目录
一.图书管理系统分析
1.1系统设计要求
1.2设计思路
二.操作代码的实现
2.1书架书籍代码实现
2.2用户操作代码实现
2.2.1增加书籍
2.2.2移除书籍
2.2.3查询书籍
2.2.4展示书架书籍信息
2.2.5借阅书籍代码
2.2.6归还图书代码
2.2.7退出系统
3.用户登录操作
四.主函数的调用
总结
?个人主页: tq02的博客_CSDN博客-C语言,Java领域博主
?梦中理想:努力学习,向Java进发,拼搏一切,找到一份朝九晚五,有假期的工作,让 自己的未来不会有遗憾。
?欢迎各位→点赞? + 收藏⭐ + 评论?+关注✨
本章讲解内容:图书馆管理系统简略版
使用编译器:IDEA

注:本文有些长,请耐心观看,看完之后,不懂打我。
一.图书管理系统分析
1.1系统设计要求
为图书馆管理人员实现一个图书管理系统,主要设计:实现对图书的管理、以及其它相关操作。
1.2设计思路
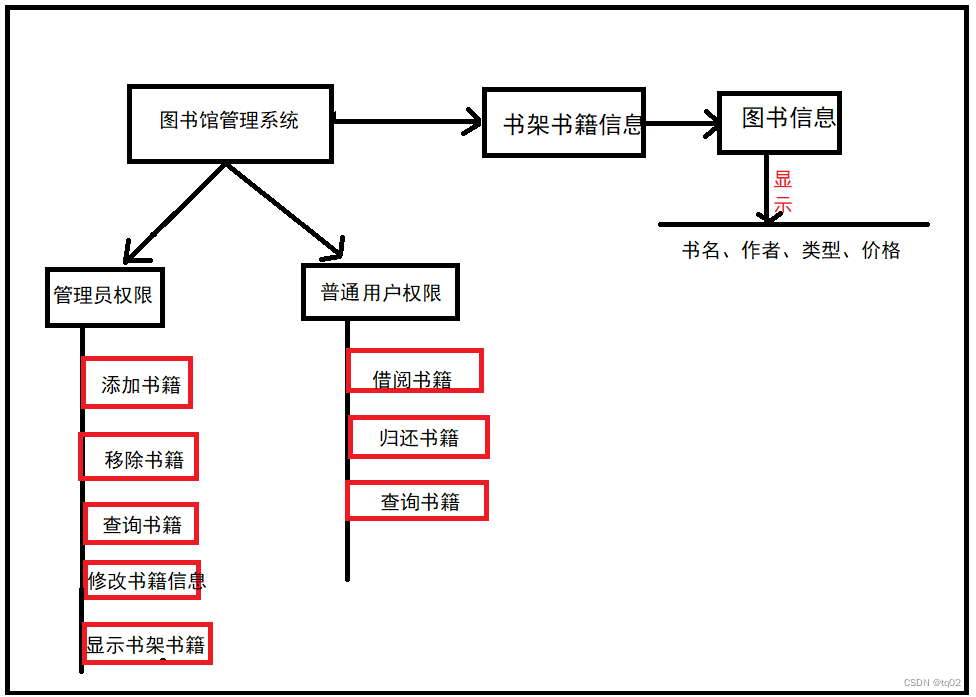
图书馆管理系统大概思路如上图,书籍放在书架当中,登陆系统有2个权限(管理员和普通用户)。
二.操作代码的实现
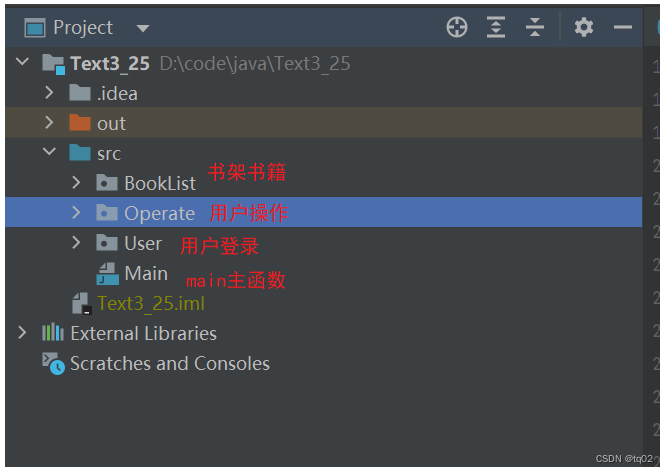
为了让代码有更高的可读性,我们可以将代码分为三个包,分别存储用户登录、书架书籍、用户操作。
用户登陆:判断用户为管理员还是普通用户。
用户操作:对书架的书籍进行操作。
书架书籍:在用户操作之后,记录此时书架的书籍状态。
如此图:
2.1书架书籍代码实现
书架书籍,顾名思义,记录书架上的书和书本的信息。使用需要建立两个类,书架类和存放书本信息类。 也可以说,书架类,存放的是书本信息的数组。而数组大小取决于书的多少
书籍信息代码实现:
public class Book { private String name; //书名 private String author; //作者 private int price; //价格 private String type; //类型 private boolean isBorrow; //是否借出 public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; this.type = type; } @Override public String toString() { return "书名:"+name+" 价格:"+price+" 作者:"+author+" 类型:"+type+" 状态:"+ ((this.isBorrow==true)?"已借出":"未借出"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public boolean isBorrow() { return isBorrow; } public void setBorrow(boolean borrow) { isBorrow = borrow; }}书架信息实现:
public class BookList { Book[] books=new Book[10]; //书架存放量; public int size; //已存放量 public BookList() { books[0]=new Book("西游记","吴承恩",22,"小说"); books[1]=new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",20,"小说"); books[2]=new Book("水浒传","施耐庵",25,"小说"); books[3]=new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",28,"小说"); this.size=4; } public int getSize() { return size; } public void setSize(int size) { this.size = size; } public Book getBook(int pos) { return books[pos]; } public void setBook(int pos,Book book) { books[pos] = book; }}
2.2用户操作代码实现
用户操作,操作的是书架上的书籍,对其进行增删查改等操作。而这一切都同一个方法名和参数。
所以我们可以写一个接口,使所有的操作都继承于它,而这个接口的创建有利于用户登录后的选择操作。
接口:
public interface IOPeration { void work(BookList bookList);}
2.2.1增加书籍
增加图书,得增加图书的各类信息
public class AddOperation implements IOPeration{ //将书架地址传入,对其修改 public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("新增图书!");//业务逻辑!!! Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:"); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书的作者:"); String author = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书的类型:"); String type = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书的价格:"); int price = scanner.nextInt(); Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type); int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); bookList.setBooks(currentSize,book); bookList.setUsedSize(currentSize+1); System.out.println("新增图书成功!!"); }}2.2.2移除书籍
