文章目录
- 1、激活函数的实现
- 1.1 sigmoid
- 1.1.1 函数
- 1.1.2 导数
- 1.1.3 代码实现
- 1.2 softmax
- 1.2.1 函数
- 1.2.2 导数
- 1.2.3 代码实现
- 1.3 tanh
- 1.3.1 函数
- 1.3.2 导数
- 1.3.3 代码实现
- 1.4 relu
- 1.4.1 函数
- 1.4.2 导数
- 1.4.3 代码实现
- 1.5 leakyrelu
- 1.5.1 函数
- 1.5.2 导数
- 1.5.3 代码实现
- 1.6 ELU
- 1.61 函数
- 1.6.2 导数
- 1.6.3 代码实现
- 1.7 selu
- 1.7.1 函数
- 1.7.2 导数
- 1.7.3 代码实现
- 1.8 softplus
- 1.81 函数
- 1.8.2 导数
- 1.8.3 代码实现
- 1.9 Swish
- 1.9.1 函数
- 1.9.2 导数
- 1.9.3 代码实现
- 1.10 Mish
- 1.10.1 函数
- 1.10.2 导数
- 1.10.3 代码实现
- 1.11 SiLU
- 1.11.1 函数
- 1.11.2 导数
- 1.11.3 代码实现
- 1.12 完整代码
1、激活函数的实现
1.1 sigmoid
1.1.1 函数
函数: f ( x ) = 1 1 + e − x f(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} f(x)=1+e−x1
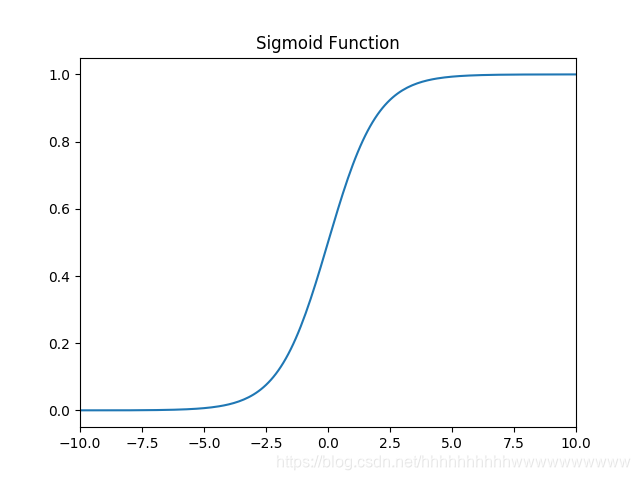
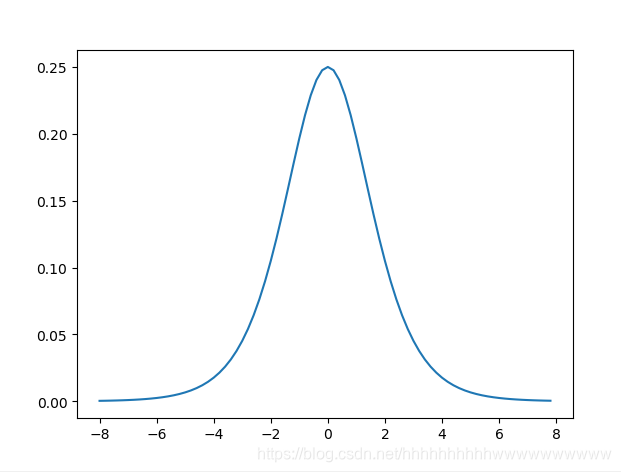
1.1.2 导数
求导过程:
根据:
(
u
v
)
′
=
u
′
v
−
u
v
′
v
2
\left ( \frac{u}{v} \right ){}'=\frac{{u}'v-u{v}'}{v^{2}}
(vu)′=v2u′v−uv′
f
(
x
)
′
=
(
1
1
+
e
−
x
)
′
=
1
′
×
(
1
+
e
−
x
)
−
1
×
(
1
+
e
−
x
)
′
(
1
+
e
−
x
)
2
=
e
−
x
(
1
+
e
−
x
)
2
=
1
+
e
−
x
−
1
(
1
+
e
−
x
)
2
=
(
1
1
+
e
−
x
)
(
1
−
1
1
+
e
−
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
(
1
−
f
(
x
)
)
\begin{aligned} f(x)^{\prime} &=\left(\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}\right)^{\prime} \\ &=\frac{1^{\prime} \times\left(1+e^{-x}\right)-1 \times\left(1+e^{-x}\right)^{\prime}}{\left(1+e^{-x}\right)^{2}} \\ &=\frac{e^{-x}}{\left(1+e^{-x}\right)^{2}} \\ &=\frac{1+e^{-x}-1}{\left(1+e^{-x}\right)^{2}} \\ &=\left(\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}\right)\left(1-\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}\right) \\ &=\quad f(x)(1-f(x)) \end{aligned}
f(x)′=(1+e−x1)′=(1+e−x)21′×(1+e−x)−1×(1+e−x)′=(1+e−x)2e−x=(1+e−x)21+e−x−1=(1+e−x1)(1−1+e−x1)=f(x)(1−f(x))
1.1.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class Sigmoid():
def __call__(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.__call__(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
1.2 softmax
1.2.1 函数
softmax用于多分类过程中,它将多个神经元的输出,映射到(0,1)区间内,可以看成概率来理解,从而来进行多分类!
假设我们有一个数组,V,Vi表示V中的第i个元素,那么这个元素的softmax值就是:
S
i
=
