我要扼住命运的咽喉,他却不能使我完全屈服。 --贝多芬

目录
一.带头循环的双向链表的特点
二.不带头不循环单向链表和带头循环的双向链表的对比
三.初始化链表,创建哨兵结点
四.双向链表的各种功能的实现
1.双向链表的尾插
2.双向链表的打印
3.双向链表的头插
4.双向链表的头删
5.双向链表的尾删
6.查找函数
7.在pos位置的前面插入一个数
8.删除pos位置的值
9.头插,尾插直接复用插入函数。头删,尾删直接复用删除函数
10.求双向链表的长度
11.最后销毁双向链表
五.双向链表全部的代码
1.List.h:
2.List.c:
3.test.c:
一.带头循环的双向链表的特点
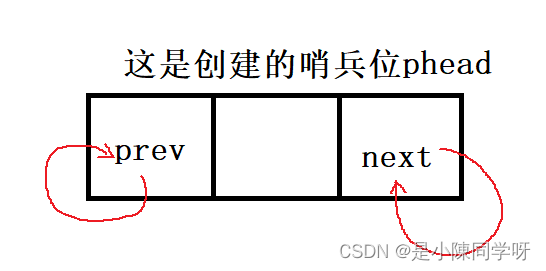
这里的带头就是带一个哨兵位的头结点,这个头结点只是在头位置起一个引导作用,不存放数据。
(后面我们会说头结点具体的作用)循环就是说双向链表是闭合起来的,头尾是相连起来的,双向的意思就是说一个结点有两个指针,一个next指针指向下一个结点,另一个prev指针指向上一个结点。

这是一个逻辑结构,也就是我们想象出来的结构,这大抵就是一个带头循环双向链表的结构。
带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个链表虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现能带来很多优势。
带头双向循环链表其实看起来复杂,如果你理解了,其实实现起来要比单链表简单的。等会你就知道了。
带头循环的双向链表的创建:
typedef int SLDataType;typedef struct ListNode{struct ListNode* next;struct ListNode* prev;SLDataType data;}ListNode;二.不带头不循环单向链表和带头循环的双向链表的对比
查找效率:单向链表,查找的方向只能是一个方向,从头开始向后查找。而双向链表可以向前或者向后查找。查找到一个结点之后,如果还要查找这个结点的前一个结点时,单链表又只有从前开始遍历链表进行查找,时间复杂度时O(N)。而双链表可以使用前一个指针找到前一个结点,时间复杂度是O(N),双向链表效率更高。
单向链表不能自我删除,需要靠辅助节点 ,如果要删除中间的某个结点,你还必须要遍历找到你要删除结点的前一个结点。比较麻烦。
而双向链表就可以解决这个问题,如果你要删除某个结点,你只需要把使用prev指针直接找到前一个结点,使用next指针找到后一个结点,然后把它们链接起来,再free掉你要删除的结点,非常的方便。
关于头结点的使用:昨天我们写的单链表没有使用头结点,其实头结点的用处是非常大的。在不带头的单链表中,如果要头插,每次都会改变头结点的指针,所以我们昨天写的头插函数使用的是传址调用,也就是传了双指针。但是今天要学习的带头双链表,因为它带头结点,无论你是什么插入或者删除,头结点一直不会变,也就避免了使用双指针的问题。使用了头结点也不用考虑空指针的问题,它可以把它们统一处理。(这里我们等会会说)。
三.初始化链表,创建哨兵结点
创建一个函数,在每次需要新的结点时,直接调用这个函数即可。
//创建一个新的结点ListNode*BuyListNode(SLDataType x){ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;}创建一个哨兵头结点,起一个链表的带头作用。
//初始化链表,创建哨兵结点ListNode* ListInit(){ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;}这里为什么要写成phead->next=phead,phead->prev = phead呢?自己指向自己,这里等会会有大用处,可以将NULL的情况统一处理。非常的nice。
四.双向链表的各种功能的实现
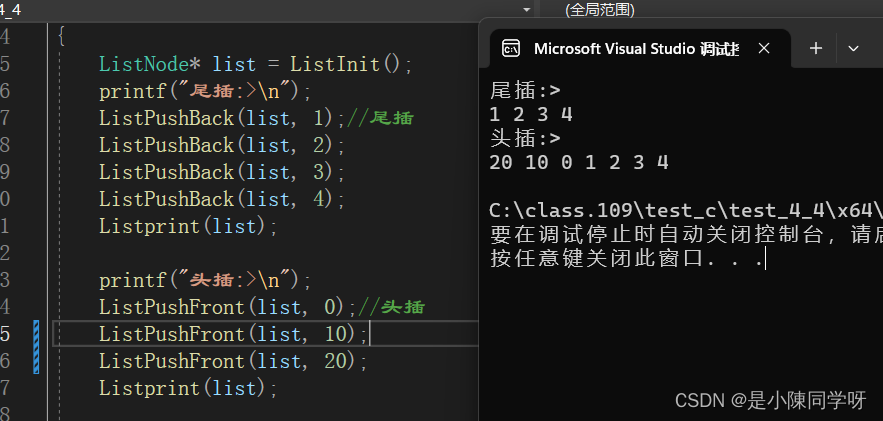
1.双向链表的尾插