当移除图书时,得先判断是否存在此书籍,然后删除,删除方式:从需要删除的书籍之后开始,将后面的每一个书籍信息覆盖在前面一个,并且将数组最后一个置空,书本量减一。
public class DelOperation implements IOPeration{ public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("删除图书!"); //1、找到你要删除的图书是否存在? Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要删除的图书名字:"); String name = scanner.nextLine();//水浒传 int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); int delIndex = -1; int i = 0; for (; i < currentSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBook(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)) { delIndex = i; break; } } if(i == currentSize) { System.out.println("没有你删除的这本书!"); return; } for (int j = delIndex; j < currentSize-1; j++) { //[j] = [j+1] Book book = bookList.getBook(j+1); bookList.setBooks(j,book); } bookList.setBooks(currentSize-1,null); bookList.setUsedSize(currentSize-1); System.out.println("删除图书成功!"); }}2.2.3查询书籍
在书架上查找书籍,自然而然从第一步开始查找。当然也存在此书籍不存在的情况。
public class FindOperation implements IOPeration{ public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("查找图书!"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要查找的图书姓名:"); String name = scanner.nextLine();//水浒传 int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBook(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)) { System.out.println("找到这本书了!"); System.out.println(book); return; } } System.out.println("没有你要查找的这本书!"); }}2.2.4展示书架书籍信息
public class ShowOperation implements IOPeration{ public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("打印所有图书!"); int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBook(i); System.out.println(book); } }}2.2.5借阅书籍代码
当书籍借阅之后,需要进行备注,已借出。
public class BorrowOperation implements IOPeration{ public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("借阅图书!"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要借阅的图书的名字:"); String name = scanner.nextLine();//水浒传 int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBook(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)) { if(book.isBorrowed()) { System.out.println("该书已经被借出!"); }else{ book.setBorrowed(true); } return; } } System.out.println("没有你要借阅的图书!"); }}2.2.6归还图书代码
public class ReturnOperation implements IOPeration{ public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("归还图书!"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要归还的图书的名字:"); String name = scanner.nextLine();//水浒传 int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBook(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)) { book.setBorrowed(false); return; } } System.out.println("没有你要归还的图书!"); }}2.2.7退出系统
当操作完毕之后,需要退出系统。
public class ExitOperation implements IOPeration{ @Override public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("退出系统!"); System.exit(0); }}