e
i
∑
j
e
j
S_{i}=\frac{e^{i}}{\sum _{j}e^{j}}
Si=∑jejei
更形象的如下图表示:
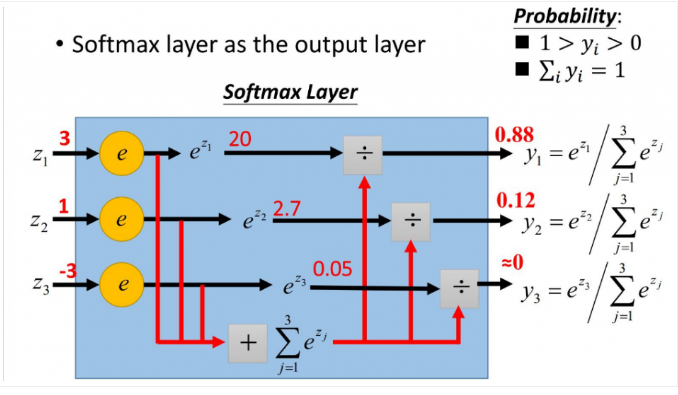
y
1
=
e
z
1
e
z
1
+
e
z
2
+
e
z
3
y
2
=
e
z
2
e
z
1
+
e
z
2
+
e
z
3
y
3
=
e
z
3
e
z
1
+
e
z
2
+
e
z
3
(1)
y1=\frac{e^{z_{1}}}{e^{z_{1}}+e^{z_{2}}+e^{z_{3}}}\\ y2=\frac{e^{z_{2}}}{e^{z_{1}}+e^{z_{2}}+e^{z_{3}}}\\ y3=\frac{e^{z_{3}}}{e^{z_{1}}+e^{z_{2}}+e^{z_{3}}}\\ \tag{1}
y1=ez1+ez2+ez3ez1y2=ez1+ez2+ez3ez2y3=ez1+ez2+ez3ez3(1)
要使用梯度下降,就需要一个损失函数,一般使用交叉熵作为损失函数,交叉熵函数形式如下:
L
o
s
s
=
−
∑
i
y
i
l
n
a
i
(2)
Loss = -\sum_{i}^{}{y_{i}lna_{i} } \tag{2}
Loss=−i∑yilnai(2)
1.2.2 导数
求导分为两种情况。
第一种j=i:
S
i
=
e
i
∑
j
e
j
=
e
i
∑
i
e
i
S_{i}=\frac{e^{i}}{\sum _{j}e^{j}}=\frac{e^{i}}{\sum _{i}e^{i}}
Si=∑jejei=∑ieiei
推导过程如下:
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 59: …\right ){}' \\ &̲=&\frac{\left (…
1.2.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class Softmax():
def __call__(self, x):
e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True))
return e_x / np.sum(e_x, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
def gradient(self, x):
p = self.__call__(x)
return p * (1 - p)
1.3 tanh
1.3.1 函数
t a n h ( x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x tanh(x)=\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}} tanh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x
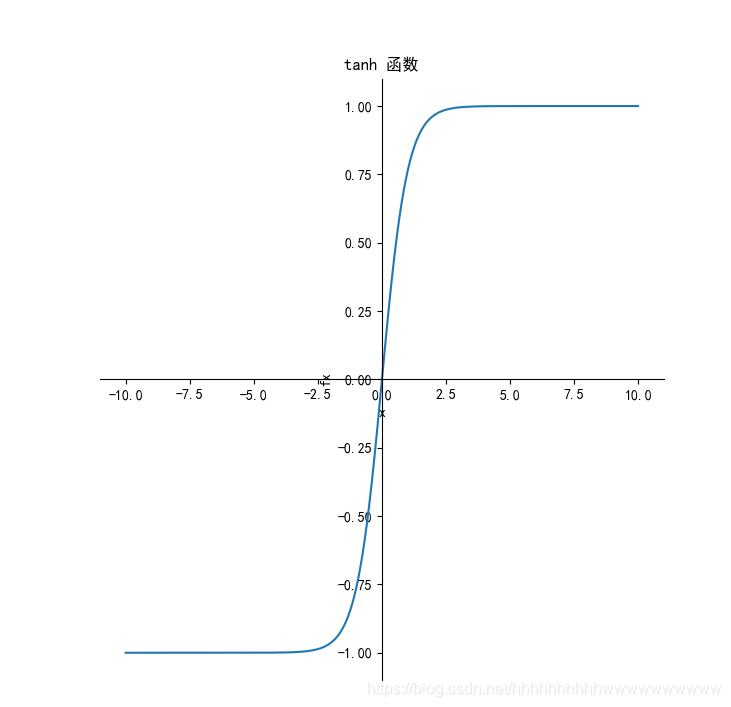
1.3.2 导数
求导过程:
tanh
(
x
)
′
=
(
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
′
=
(
e
x
−
e
−
x
)
′
(
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
−
(
e
x
−
e
−
x
)
(
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
′
(
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
2
=
(
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
2
−
(
e
x
⋅
e
−
x
)
2
(
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
2
=
1
−
(
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
)
2
=
1
−
tanh
(
x
)
2