这里尾插就会体现我们之前设置的头结点的优势和循环的优势,我们在已有的 1 2 3 后面插上4,我们会怎么做呢?我们要先找到尾,然后再尾后面插上4。下面图是原本的链表样子。我们的目的就是在3的后面再链接一个4。
我们先找到链表的尾,因为这个链表是循环的,所以链表的尾就是phead->prev,剩下的就依次把它们链接起来即可。
void ListPushBack(ListNode*phead, SLDataType x){ListNode* tail = phead->prev;//这是找到的尾ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);tail->next = newnode;//让尾的next指向尾接的新结点newnode->prev = tail;//让新结点的prev指向尾phead->prev = newnode;//头结点循环指向新结点newnode->next = phead;//新结点循环指向头结点}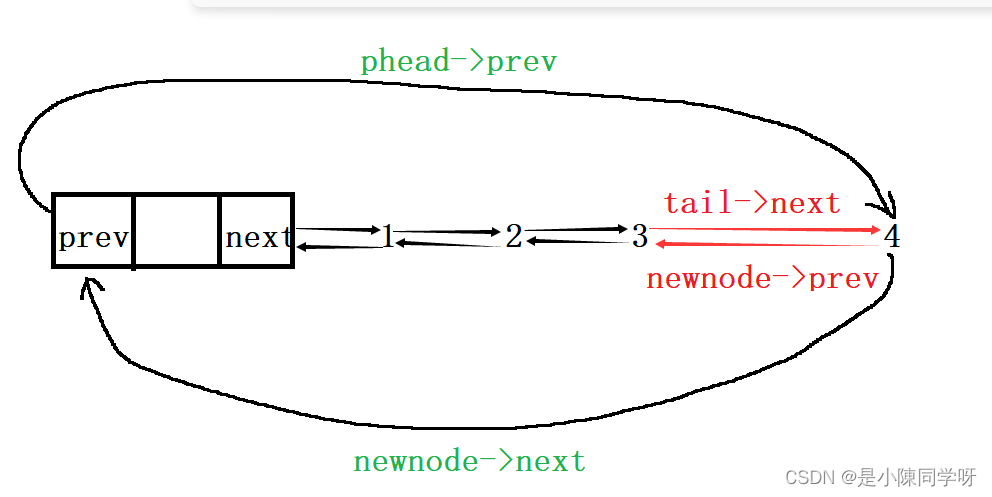
在上述中是表示的链表有内容的时候尾插,还是比较简单。在单链表尾插的时候,我们还要先判断一下链表是否为空。而这里双链表尾插需要考虑链表为空的情况吗?答案是不用,这里就体现了我们设置头结点好处,和之前设置的phead->next=phead,phead->prev = phead的好处。当链表为空的时候,也就是只有一个头结点。

这就是带头循环带头链表的魅力。
2.双向链表的打印
尾插了数字之后,我们就可以把它们打印出来看一下。我们就可以写一个打印函数。
void Listprint(ListNode* phead){ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead)//结束条件就是指针走到了头指针的位置{printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");}
3.双向链表的头插
头插也就是在头结点的后一个位置插入一个数进去,我们不能创建一个新结点直接链接到头结点上,如果这样做了,那么就和下一个结点断开了链接,也就是无法找到下一个结点了。所以我们在头接结点和新结点链接的时候,必须要先保存下一个结点的地址,防止结点的丢失。
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, SLDataType x){ListNode* first = phead->next;//first就是先保存的下一个结点ListNode*newnode= BuyListNode(x);phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode;}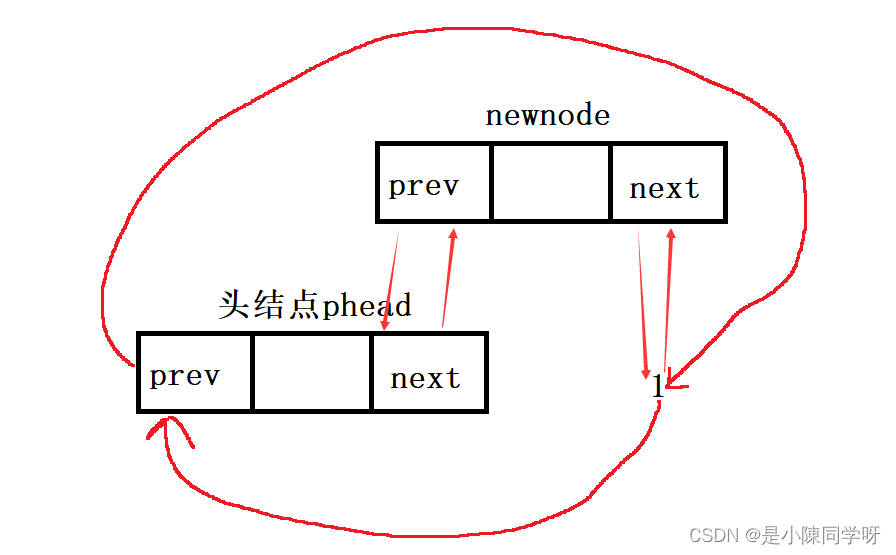
4.双向链表的头删
头删还是很简单的,我们自己free掉第一个结点即可,我们要注意的是我们在头删的时候,需要如何链接剩下的结点,需要注意哪些细节。和刚刚的头插差不多我们需要把要链接的结点先保存下来,不要等会就找不到了。
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead){assert(phead != phead->next);ListNode* first = phead->next;//保存第一个结点的位置ListNode* second = first->next;//保存第二个结点的位置phead->next = second;second->prev = phead;free(first);first = NULL;}
5.双向链表的尾删
要尾删肯定要知道尾结点的位置在哪里才行,在无循环的单链表中,我们还要遍历一遍链表,才能找到尾结点,但是在循环的双链表中,尾结点不就是头结点的上一个结点吗,也就是phead->prev
这里再次体现了循环双向链表的优越性。
assert(phead != phead->next);ListNode* end = phead->prev;ListNode* penult = end->prev;//这里的penult是倒数第二个的意思penult->next = phead;phead->prev = penult;free(end);end = NULL;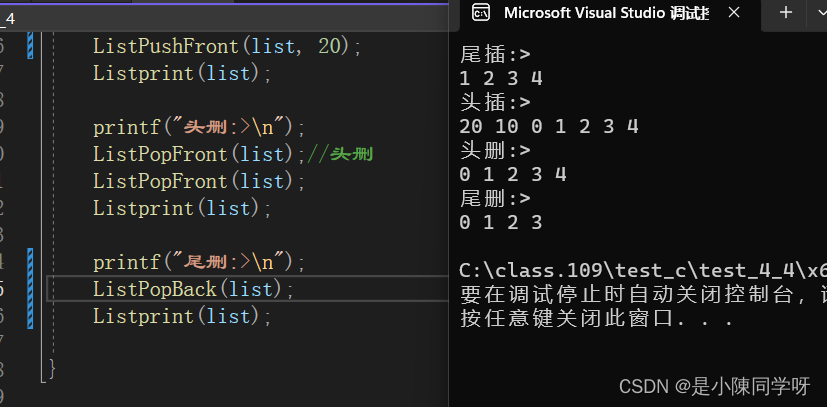
