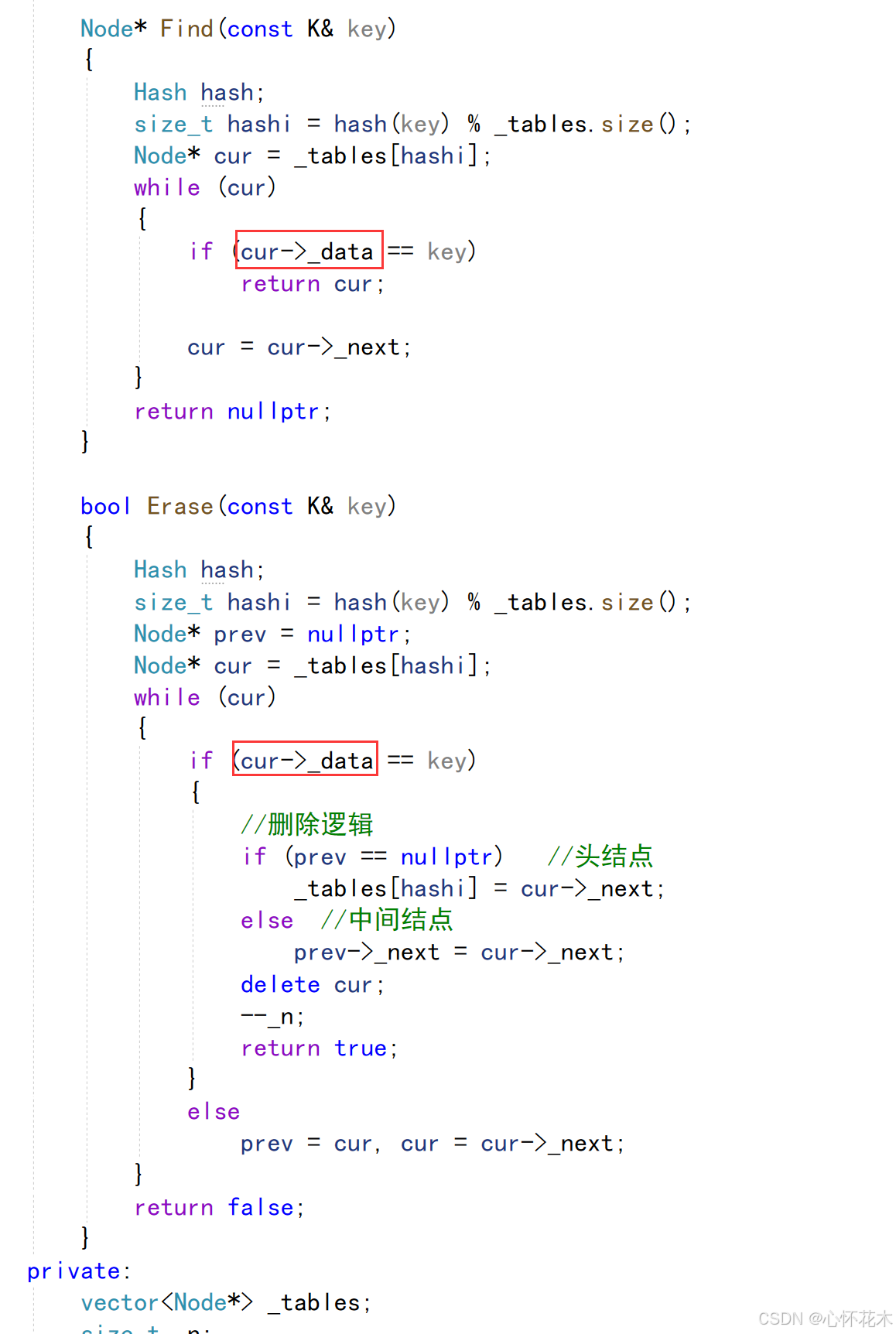
这时大家不难发现,修改后的HashTable中模板参数少了K,如果少了K,那么Find和Erase中的形参就是无稽之谈了,Find和Erase就是靠K来进行功能设计的,所以HashTable中的模板参数必须有K:

初步封装unordered_set:
#pragma once#include "HashTable.h"namespace blue{template<class K,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_set{public:bool insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, Hash> _ht;};}初步封装unordered_map:
#pragma once#include "HashTable.h"namespace blue{template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_map{public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash> _ht;};}这样我们就可以通过模板参数T来控制unordered_set和unordered_map共用一个哈希表啦!