\begin{aligned} \tanh (x)^{\prime} &=\left(\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}\right)^{\prime} \\ &=\frac{\left(e^{x}-e^{-x}\right)^{\prime}\left(e^{x}+e^{-x}\right)-\left(e^{x}-e^{-x}\right)\left(e^{x}+e^{-x}\right)^{\prime}}{\left(e^{x}+e^{-x}\right)^{2}} \\ &=\frac{\left(e^{x}+e^{-x}\right)^{2}-\left(e^{x} \cdot e^{-x}\right)^{2}}{\left(e^{x}+e^{-x}\right)^{2}} \\ &=1-\left(\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}\right)^{2} \\ &=1-\tanh (x)^{2} \end{aligned}
tanh(x)′=(ex+e−xex−e−x)′=(ex+e−x)2(ex−e−x)′(ex+e−x)−(ex−e−x)(ex+e−x)′=(ex+e−x)2(ex+e−x)2−(ex⋅e−x)2=1−(ex+e−xex−e−x)2=1−tanh(x)2
1.3.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class TanH():
def __call__(self, x):
return 2 / (1 + np.exp(-2*x)) - 1
def gradient(self, x):
return 1 - np.power(self.__call__(x), 2)
1.4 relu
1.4.1 函数
f ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) f(x)=\max (0, x) f(x)=max(0,x)
1.4.2 导数
f ′ ( x ) = { 1 if ( x > 0 ) 0 if ( x < = 0 ) f^{\prime}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} 1 & \text { if } (x>0) \\ 0 & \text { if } (x<=0) \end{array}\right. f′(x)={10 if (x>0) if (x<=0)
1.4.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class ReLU():
def __call__(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, x, 0)
def gradient(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, 1, 0)
1.5 leakyrelu
1.5.1 函数
f ( x ) = max ( a x , x ) f(x)=\max (a x, x) f(x)=max(ax,x)
1.5.2 导数
f ′ ( x ) = { 1 if ( x > 0 ) a if ( x < = 0 ) f^{\prime}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl} 1 & \text { if } (x>0) \\ a & \text { if }(x<=0) \end{array}\right. f′(x)={1a if (x>0) if (x<=0)
1.5.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class LeakyReLU():
def __init__(self, alpha=0.2):
self.alpha = alpha
def __call__(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, x, self.alpha * x)
def gradient(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, 1, self.alpha)
1.6 ELU
1.61 函数
f ( x ) = { x , if x ≥ 0 a ( e x − 1 ) , if ( x < 0 ) f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cll} x, & \text { if } x \geq 0 \\ a\left(e^{x}-1\right), & \text { if } (x<0) \end{array}\right. f(x)={x,a(ex−1), if x≥0 if (x<0)
1.6.2 导数
当x>=0时,导数为1。
当x<0时,导数的推导过程:
f
(
x
)
′
=
(
a
(
e
x
−
1
)
)