6.查找函数
和单链表一样,在需要删除和增加的时候,需要知道位置,这里我们就写一个查找函数来查找位置,需要删除和增加的时候知道返回找的的地址即可。
遍历整个链表,如果找到了,直接返回这个地址,如果没有找到直接返回NULL。
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, SLDataType x){assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;}7.在pos位置的前面插入一个数
还是和头插,尾插基本上是一样的,也是先把后一个结点先存起来,再依次链接起来。
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, SLDataType x){assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;//先存pos位置的下一个结点ListNode*newnode= BuyListNode(x);prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;}
8.删除pos位置的值
这个又和头删,尾删基本上是一样的,存好两个结点,再依次链接起来,再释放掉你要删除位置的地址。
void ListErase(ListNode* pos){assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);pos = NULL;}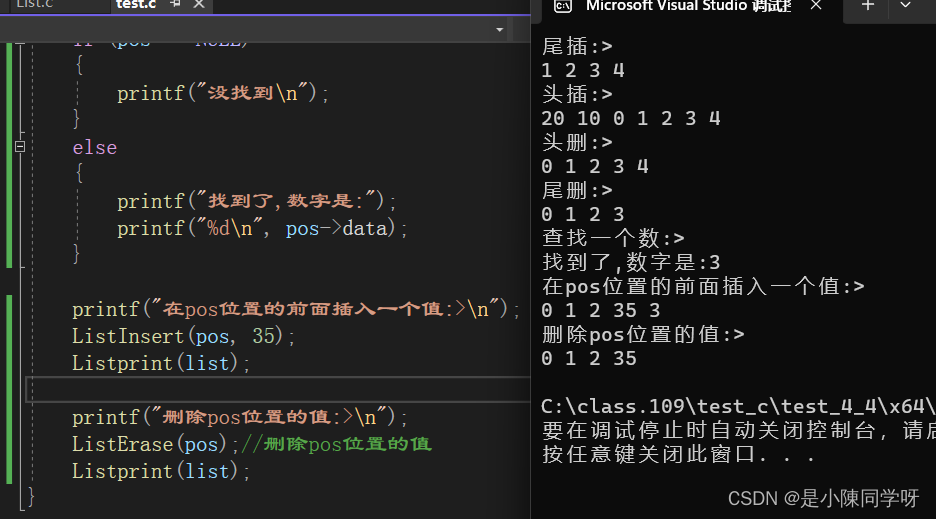
9.头插,尾插直接复用插入函数。头删,尾删直接复用删除函数
上述的头插和尾插其实和指定插函数的功能是一样的。而头删和尾删其实也是和指定删函数的功能是一样的。我们在头插和尾插的时候直接调用一下指定插函数即可,头删和尾删的时候直接调用一下指定删函数即可。用起来就非常的爽。
尾插复用:
//尾插void ListPushBack(ListNode*phead, SLDataType x){//ListNode* tail = phead->prev;//ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);//tail->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = tail;//phead->prev = newnode;//newnode->next = phead;ListInsert(phead, x);}头插复用:
//头插void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, SLDataType x){//ListNode* first = phead->next;//first就是先保存的下一个结点//ListNode*newnode= BuyListNode(x);//phead->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = phead;//newnode->next = first;//first->prev = newnode;ListInsert(phead->next, x);}头删复用:
//头删void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead){assert(phead != phead->next);//ListNode* first = phead->next;//ListNode* second = first->next;//phead->next = second;//second->prev = phead;//free(first);//first = NULL;ListErase(phead->next);}尾删复用:
//尾删void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead){assert(phead != phead->next);//ListNode* end = phead->prev;//ListNode* penult = end->prev;//这里的penult是倒数第二个的意思//penult->next = phead;//phead->prev = penult;//free(end);//end = NULL;ListErase(phead->prev);}10.求双向链表的长度
这个就超级简单了,直接遍历一遍链表即可,如果链表为空,直接返回0。如果链表不为空,遍历链表,如果头结点的走到头结点的位置即循环结束,返回链表的长度。
int Listlong(ListNode* phead){assert(phead);int count = 0;if (phead->next == phead){return 0;}else{ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){count++;cur = cur->next;}return count;}}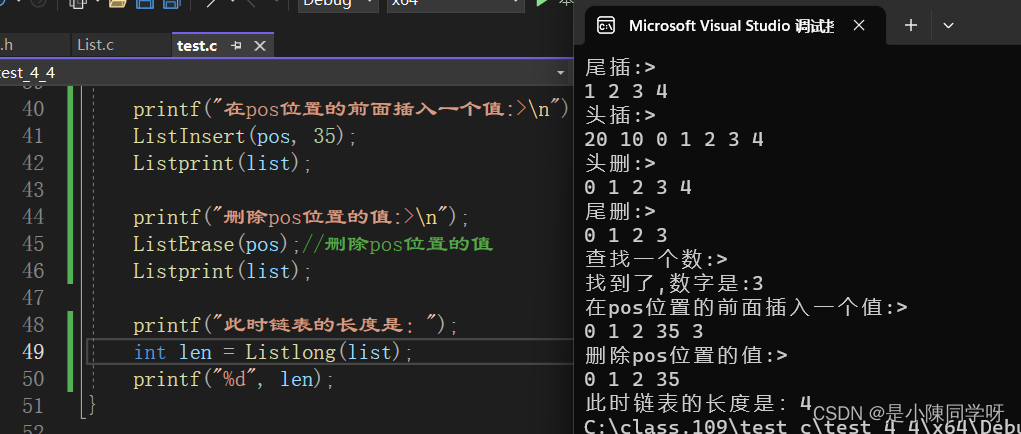
11.最后销毁双向链表
最后销毁一下链表即可。
//销毁链表void ListDestory(ListNode* phead){assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL;}五.双向链表全部的代码
1.List.h:
#pragma once#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<assert.h>typedef int SLDataType;typedef struct ListNode{struct ListNode* next;struct ListNode* prev;SLDataType data;}ListNode;//初始化链表ListNode*ListInit();//尾插void ListPushBack(ListNode*phead, SLDataType x);//打印链表void Listprint(ListNode* phead);//头插void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead);//头删void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);//尾删void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);//查找ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, SLDataType x);//删除pos位置的值void ListErase(ListNode* pos);//在pos位置前面插入一个值void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, SLDataType x);//求链表的长度int Listlong(ListNode* phead);//销毁链表void ListDestory(ListNode* phead);2.List.