二、 哈希表中Insert带来的问题
通过观察上面哈希表中Insert的代码,其实会有问题:
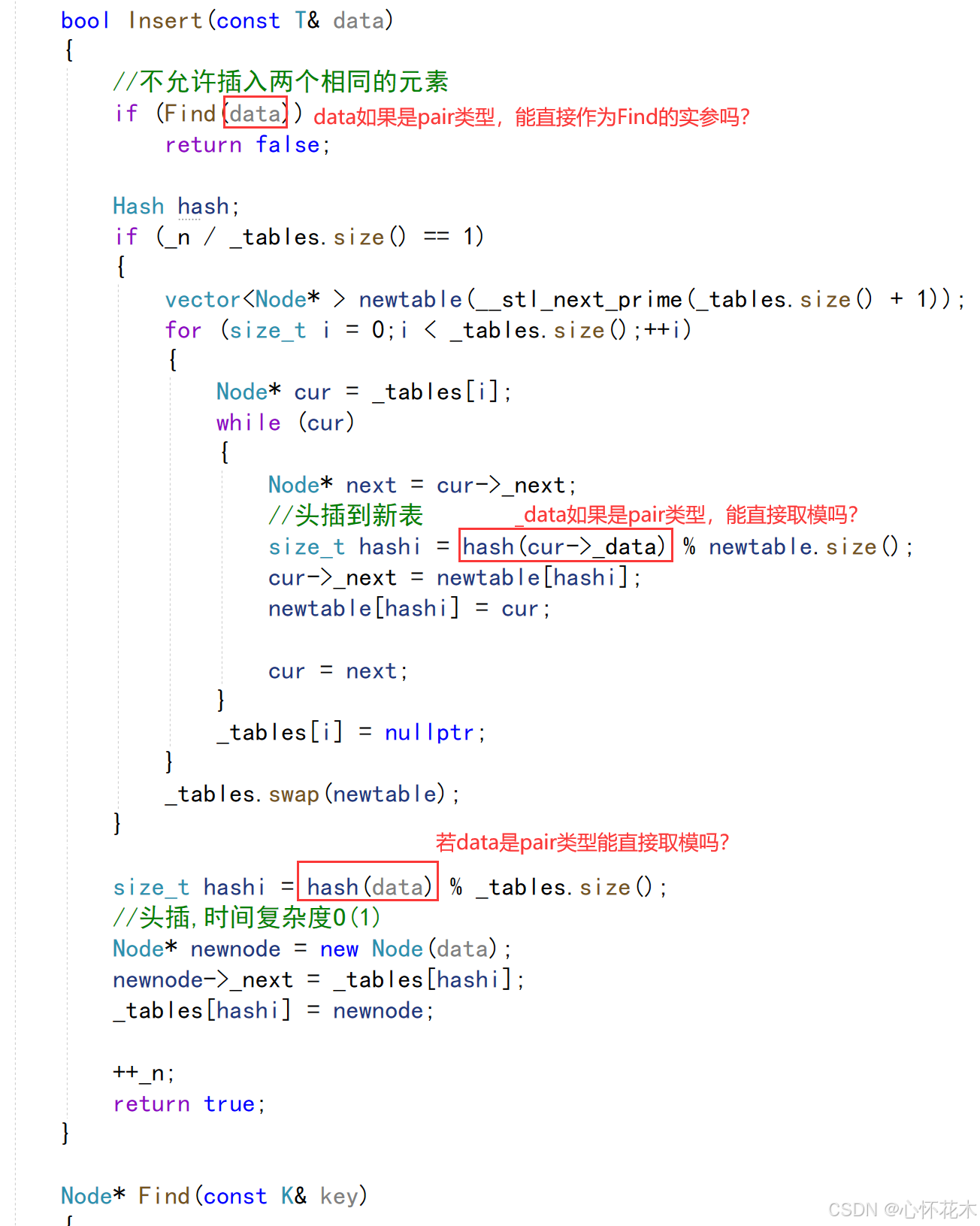
data若是key类型,上述当然是没问题的,但是若是pair类型,就会出错,所以我们可以在unordered_set和unordered_map类中分别写一个仿函数,通过仿函数来获取K,具体做法如下:
//unordered_set类中的仿函数struct USetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};//unordered_map类中的仿函数struct UMapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};我们明确知道map是需要这个仿函数来获取K值的,但是在set中也写一个仿函数来获取K值,有人开始会觉得这是多余的,因为set中的元素类型本身就是K类型,但是不要忽略一点,unordered_set和unordered_map是共用同一份模板的,unordered_map需要这个仿函数,那么unordered_set也必须有这个仿函数,unordered_set这里的仿函数就是为了兼容unordered_map,所以,哈希表的第四个模板参数KeyOfT就应运而生了,用来获取它们两个的仿函数:
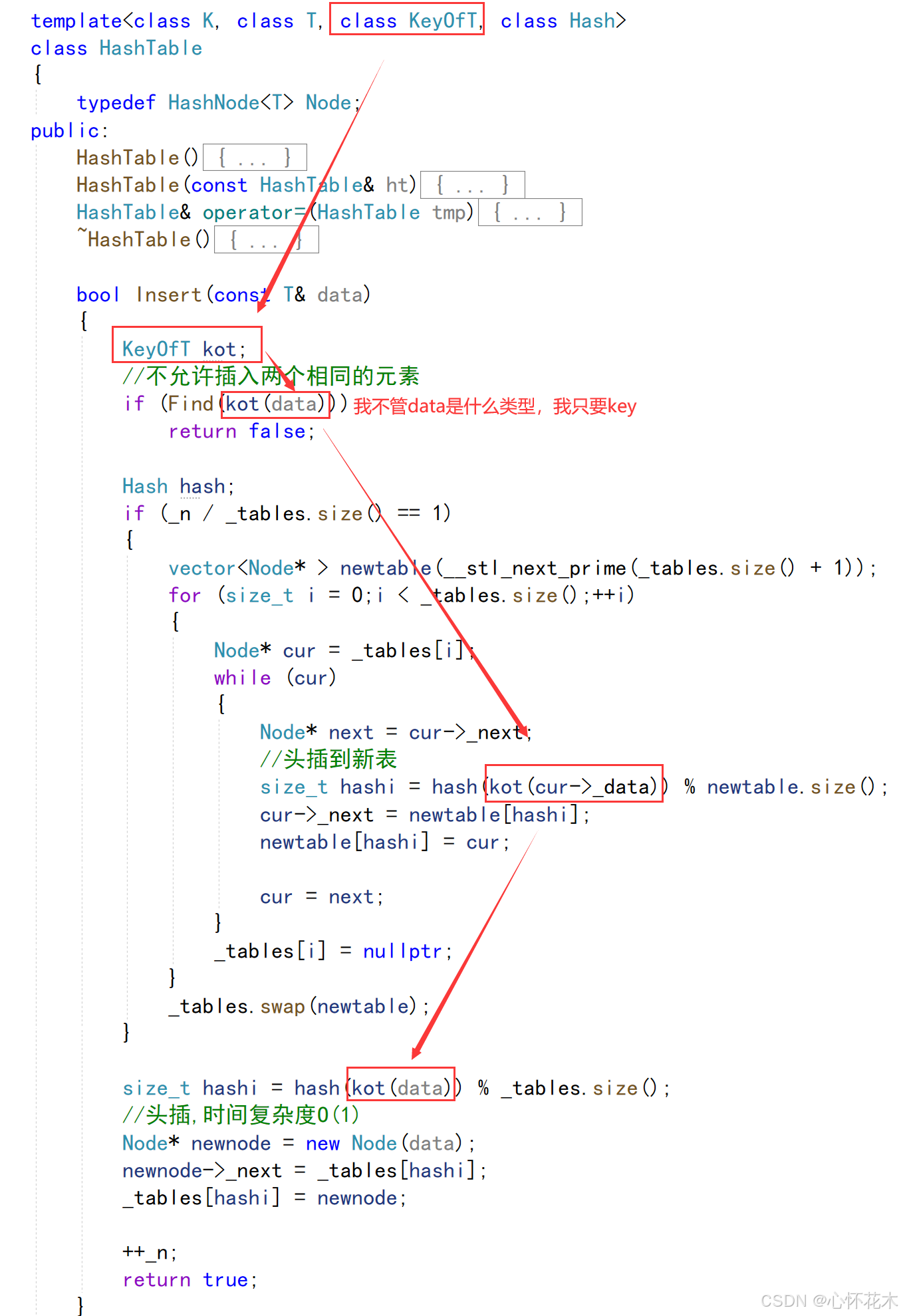
那么Find和Erase中的一些部分也要跟着改:
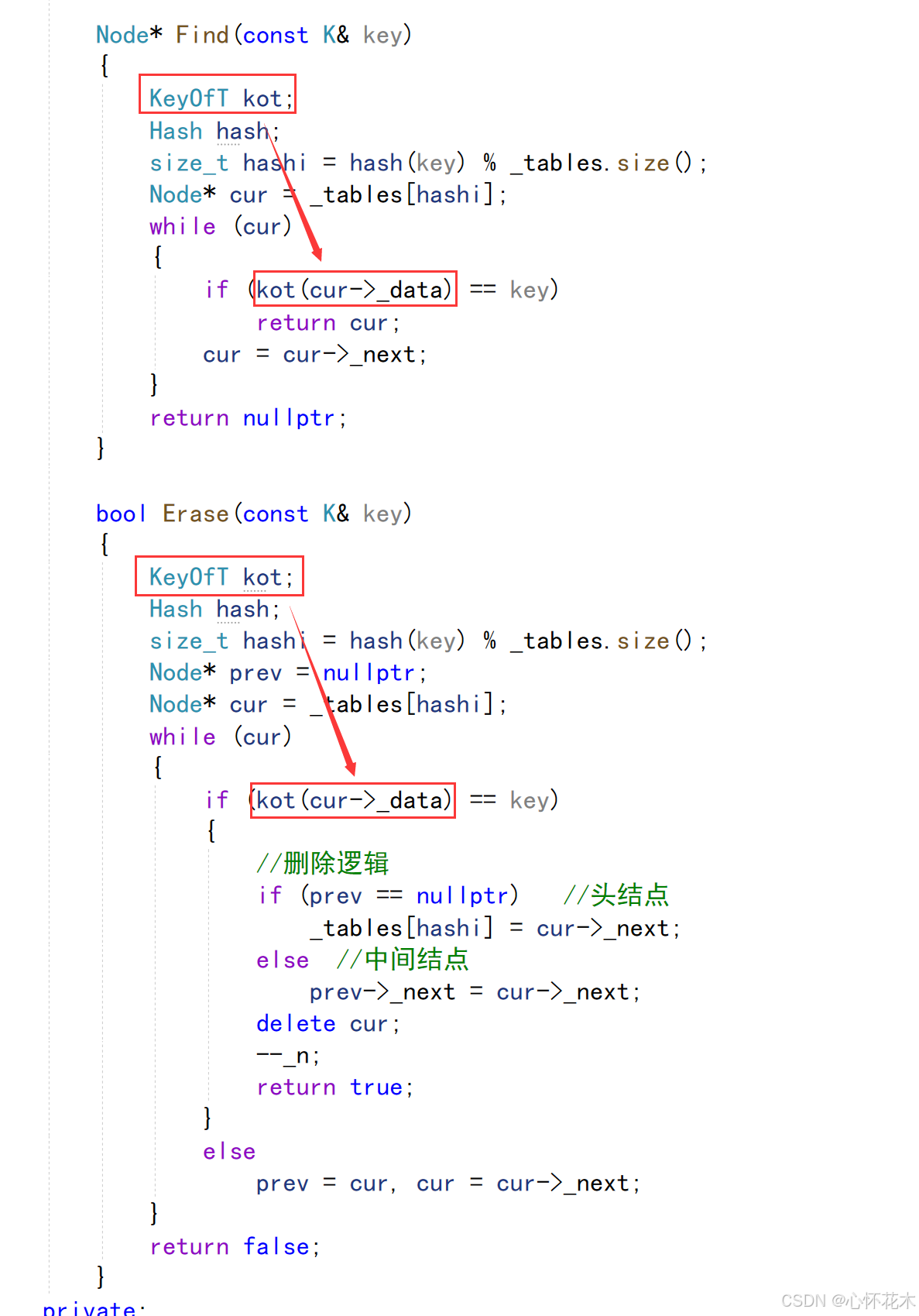
三、迭代器
我们知道unordered_set和unordered_map的底层是哈希桶,哈希桶的本质是单链表,所以我们要单独用一个类来封装结点的指针,再通过重载运算符实现,让迭代器具有像指针一样访问的行为:
template<class K, class T,class Ref,class Ptr,class KeyOfT, class Hash>struct HashIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;typedef HashIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;Node* _node;HT* _ht;HashIterator(Node* node, HT* ht):_node(node), _ht(ht){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};上面的代码相信大家一看便懂,接下来我们将重心放在如何重载++上,我们知道它的底层是哈希桶,在哈希桶中如何实现++呢?分为以下两种情况考虑:
1、当前结点后面有结点(当前桶还没有走完)
直接将返回下一个结点即可。
2、当前结点后面没有结点(当前桶走完了)
这时我们需要找到下一个非空桶的编号,如果编号超过哈希表的大小就说明走到最后一个位置了,若没有就返回新桶的首个非空结点。
具体代码实现为:
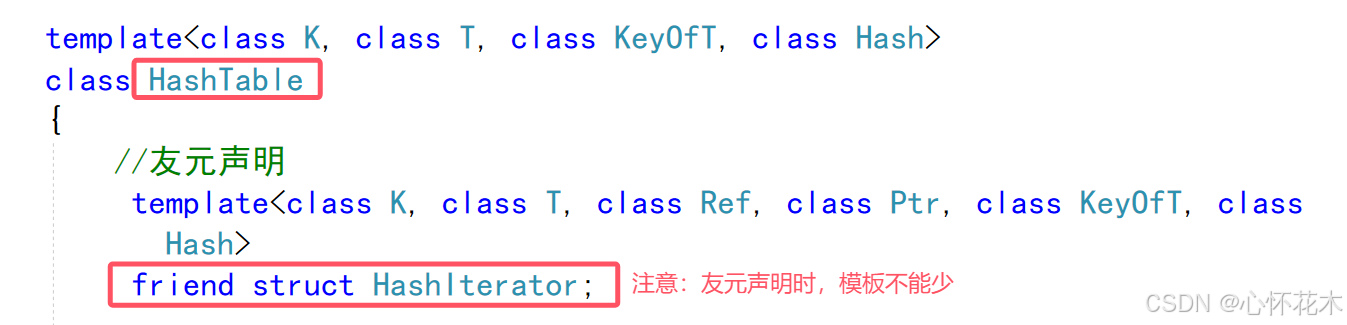
Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next)_node = _node->_next;else{//当前桶走完了,那就找下一个不为空的桶Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;int hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();++hashi; //下一个桶的编号while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size()) //满足条件说明该桶存在{_node = _ht->_tables[hashi]; if (_node) //如果不为空,就是我们要的结点break;else++hashi; //为空就到下一个桶}if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size()) //说明当前结点已经是最后一个了,再++就到结尾了,结尾为nullptr_node = nullptr;}return *this;}当前++逻辑还有一个问题,那就是哈希表中的_tables是私有成员,那么执行"_ht->_tables"就会报错,在HashTable外部是不能访问其类中的私有成员的,要解决这个问题,我们可以使用友元:
迭代器封装任务基本上已经完成了,接下来就是使用了:

在unordered_set中:
#pragma once#include "HashTable.h"namespace blue{template<class K,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_set{struct USetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, USetKeyOfT, Hash>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, USetKeyOfT, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.Begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.End();}bool insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, USetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;};}在unordered_map中:
#pragma once#include "HashTable.h"namespace blue{template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_map{struct UMapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, UMapKeyOfT, Hash>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, UMapKeyOfT, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.Begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.End();}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, UMapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;};}四、测试
我们大致的任务已经完成了,接下来我们来写一段代码验证一下(看看是否会出现错误):
#include "MyUnorderedSet.h"#include "MyUnorderedMap.h"void TestUSet(){blue::unordered_set<int> s;int a[] = { 30000,1,6,7,888,2,1,1,5,99996,7,6 };for (auto e : a)s.insert(e);blue::unordered_set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit << " ";++sit;}cout << endl;for (auto& e : s)cout << e << " ";cout << endl;}void TestUMap(){blue::unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });dict.insert({ "string", "字符串" });dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });for (auto& kv : dict)cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;cout << endl;blue::unordered_map<string, string>::iterator mit = dict.begin();while (mit != dict.end()){cout << mit->first << ":" << mit->second << endl;++mit;}cout << endl;}int main(){TestUSet();cout << "----------------------" << endl;TestUMap();return 0;}运行结果:

运行结果没有什么问题,这说明我们上面的代码逻辑应该没什么问题。但是,有一点不要疏忽了,那就是Key值不能修改!Key一旦修改,那么哈希映射关系就可能会混乱,所以我们是不能让Key发生变化的,但上面的代码我们并没有限制Key,所以我们现在要对Key进行限制:
在unordered_set中:
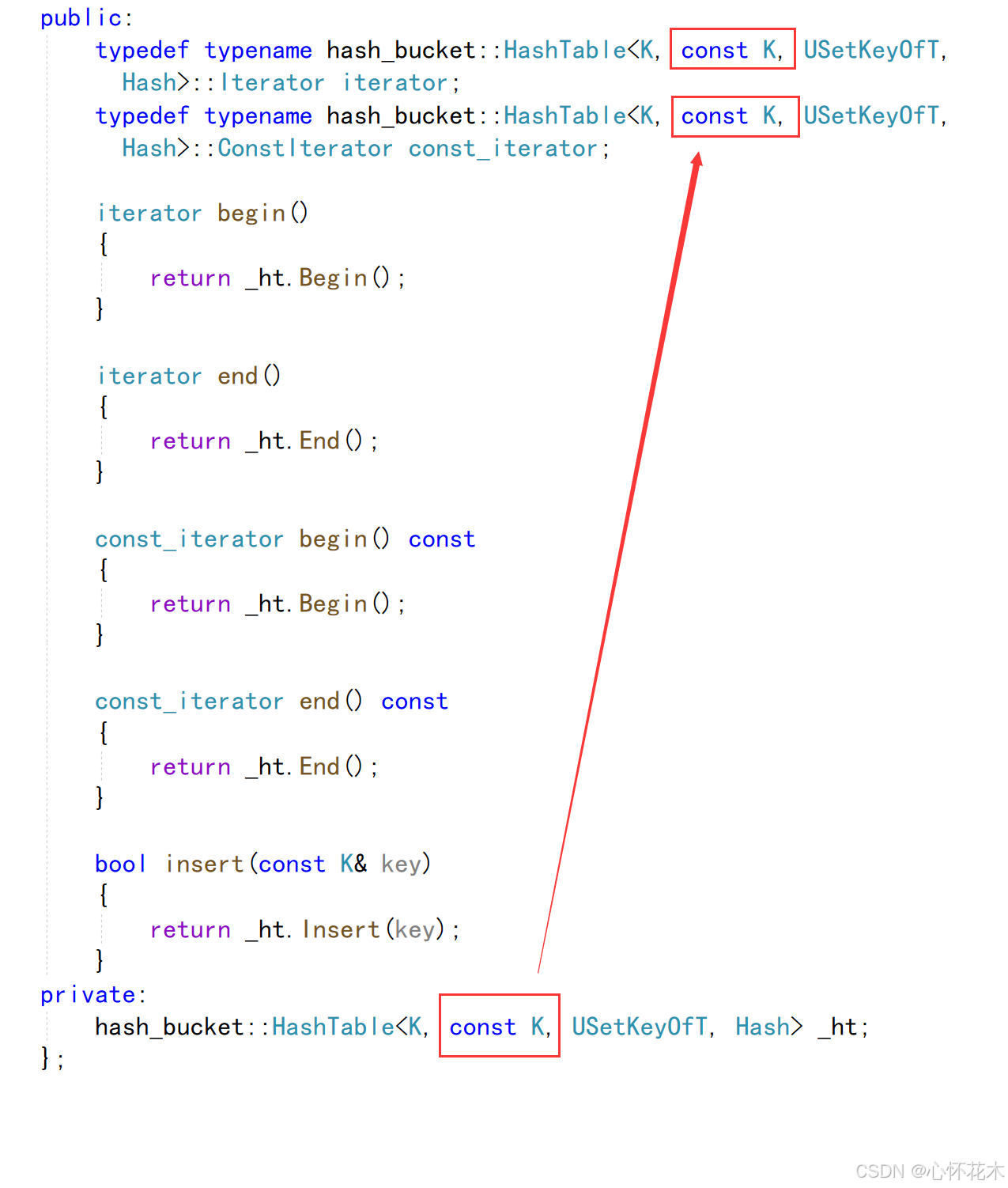
在unordered_map中:
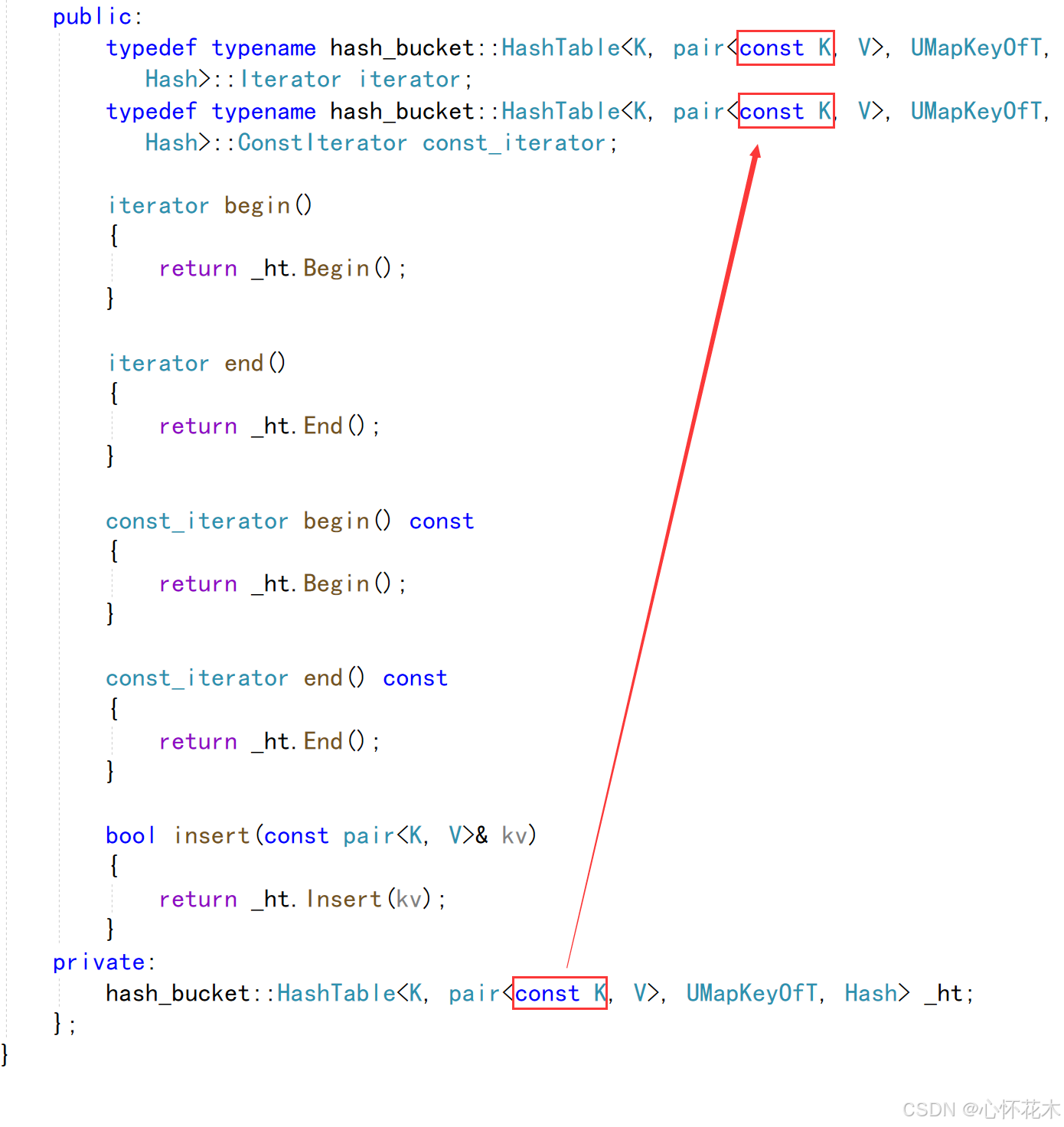
还有一个问题,在迭代器中:
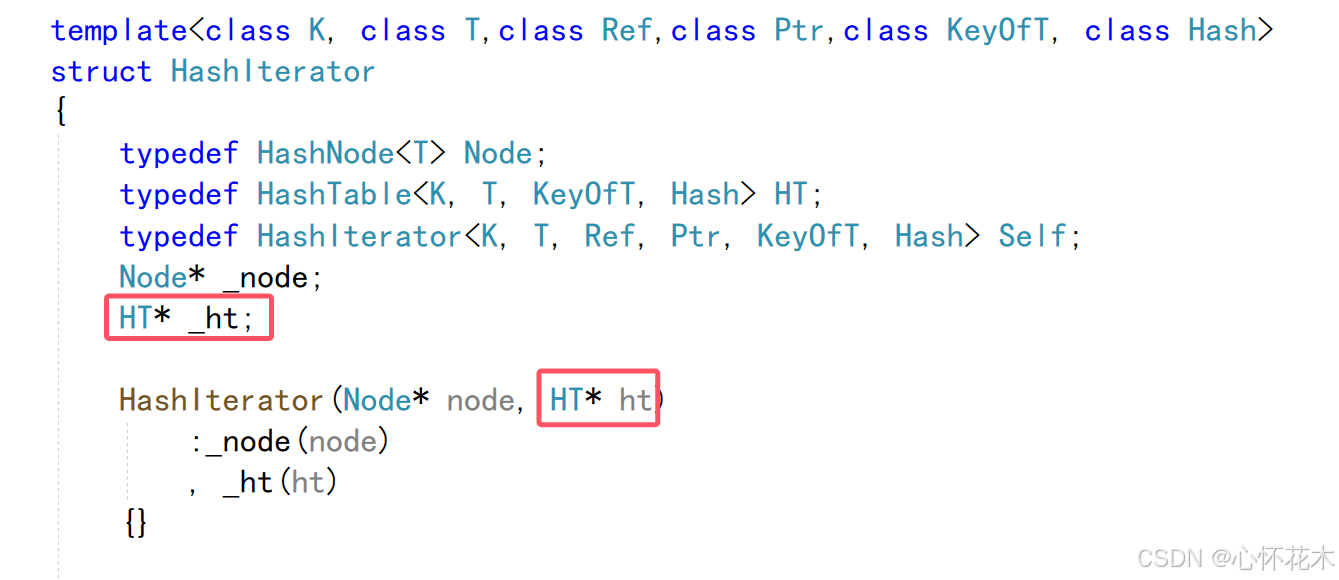
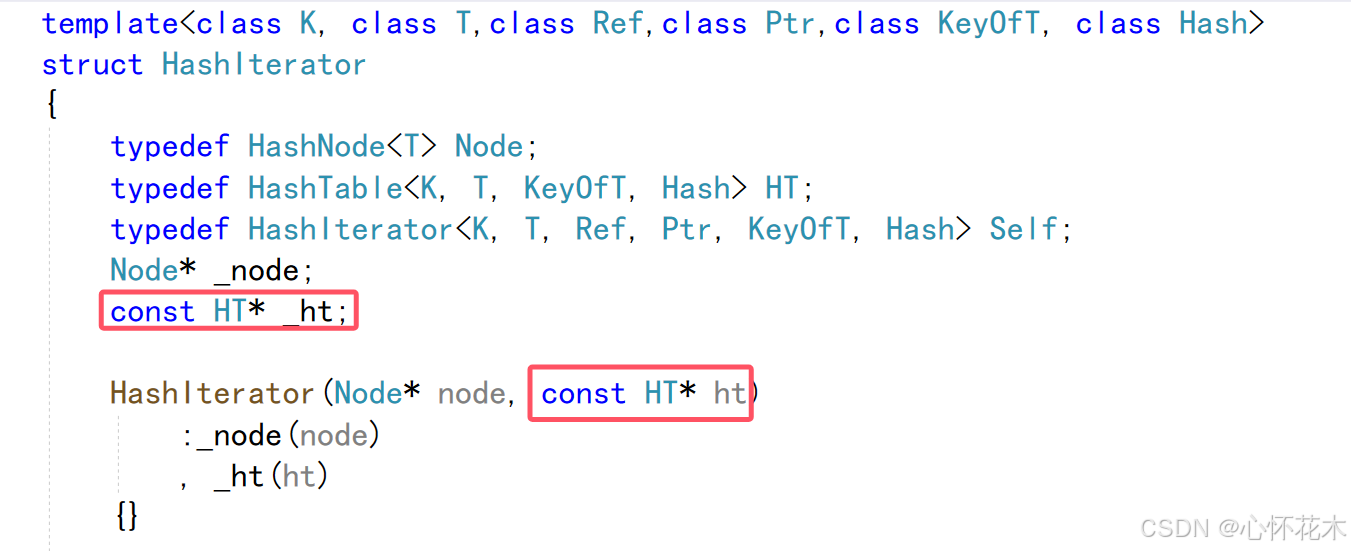
如果是一个const迭代器,也就是哈希表被const修饰,那么_ht应该是const类型,但是我们封装迭代器是默认为没有用const修饰_ht,这就会导致权限放大,会出现错误,所以我们要在_ht前面加上const:
五、unordered_map中的[]
上面的大框架逻辑已经基本实现完毕,接下来,我们来搞定unordered_map中的[]操作符,[]的逻辑其实就是利用了insert接口。
我们在哈希表中实现Insert的返回值是bool,接下来我们将它改为pair<Iterator,bool>类型,改之前,我们先改一下Find的返回值类型:
Iterator Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key)return Iterator(cur, this);cur = cur->_next;}return Iterator(nullptr, this);}接下来,我们改Insert:
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;//不允许插入两个相同的元素Iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it != End())return {it, false};Hash hash;if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){vector<Node* > newtable(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size() + 1));for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;//头插到新表size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.size();cur->_next = newtable[hashi];newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();//头插,时间复杂度O(1)Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return {Iterator(newnode, this), true};}完成对Insert的调整后,在unordered_set和unordered_map的insert也要跟着调:
在unordered_set中:

在unordered_map中:

接下来我们就着手实现unordered_map中的[]:
V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert( { key, V() } );return (ret.first)->second;}是不是非常简单!