′
=
a
e
x
=
a
(
e
x
−
1
)
+
a
=
f
(
x
)
+
a
=
a
e
x
\begin{aligned} \\ f(x)^{\prime} &=\left(a\left(e^{x}-1\right)\right)^{\prime} \\ &=a e^{x} \\ &\left.=a (e^{x}-1\right)+a \\ &=f(x)+a=ae^{x} \end{aligned}
f(x)′=(a(ex−1))′=aex=a(ex−1)+a=f(x)+a=aex
所以,完整的导数为:
f
′
=
{
1
if
x
≥
0
f
(
x
)
+
a
=
a
e
x
if
x
<
0
f^{\prime}=\left\{\begin{array}{cll} 1 & \text { if } & x \geq 0 \\ f(x)+a=ae^{x} & \text { if } & x<0 \end{array}\right.
f′={1f(x)+a=aex if if x≥0x<0
1.6.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class ELU():
def __init__(self, alpha=0.1):
self.alpha = alpha
def __call__(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0.0, x, self.alpha * (np.exp(x) - 1))
def gradient(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0.0, 1, self.__call__(x) + self.alpha)
1.7 selu
1.7.1 函数
selu ( x ) = λ { x if ( x > 0 ) α e x − α if ( x ⩽ 0 ) \operatorname{selu}(x)=\lambda \begin{cases}x & \text { if } (x>0) \\ \alpha e^{x}-\alpha & \text { if } (x \leqslant 0)\end{cases} selu(x)=λ{xαex−α if (x>0) if (x⩽0)
1.7.2 导数
selu ′ ( x ) = λ { 1 x > 0 α e x ⩽ 0 \operatorname{selu}^{\prime}(x)=\lambda \begin{cases}1 & x>0 \\ \alpha e^{x} & \leqslant 0\end{cases} selu′(x)=λ{1αexx>0⩽0
1.7.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class SELU():
# Reference : https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02515,
# https://github.com/bioinf-jku/SNNs/blob/master/SelfNormalizingNetworks_MLP_MNIST.ipynb
def __init__(self):
self.alpha = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717
self.scale = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946
def __call__(self, x):
return self.scale * np.where(x >= 0.0, x, self.alpha*(np.exp(x)-1))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.scale * np.where(x >= 0.0, 1, self.alpha * np.exp(x))
1.8 softplus
1.81 函数
Softplus ( x ) = log ( 1 + e x ) \operatorname{Softplus}(x)=\log \left(1+e^{x}\right) Softplus(x)=log(1+ex)
1.8.2 导数
log默认的底数是
e
e
e
f
′
(
x
)
=
e
x
(
1
+
e
x
)
ln
e
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
σ
(
x
)
