?个人主页: 鑫宝Code
?热门专栏: 闲话杂谈| 炫酷HTML | JavaScript基础
?个人格言: "如无必要,勿增实体"

文章目录
React Router:深入理解前端路由的工作原理路由的演进历程传统多页面应用路由单页面应用路由的革命 React Router 的核心架构路由匹配机制路由上下文 (Router Context) 路由模式详解History 模式Hash 模式 路由渲染原理路由匹配流程嵌套路由实现 路由守卫与权限控制路由拦截机制 性能优化策略代码分割路由缓存 最佳实践路由配置建议 未来展望结语
React Router:深入理解前端路由的工作原理
在现代单页应用(SPA)开发中,路由是不可或缺的核心功能。React Router 作为 React 生态系统中最流行的路由库,为开发者提供了强大且灵活的路由解决方案。本文将深入探讨 React Router 的工作原理,帮助开发者更好地理解其内部机制。

路由的演进历程
传统多页面应用路由
在传统的多页面应用中,路由是由服务器完全控制的。每次页面跳转都需要向服务器请求新的 HTML 页面,这导致了页面加载缓慢和用户体验不佳。
单页面应用路由的革命
随着前端技术的发展,单页面应用(SPA)应运而生。SPA 通过在客户端动态渲染页面,大大提升了用户体验。React Router 正是这一革命的重要工具。
React Router 的核心架构
路由匹配机制
React Router 的路由匹配是通过一系列复杂的算法实现的。其核心是将路径字符串与预定义的路由规则进行匹配。
// 路由匹配简化示例function matchRoutes(routes, location) { for (let route of routes) { if (route.path === location.pathname) { return route; } } return null;}路由上下文 (Router Context)
React Router 使用上下文机制来在组件树中传递路由信息。这允许任何嵌套的组件都能访问路由状态。
const RouterContext = React.createContext({ location: null, history: null});路由模式详解
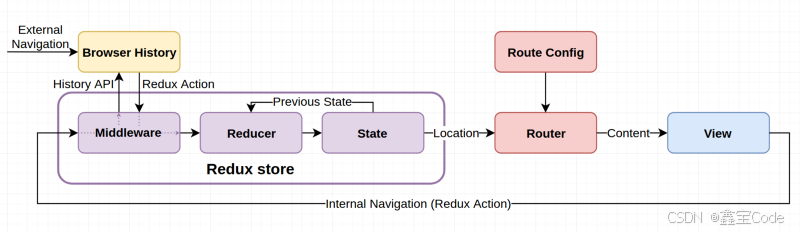
History 模式
History 模式是 React Router 最常用的路由模式,它利用 HTML5 的 History API 实现无刷新的页面跳转。
// History 模式核心实现class BrowserHistory { constructor() { this.listeners = []; window.addEventListener('popstate', this.handlePopState); } push(path) { window.history.pushState(null, '', path); this.notifyListeners(); } listen(listener) { this.listeners.push(listener); } handlePopState = () => { this.notifyListeners(); } notifyListeners() { this.listeners.forEach(listener => listener(window.location) ); }}Hash 模式
Hash 模式通过 URL 的 hash 部分实现路由,主要用于兼容老旧浏览器。
// Hash 模式实现class HashHistory { constructor() { window.addEventListener('hashchange', this.handleHashChange); } handleHashChange = () => { // 处理 hash 变化 }}路由渲染原理
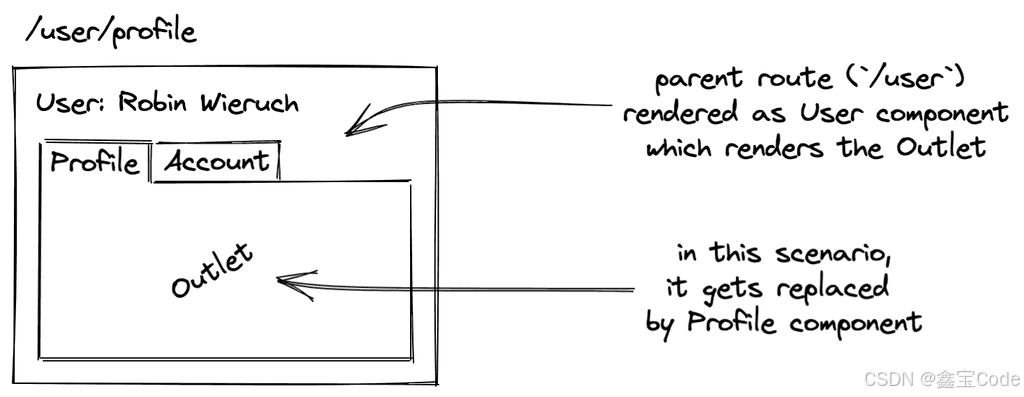
路由匹配流程
React Router 的路由匹配是一个多步骤的过程:
解析当前 URL遍历路由配置找到匹配的路由组件渲染对应的组件function Router({ routes, location }) { const matchedRoute = routes.find(route => matchPath(location.pathname, route.path) ); return matchedRoute ? <matchedRoute.component /> : <NotFound />;}嵌套路由实现
React Router 通过递归渲染实现复杂的嵌套路由结构。
function NestedRouter({ routes, parentPath = '' }) { return routes.map(route => { const fullPath = `${parentPath}${route.path}`; return ( <Route path={fullPath} render={(props) => ( <> <route.component {...props} /> {route.children && ( <NestedRouter routes={route.children} parentPath={fullPath} /> )} </> )} /> ); });}路由守卫与权限控制

路由拦截机制
React Router 可以通过高阶组件或自定义 Hook 实现路由守卫。
function PrivateRoute({ component: Component, ...rest }) { const isAuthenticated = checkUserAuthentication(); return ( <Route {...rest} render={props => isAuthenticated ? ( <Component {...props} /> ) : ( <Redirect to="/login" /> ) } /> );}性能优化策略
代码分割
React Router 结合 React.lazy 可以实现路由级别的代码分割。
const Home = React.lazy(() => import('./Home'));const About = React.lazy(() => import('./About'));function App() { return ( <Suspense fallback={<Loading />}> <Switch> <Route path="/home" component={Home} /> <Route path="/about" component={About} /> </Switch> </Suspense> );}路由缓存
通过缓存已加载的路由组件,可以提高页面切换的性能。
最佳实践
路由配置建议
保持路由配置的扁平化使用嵌套路由管理复杂页面合理使用路由守卫优化代码分割未来展望
随着 React Router v6 的推出,路由库正变得更加声明式和简单。未来的发展趋势将更加关注:
更简洁的API更好的性能更强大的代码分割能力结语
深入理解 React Router 的工作原理,不仅能帮助开发者更好地使用这个库,还能提升对前端路由的整体认知。路由不仅仅是页面跳转,更是构建现代 Web 应用的重要基石。
通过本文,相信读者已经对 React Router 有了更深入的理解。希望这些insights能够帮助大家在实际开发中更好地运用路由技术。