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"List.h"//创建一个新的结点ListNode*BuyListNode(SLDataType x){ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;}//初始化链表,创建哨兵结点ListNode* ListInit(){ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;}//尾插void ListPushBack(ListNode*phead, SLDataType x){//ListNode* tail = phead->prev;//ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);//tail->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = tail;//phead->prev = newnode;//newnode->next = phead;ListInsert(phead, x);}//打印void Listprint(ListNode* phead){ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");}//头插void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, SLDataType x){//ListNode* first = phead->next;//first就是先保存的下一个结点//ListNode*newnode= BuyListNode(x);//phead->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = phead;//newnode->next = first;//first->prev = newnode;ListInsert(phead->next, x);}//头删void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead){assert(phead != phead->next);//ListNode* first = phead->next;//ListNode* second = first->next;//phead->next = second;//second->prev = phead;//free(first);//first = NULL;ListErase(phead->next);}//尾删void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead){assert(phead != phead->next);//ListNode* end = phead->prev;//ListNode* penult = end->prev;//这里的penult是倒数第二个的意思//penult->next = phead;//phead->prev = penult;//free(end);//end = NULL;ListErase(phead->prev);}//查找ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, SLDataType x){assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;}//删除pos位置的值void ListErase(ListNode* pos){assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);pos = NULL;}//在pos位置前面插入一个值void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, SLDataType x){assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;//先存pos位置的下一个结点ListNode*newnode= BuyListNode(x);prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;}//求链表的长度int Listlong(ListNode* phead){assert(phead);int count = 0;if (phead->next == phead){return 0;}else{ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){count++;cur = cur->next;}return count;}}//销毁链表void ListDestory(ListNode* phead){assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL;}3.test.c:
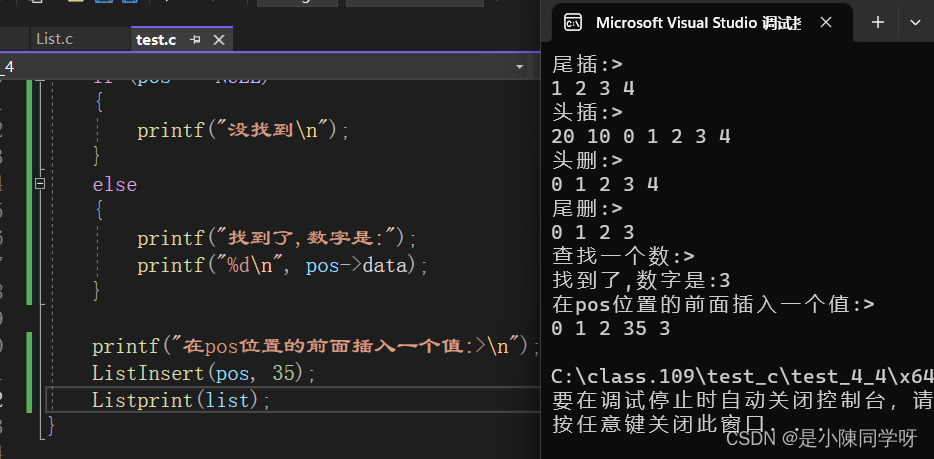
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"List.h"void ListTest1(){ListNode* list = ListInit();printf("尾插:>\n");ListPushBack(list, 1);//尾插ListPushBack(list, 2);ListPushBack(list, 3);ListPushBack(list, 4);Listprint(list);printf("头插:>\n");ListPushFront(list, 0);//头插ListPushFront(list, 10);ListPushFront(list, 20);Listprint(list);printf("头删:>\n");ListPopFront(list);//头删ListPopFront(list);Listprint(list);printf("尾删:>\n");ListPopBack(list);Listprint(list);printf("查找一个数:>\n");ListNode* pos = ListFind(list, 3);if (pos == NULL){printf("没找到\n");}else{printf("找到了,数字是:");printf("%d\n", pos->data);}printf("在pos位置的前面插入一个值:>\n");ListInsert(pos, 35);Listprint(list);printf("删除pos位置的值:>\n");ListErase(pos);//删除pos位置的值Listprint(list);printf("此时链表的长度是:");int len = Listlong(list);printf("%d", len);}void ListTest2(){ListNode* list = ListInit();printf("尾插:>\n");ListPushBack(list, 1);//尾插ListPushBack(list, 2);ListPushBack(list, 3);ListPushBack(list, 4);ListPushBack(list, 5);ListPushBack(list, 6);Listprint(list);printf("尾删:>\n");ListPopBack(list);ListPopBack(list);Listprint(list);printf("查找一个数:>");ListNode* pos = ListFind(list, 3);if (pos == NULL){printf("没找到\n");}else{printf("找到了,数字是:");printf("%d\n", pos->data);}printf("把找到的数字修改为:");pos->data = 10;Listprint(list);printf("在pos位置的前面插入一个值:>\n");ListInsert(pos, 35);Listprint(list);printf("删除pos位置的值:>\n");ListErase(pos);//删除pos位置的值Listprint(list);printf("此时链表的长度是:");int len = Listlong(list);printf("%d", len);//销毁链表ListDestory(list);}int main(){ListTest1();//ListTest2();return 0;}这就是全部的内容,感谢大家的支持。