3.用户登录操作
用户,分为管理员和普通用户,不同的用户身份,拥有不同的权限,因此我们需要两个菜单来供不同的用户选择操作。又因为管理员和普通用户又有许多相同的内容,为了减少代码的冗余性,以及之后的主函数多态调用,所以可以进行继承的方式。
用户代码:
public abstract class User { protected String name; public IOPeration[] ioPerations;//这里我没有分配空间 public User(String name) { this.name = name; } public abstract int menu(); public void doOperation(int choice, BookList bookList){ this.ioPerations[choice].work(bookList); }}我们可以看见在用户操作时,创建的接口的作用:利用接口,创建数组存储着不同的用户的操作。而doOperation()方法,则是调用对应的用户操作方法
普通用户代码:
public class NormalUser extends User{ public NormalUser(String name) { super(name); this.ioPerations = new IOPeration[] { new ExitOperation(), new FindOperation(), new BorrowOperation(), new ReturnOperation() }; } public int menu() { System.out.println("普通用户的菜单!"); System.out.println("************************************************"); System.out.println(" hello " + this.name +" 欢迎来到图书馆管理系统"); System.out.println("***********1. 查找图书 2. 借阅图书***********"); System.out.println("***********3. 归还图书 0. 退出系统!**********"); System.out.println("************************************************"); System.out.println("请输入你的操作:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = scanner.nextInt(); return choice; }}管理员代码:
public class AdminUser extends User{ public AdminUser(String name) { super(name); this.ioPerations = new IOPeration[] { new ExitOperation(), new FindOperation(), new AddOperation(), new DelOperation(), new ShowOperation() }; } public int menu() { System.out.println("管理员菜单!"); System.out.println("************************************************"); System.out.println(" hello " + this.name +" 欢迎来到图书馆管理系统"); System.out.println("***********1. 查找图书 2.新增图书 ***********"); System.out.println("***********3. 删除图书 0. 退出系统!**********"); System.out.println("************************************************"); System.out.println("请输入你的操作:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = scanner.nextInt(); return choice; }}
四.主函数的调用
主函数的调用,重点在于 区分普通用户和管理员用户、创建书架书籍、调用用户操作等。
代码实例:
public class Main { public static User login() { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:"); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入你的身份:1代表管理员,0代表普通用户-》"); int choice = scanner.nextInt(); if(choice == 1) { return new AdminUser(name); }else { return new NormalUser(name); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BookList bookList = new BookList(); //user最终指向哪个用户?? User user = login(); while (true) { //这里调用谁的menu菜单??? int choice = user.menu(); //根据这个choice 来调用指定的 操作?? user.doOperation(choice, bookList); } }}总结
1. 本文章是最为基础的图书馆管理系统,但是即使再简单,也得学会封装、继承、抽象、多态、接口等知识,因为此系统建立在这些知识的基础上。
如果想了解或者回忆这些知识点,可查询 http://t.csdn.cn/Y3UsQ
2. 如果你可以看懂,可以试着尝试,并且自己成功写出来之后,恭喜你Java的基础语法阶段你已经掌握的差不多了 ,可以开始你的新篇章了。