f^{\prime}(x)=\frac{e^{x}}{(1+e^{x})\ln e}=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}=\sigma(x)
f′(x)=(1+ex)lneex=1+e−x1=σ(x)
1.8.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class SoftPlus():
def __call__(self, x):
return np.log(1 + np.exp(x))
def gradient(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
1.9 Swish
1.9.1 函数
f ( x ) = x ⋅ sigmoid ( β x ) f(x)=x \cdot \operatorname{sigmoid}(\beta x) f(x)=x⋅sigmoid(βx)
1.9.2 导数
f ′ ( x ) = σ ( β x ) + β x ⋅ σ ( β x ) ( 1 − σ ( β x ) ) = σ ( β x ) + β x ⋅ σ ( β x ) − β x ⋅ σ ( β x ) 2 = β x ⋅ σ ( x ) + σ ( β x ) ( 1 − β x ⋅ σ ( β x ) ) = β f ( x ) + σ ( β x ) ( 1 − β f ( x ) ) \begin{aligned} f^{\prime}(x) &=\sigma(\beta x)+\beta x \cdot \sigma(\beta x)(1-\sigma(\beta x)) \\ &=\sigma(\beta x)+\beta x \cdot \sigma(\beta x)-\beta x \cdot \sigma(\beta x)^{2} \\ &=\beta x \cdot \sigma(x)+\sigma(\beta x)(1-\beta x \cdot \sigma(\beta x)) \\ &=\beta f(x)+\sigma(\beta x)(1-\beta f(x)) \end{aligned} f′(x)=σ(βx)+βx⋅σ(βx)(1−σ(βx))=σ(βx)+βx⋅σ(βx)−βx⋅σ(βx)2=βx⋅σ(x)+σ(βx)(1−βx⋅σ(βx))=βf(x)+σ(βx)(1−βf(x))
1.9.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
class Swish(object):
def __init__(self, b):
self.b = b
def __call__(self, x):
return x * (np.exp(self.b * x) / (np.exp(self.b * x) + 1))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.b * x / (1 + np.exp(-self.b * x)) + (1 / (1 + np.exp(-self.b * x)))(
1 - self.b * (x / (1 + np.exp(-self.b * x))))
1.10 Mish
1.10.1 函数
f ( x ) = x ∗ tanh ( ln ( 1 + e x ) ) f(x)=x * \tanh \left(\ln \left(1+e^{x}\right)\right) f(x)=x∗tanh(ln(1+ex))
1.10.2 导数
f
′
(
x
)
=
sech
2
(
soft
plus
(
x
)
)
x
sigmoid
(
x
)
+
f
(
x
)
x
=
Δ
(
x
)
s
w
i
sh
(
x
)
+
f
(
x
)
x
\begin{gathered} f^{\prime}(x)=\operatorname{sech}^{2}(\operatorname{soft} \operatorname{plus}(x)) x \operatorname{sigmoid}(x)+\frac{f(x)}{x} \\ =\Delta(x) s w i \operatorname{sh}(x)+\frac{f(x)}{x} \end{gathered}
f′(x)=sech2(softplus(x))xsigmoid(x)+xf(x)=Δ(x)swish(x)+xf(x)
where softplus
(
x
)
=
ln
(
1
+
e
x
)
(x)=\ln \left(1+e^{x}\right)
(x)=ln(1+ex) and sigmoid
(
x
)
=
1
/
(
1
+
e
−
x
)
(x)=1 /\left(1+e^{-x}\right)
(x)=1/(1+e−x).