六、源码
(1)HashTable.h
#pragma once#include <iostream>#include <vector>using namespace std;enum State{EXIST,EMPTY,DELETE};template<class K>struct HashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}};template<>struct HashFunc<string>{size_t operator()(const string& s){size_t hash = 0;for (auto ch : s)hash += ch, hash *= 131;return hash;}};inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n){static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] ={53, 97, 193, 389, 769,1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291};const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list + __stl_num_primes;const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;}//链地址法实现哈希桶namespace hash_bucket{template<class T>struct HashNode{T _data;HashNode<T>* _next; //单链表HashNode(const T& data):_data(data), _next(nullptr){}};//前置声明template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>class HashTable;template<class K, class T,class Ref,class Ptr,class KeyOfT, class Hash>struct HashIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;typedef HashIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;Node* _node;const HT* _ht;HashIterator(Node* node, const HT* ht):_node(node), _ht(ht){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next)_node = _node->_next;else{//当前桶走完了,那就找下一个不为空的桶Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;int hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();++hashi; //下一个桶的编号while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size()) //满足条件说明该桶存在{_node = _ht->_tables[hashi]; if (_node) //如果不为空,就是我们要的结点break;else++hashi; //为空就到下一个桶}if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size()) //说明当前结点已经是最后一个了,再++就到结尾了,结尾为nullptr_node = nullptr;}return *this;}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>class HashTable{//友元声明template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>friend struct HashIterator;typedef HashNode<T> Node;public:typedef HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator; //普通迭代器typedef HashIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> ConstIterator; // const迭代器Iterator Begin(){if (_n == 0)return { nullptr,this };for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];if (cur)return Iterator(cur, this);}return Iterator(nullptr, this);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr, this);}ConstIterator Begin() const{if (_n == 0)return { nullptr,this };for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];if (cur)return ConstIterator(cur, this);}return ConstIterator(nullptr, this);}ConstIterator End() const{return ConstIterator(nullptr, this);}HashTable():_tables(__stl_next_prime(0), nullptr), _n(0){}HashTable(const HashTable& ht): _tables(ht._tables.size(), nullptr), _n(ht._n){for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); ++i){Node* cur = ht._tables[i];while (cur){Node* newnode = new Node(cur->_data);newnode->_next = _tables[i];_tables[i] = newnode;cur = cur->_next;}}}HashTable& operator=(HashTable tmp){_tables.swap(tmp._tables);std::swap(_n, tmp._n);return *this;}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}}pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;//不允许插入两个相同的元素Iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it != End())return { it, false };Hash hash;if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){vector<Node* > newtable(__stl_next_prime(_tables.size() + 1));for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();++i){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;//头插到新表size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.size();cur->_next = newtable[hashi];newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();//头插,时间复杂度O(1)Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return { Iterator(newnode, this), true };}Iterator Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key)return Iterator(cur, this);cur = cur->_next;}return Iterator(nullptr, this);}bool Erase(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* prev = nullptr;Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){//删除逻辑if (prev == nullptr) //头结点_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;else //中间结点prev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;--_n;return true;}elseprev = cur, cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n;};}(2) MyUnorderedSet.h
#pragma once#include "HashTable.h"namespace blue{template<class K,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_set{struct USetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, const K, USetKeyOfT, Hash>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, const K, USetKeyOfT, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.Begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.End();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, const K, USetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;};}(3)MyUnorderedMap.h
#pragma once#include "HashTable.h"namespace blue{template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_map{struct UMapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, UMapKeyOfT, Hash>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, UMapKeyOfT, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.Begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.End();}const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.Begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.End();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key, V() });return (ret.first)->second;}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, UMapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;};}(4)Test.cpp
#include "MyUnorderedSet.h"#include "MyUnorderedMap.h"void Print(const blue::unordered_set<int>& s){blue::unordered_set<int>::const_iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit << " ";++sit;}cout << endl;for (auto e : s)cout << e << " ";cout << endl;}void TestUSet(){blue::unordered_set<int> s;int a[] = { 30000,1,6,7,888,2,1,1,5,99996,7,6 };for (auto e : a)s.insert(e);blue::unordered_set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit << " ";++sit;}cout << endl;for (auto& e : s)cout << e << " ";cout << endl;Print(s);}void TestUMap(){blue::unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });dict.insert({ "字符串", "string" });dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });dict["left"] = "左边,剩余";dict["insert"] = "插入";dict["string"];for (auto& kv : dict)cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;cout << endl;blue::unordered_map<string, string>::iterator mit = dict.begin();while (mit != dict.end()){// 不能修改first,可以修改second//mit->first += 'x';mit->second += 'x';cout << mit->first << ":" << mit->second << endl;++mit;}cout << endl;}int main(){TestUSet();cout << "----------------------" << endl;TestUMap();return 0;}七、结语
本篇到这里就结束了,主要讲了用哈希表封装unordered_set和unordered_map的详细过程,希望对大家有帮助,祝生活愉快!