Pytorch深度学习实战3-2:什么是张量?Tensor的创建与索引
文章标签:
《随便一记》
目录
1 什么是张量?2 Pytorch数据类型与转化3 张量Tensor的创建3.1 类型创建3.2 序列转换3.3 0/1张量3.4 对角张量3.5 正态张量3.6 随机向量3.7 线性张量 4 张量Tensor的索引4.1 下标索引4.2 条件索引4.3 附加控制索引
1 什么是张量?
张量(Tensor)是多维数组结构,在人工智能领域应用广泛,例如输入彩色图片即是3维张量——RGB三维且每维都是二维平面像素矩阵。
下面这张表直观地总结了张量的形式,这张表可以解决大部分的张量理解问题
| 维数 | 图例 | 名称 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 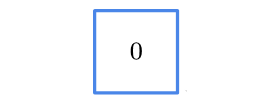 | 标量 |
| 1 | 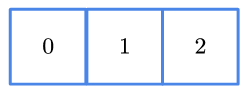 | 向量 |
| 2 | 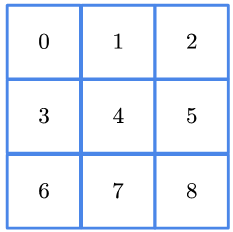 | 矩阵 |
| 3 | 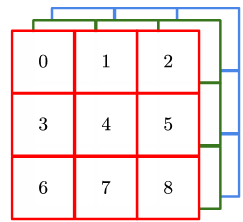 | 三阶张量 |
| N N N | 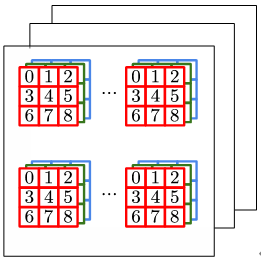 | N N N阶张量 |
2 Pytorch数据类型与转化
| 数据类型 | CPU Tensor | GPU Tensor |
|---|---|---|
| 32位浮点 | torch.FloatTensor | torch.cuda.FloatTensor |
| 64位浮点 | torch.DoubleTensor | torch.cuda.DoubleTensor |
| 16位半精度浮点 | N/A | torch.cuda.HalfTensor |
| 8位无符号整型 | torch.ByteTensor | torch.cuda.ByteTensor |
| 8位有符号整型 | torch.CharTensor | torch.cuda.CharTensor |
| 16位有符号整型 | torch.ShortTensor | torch.cuda.ShortTensor |
| 32位有符号整型 | torch.IntTensor | torch.cuda.IntTensor |
| 64位有符号整型 | torch.LongTensor | torch.cuda.LongTensor |
Pytorch中Tensor数据类型的转换可以使用
显式的type(new_type)隐式的type_as(var) 举例如下:
a = torch.Tensor(2, 2)b = a.type(torch.DoubleTensor)c = a.type_as(b)>> a: tensor([[0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00], [8.4078e-45, 0.0000e+00]])>> b: tensor([[0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00], [8.4078e-45, 0.0000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)>> c: tensor([[0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00], [8.4078e-45, 0.0000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)3 张量Tensor的创建
张量Tensor主要的创建方法如下所示。
3.1 类型创建
创建方法
torch.Tensor()torch.DoubleTensor()… 实例
b = torch.cuda.DoubleTensor(2,2)>> b: tensor([[0., 0.], [0., 0.]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64)3.2 序列转换
创建方法
torch.Tensor(list)torch.Tensor(narray) 实例
a = torch.DoubleTensor([[1, 2],[3, 4]])>> a: tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]], dtype=torch.float64)3.3 0/1张量
创建方法
torch.zeros()torch.ones() 实例
a = torch.ones(2,2)>> a: tensor([[1., 1.], [1., 1.]])3.4 对角张量
创建方法
torch.eye() 实例
a = torch.eye(2,2)>> a: tensor([[1., 0.], [0., 1.]])3.5 正态张量
创建方法
torch.randn() 实例
a = torch.randn(2,2)>> a: tensor([[-0.0451, -0.1602], [-0.1116, 0.8266]])3.6 随机向量
创建方法
torch.randperm(n):将0~n-1的整数随机排列成向量 实例
a = torch.randperm(3)>> a: tensor([2, 0, 1])3.7 线性张量
创建方法
torch.arrange(s,e,step):生成从s到e间隔step的向量torch.linspace(s,e,num):生成从s到e共num的均匀向量 实例
a = torch.arange(1,8,3)>> tensor([1, 4, 7])b = torch.linspace(1,8,3)>> tensor([1.0000, 4.5000, 8.0000])4 张量Tensor的索引
对于一个给定Tensor,可通过Tensor的shape属性或size()方法查看其维度,通过numel()方法查看元素总数
a = torch.eye(3,3)print("shape维度", a.shape)print("size维度", a.size())print("numel元素个数", a.numel())>> shape维度 torch.Size([3, 3])>> size维度 torch.Size([3, 3])>> numel元素个数 9Tensor维度按从左到右顺序分配dim索引号如下,新增维度的dim索引号总为0
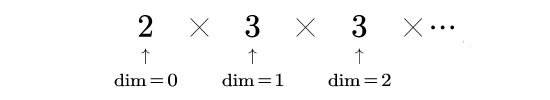
具体的索引方式如下,设a=torch.Tensor([[0,1],[2,3]]))
4.1 下标索引
索引方法
tensor[num] 实例
a[1]>> tensor([2., 3.])a[0,1]>> tensor(1.)4.2 条件索引
索引方法
tensor>0:符合条件为Truetensor[tensor>0]:取出符合条件的元素torch.nonzero(tensor):取出非零元素坐标 实例
a>0>> tensor([[False, True], [ True, True]])a[a>0]>> tensor([1., 2., 3.])torch.nonzero(a)>> tensor([[0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])4.3 附加控制索引
索引方法
torch.where(condition,x,y):两个同型张量x、y,符合条件输出x相应位置元素,否则输出ytensor.clamp(min,max):限制元素极值 实例
torch.where(a > 1, torch.full_like(a, 1), a)>> tensor([[0., 1.], [1., 1.]])a.clamp(1,2)>> tensor([[1., 1.], [2., 2.]])? 更多精彩专栏:
《ROS从入门到精通》《Pytorch深度学习实战》《机器学习强基计划》《运动规划实战精讲》…?源码获取 · 技术交流 · 抱团学习 · 咨询分享 请联系?

登录后可发表评论
点击登录