1.10.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
def sech(x):
"""sech函数"""
return 2 / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid(x):
"""sigmoid函数"""
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def soft_plus(x):
"""softplus函数"""
return np.log(1 + np.exp(x))
def tan_h(x):
"""tanh函数"""
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
class Mish:
def __call__(self, x):
return x * tan_h(soft_plus(x))
def gradient(self, x):
return sech(soft_plus(x)) * sech(soft_plus(x)) * x * sigmoid(x) + tan_h(soft_plus(x))
1.11 SiLU
1.11.1 函数
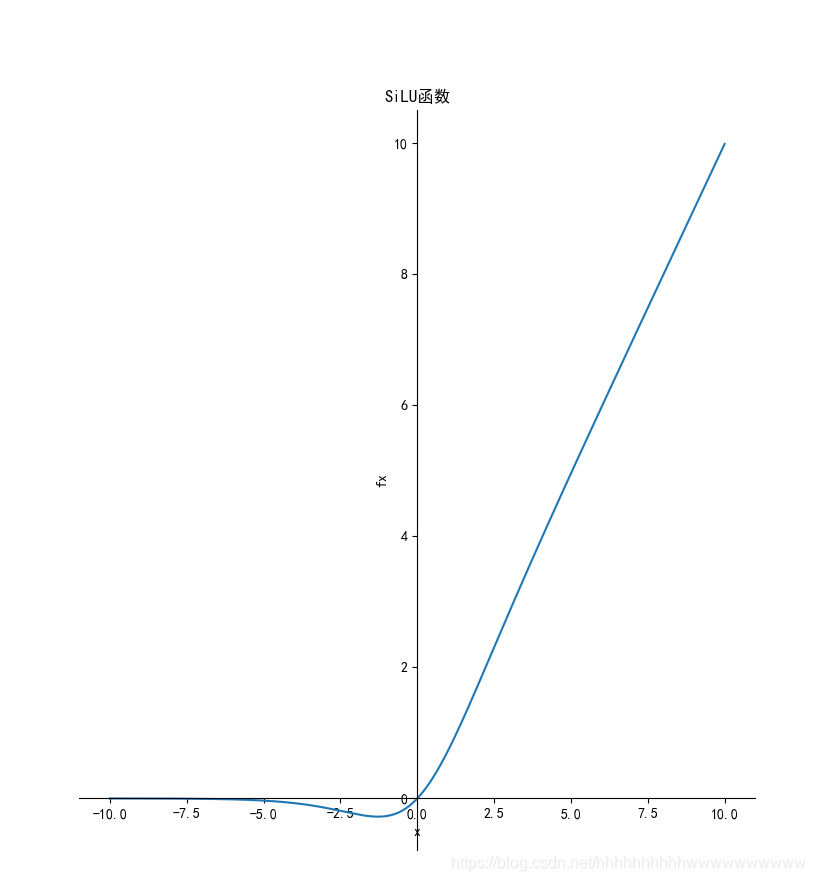
f ( x ) = x × s i g m o i d ( x ) f(x)=x \times sigmoid (x) f(x)=x×sigmoid(x)
1.11.2 导数
推导过程
f
(
x
)
′
=
(
x
⋅
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
)
′
=
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
+
x
⋅
(
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
(
1
−
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
)
=
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
+
x
⋅
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
−
x
⋅
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
2
(
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
+
sigmoid
(
x
)
(
1
−
f
(
x
)
)
\begin{aligned} &f(x)^{\prime}=(x \cdot sigmoid(x))^{\prime}\\ &=sigmoid(x)+x \cdot(sigmoid(x)(1-sigmoid(x))\\ &=sigmoid(x)+x \cdot sigmoid(x)-x \cdot sigmoid^{2}(x)\\ &=f(x)+\operatorname{sigmoid}(x)(1-f(x)) \end{aligned}
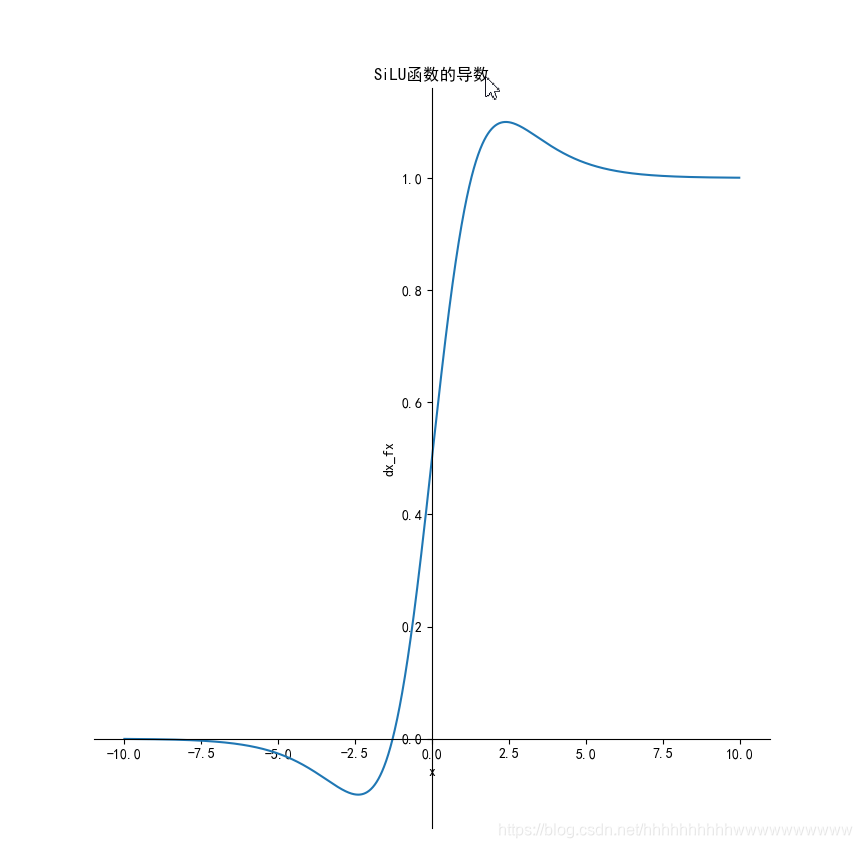
f(x)′=(x⋅sigmoid(x))′=sigmoid(x)+x⋅(sigmoid(x)(1−sigmoid(x))=sigmoid(x)+x⋅sigmoid(x)−x⋅sigmoid2(x)=f(x)+sigmoid(x)(1−f(x))
1.11.3 代码实现
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
"""sigmoid函数"""
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
class SILU(object):
def __call__(self, x):
return x * sigmoid(x)
def gradient(self, x):
return self.__call__(x) + sigmoid(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
1.12 完整代码
定义一个activation_function.py,将下面的代码复制进去,到这里激活函数就完成了。
import numpy as np
# Collection of activation functions
# Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Activation_function
class Sigmoid():
def __call__(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.__call__(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
class Softmax():
def __call__(self, x):
e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True))
return e_x / np.sum(e_x, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
def gradient(self, x):
p = self.__call__(x)
return p * (1 - p)
class TanH():
def __call__(self, x):
return 2 / (1 + np.exp(-2 * x)) - 1
def gradient(self, x):
return 1 - np.power(self.__call__(x), 2)
class ReLU():
def __call__(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, x, 0)
def gradient(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, 1, 0)
class LeakyReLU():
def __init__(self, alpha=0.2):
self.alpha = alpha
def __call__(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, x, self.alpha * x)
def gradient(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0, 1, self.alpha)
class ELU(object):
def __init__(self, alpha=0.1):
self.alpha = alpha
def __call__(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0.0, x, self.alpha * (np.exp(x) - 1))
def gradient(self, x):
return np.where(x >= 0.0, 1, self.__call__(x) + self.alpha)
class SELU():
# Reference : https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02515,
# https://github.com/bioinf-jku/SNNs/blob/master/SelfNormalizingNetworks_MLP_MNIST.ipynb
def __init__(self):
self.alpha = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717
self.scale = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946
def __call__(self, x):
return self.scale * np.where(x >= 0.0, x, self.alpha * (np.exp(x) - 1))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.scale * np.where(x >= 0.0, 1, self.alpha * np.exp(x))
class SoftPlus(object):
def __call__(self, x):
return np.log(1 + np.exp(x))
def gradient(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
class Swish(object):
def __init__(self, b):
self.b = b
def __call__(self, x):
return x * (np.exp(self.b * x) / (np.exp(self.b * x) + 1))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.b * x / (1 + np.exp(-self.b * x)) + (1 / (1 + np.exp(-self.b * x)))(
1 - self.b * (x / (1 + np.exp(-self.b * x))))
def sech(x):
"""sech函数"""
return 2 / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid(x):
"""sigmoid函数"""
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def soft_plus(x):
"""softplus函数"""
return np.log(1 + np.exp(x))
def tan_h(x):
"""tanh函数"""
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
class Mish:
def __call__(self, x):
return x * tan_h(soft_plus(x))
def gradient(self, x):
return sech(soft_plus(x)) * sech(soft_plus(x)) * x * sigmoid(x) + tan_h(soft_plus(x))
class SILU(object):
def __call__(self, x):
return x * sigmoid(x)
def gradient(self, x):
return self.__call__(x) + sigmoid(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
参考公式
(
C
)
′
=
0
(C)^{\prime}=0
(C)′=0
(
a
x
)
′
=
a
x
ln
a
\left(a^{x}\right)^{\prime}=a^{x} \ln a
(ax)′=axlna
(
x
μ
)
′
=
μ
x
μ
−
1
\left(x^{\mu}\right)^{\prime}=\mu x^{\mu-1}
(xμ)′=μxμ−1
(
e
x
)
′
=
e
x
\left(e^{x}\right)^{\prime}=e^{x}
(ex)′=ex
(
sin
x
)
′
=
cos
x
(\sin x)^{\prime}=\cos x
(sinx)′=cosx
(
log
a
x
)
′
=
1
x
ln
a
\left(\log _{a} x\right)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{x \ln a}
(logax)′=xlna1
(
cos
x
)
′
=
−
sin
x
(\cos x)^{\prime}=-\sin x
(cosx)′=−sinx
(
ln
x
)
′
=
1
x
(\ln x)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{x}
(lnx)′=x1
(
tan
x
)
′
=
sec
2
x
(\tan x)^{\prime}=\sec ^{2} x
(tanx)′=sec2x
(
arcsin
x
)
′
=
1
1
−
x
2
(\arcsin x)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}
(arcsinx)′=1−x2
1
(
cot
x
)
′
=
−
csc
2
x
(\cot x)^{\prime}=-\csc ^{2} x
(cotx)′=−csc2x
(
arccos
x
)
′
=
−
1
1
−
x
2
(\arccos x)^{\prime}=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}
(arccosx)′=−1−x2
1
(
sec
x
)
′
=
sec
x
⋅
tan
x
(\sec x)^{\prime}=\sec x \cdot \tan x
(secx)′=secx⋅tanx
(
arctan
x
)
′
=
1
1
+
x
2
(\arctan x)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{1+x^{2}}
(arctanx)′=1+x21
(
csc
x
)
′
=
−
csc
x
⋅
cot
x
(\csc x)^{\prime}=-\csc x \cdot \cot x
(cscx)′=−cscx⋅cotx
(
arccot
x
)
′
=
−
1
1
+
x
2
(\operatorname{arccot} x)^{\prime}=-\frac{1}{1+x^{2}}
(arccotx)′=−1+x21
双曲正弦:
sinh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
2
\sinh x=\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2}
sinhx=2ex−e−x
双曲余弦:
cosh
x
=
e
x
+
e
−
x
2
\cosh x=\frac{e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2}
coshx=2ex+e−x
双曲正切:
tanh
x
=
sinh
x
cosh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
\tanh x=\frac{\sinh x}{\cosh x}=\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}
tanhx=coshxsinhx=ex+e−xex−e−x
双曲余切:
coth
x
=
1
tanh
x
=
e
x
+
e
−
x
e
x
−
e
−
x
\operatorname{coth} x=\frac{1}{\tanh x}=\frac{e^{x}+e^{-x}}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}
cothx=tanhx1=ex−e−xex+e−x
双曲正割:
sech
x
=
1
cosh
x
=
2
e
x
+
e
−
x
\operatorname{sech} x=\frac{1}{\cosh x}=\frac{2}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}
sechx=coshx1=ex+e−x2
双曲余割:
csch
x
=
1
sinh
x
=
2
e
x
−
e
−
x
\operatorname{csch} x=\frac{1}{\sinh x}=\frac{2}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}
cschx=sinhx1=ex−e−x2