学习路线
java学习一、基础语法1.注释、标识符、关键字2.数据类型3.类型转换4.变量 常量 作用域5.运算符 二、Java流程控制1.Javadoc2.用户交互Scanner3.选择结构1.if单选择结构2.if双选择结构3.if多选择结构4.switch选择结构5.循环结构 三、Java方法详解1.方法定义2.方法调用3.方法重载4.命名行传参5.可变参数6.递归 四、数组1.定义与初始化3.数组使用4.二维数组与稀疏数组使用 五、面向对象编程(OPP)1.理解及定义2.方法定义及调用3.类与对象的关系4.创建和初始化对象5.opp三大特性-封装6.opp三大特性-继承7.三大特性-多态8.Static关键字、抽象类,接口9.内部类 六、异常机制1.异常定义2.异常结构体3.异常处理机制与自定义异常
java学习
资源:狂神说
一、基础语法
1.注释、标识符、关键字
(1) 建立空项目来建立java项目:
(2) 单行注释://注释
(3) 多行注释:/*
Djandjan
/
(4) 文档注释: /* */
2标识符(类名,变量名,方法名)
(5) 关键字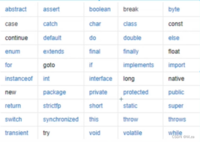
(6) 标识符注意点:
2.数据类型
(1) 要求变量严格符合规范,所有变量先定义后使用(java, c++)
(2) 弱类型语言(js,vb)
(3) 分类 ①基本类型
②引用类型
//小数;浮点数 float num5=50.1F; double num6=3.415926; //字符 char name='马'; //String不是关键字,是一个类 //String name="秦疆"; //布尔值;是非 boolean flag = true;3.类型转换
public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //整数拓展: 进制 二进制ob 十进制 八进制o 十六进制ox int i = 10; int i2 = 010; //八进制 int i3 = 0x10; //十六进制 System.out.println(i); System.out.println(i2); System.out.println(i3); System.out.println("================================="); //浮点数拓展 银行业务怎么表示 BigDecimal 数学工具类 //float 有限 离散 舍入误差 大约 接近但不相等 //double //最好避免完全使用浮点数进行比较 float f = 0.1f; //0.1 double d = 1.0/10; //0.1 System.out.println(f==d); System.out.println(f); System.out.println(d); float d1 = 32423423423f; float d2 = d1+1; System.out.println(d1==d2); //字符类拓展 System.out.println("=============================="); char c1 = 'a'; char c2 = '中'; System.out.println(c1); System.out.println((int)c1);//强制转换 System.out.println(c2); System.out.println((int)c2);//强制换行 //所有字符本质还是数字 //编码 Unicode 表:97=a 65=A 2字节 0-65536 Excel //U00000-UFFFFF char c3 ='\u0061'; System.out.println(c3);//a //转义字符 // \t 制表符 // \n 换行 //..... System.out.println("l\tl\nd"); System.out.println("========================="); String sa = new String("dcfs"); String sb = new String("dcfs"); System.out.println("sa==sb"); String sc = "qqqq"; String sd = "qqqq"; System.out.println(sc==sd); //对象 从内存分析 //布尔值拓展 boolean flag = true; if(flag==true){} if(flag){}//建议精简代码 }}public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 128; double b = i; byte c = (byte)i;//内存溢出 -128 //强制类型转换 (类型)变量名 高----低 //自动转换 低-----高 System.out.println(i); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c); /* * 注意点: *1.不能对布尔值进行转换 *2.不能吧对象转换成不相干的数据 *3.把高容量转换成低容量的要强制转换 *4.转换时会出现内存溢出问题,或者精度问题 * */ System.out.println("==============="); System.out.println((int)23.7);//23 System.out.println((int)-45.3);//-45 System.out.println("==============="); char c1 = 'a'; int d1 = c1+1; System.out.println((char) d1); //操作比较大的数,注意溢出问题 //JDK新特性,数字之间可以用下划线分割 int money = 10_0000_0000; int year = 20; int total1 = money*year;// -147484163,计算时已经溢出了 long total2 = money*year; //默认是int,转换之前已经存在问题了 long total3 = money*((long)year);//先把一个数据转换成Long System.out.println(total3); }}4.变量 常量 作用域
public class Demo5 { //属性:变量 //常量 修饰符 不存在先后顺序 static final double PI = 3.14; //类变量static static double salary = 2500; //实例变量:从属于对象;如果不初始化,这个类型的默认值0,0.0 //布尔值:默认值是false //除了基本类型,其余默认值都是null; String name; int age; //main 方法 public static void main(String[] args) { //局部变量:必须声明和初始化,局部变量只在方法快里起作用 int i = 10; System.out.println(i); //变量类型 变量名字=new Demo5(); Demo5 demo5 = new Demo5(); System.out.println(demo5.age); System.out.println(salary); System.out.println(PI); } //其他方法 public void add(){ }5.运算符
int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 25; int d = 25; System.out.println(a+b); System.out.println(a*b); System.out.println(a-b); System.out.println(a/(double)b);//注意运算结果范围 long a = 12312312312313L; int b = 123; short c = 8; byte d = 8; System.out.println(a+b+c+d);//Long System.out.println(b+c+d);//Int System.out.println(c+(double)d);//Tnt int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 21; System.out.println(a>b); System.out.println(a<b); System.out.println(a==b); System.out.println(a!=b); System.out.println(c%a);//取余 模运算 int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 21; System.out.println(a>b); System.out.println(a<b); System.out.println(a==b); System.out.println(a!=b); System.out.println(c%a);//取余 模运算 //++ -- 自增 自减 一元运算符 int a = 3; int b = a++; //"后加加",先给b赋值,再自增 // a=a+1; System.out.println(a); //a=a+1; int c = ++a;//“前加加”,先自增,再给b赋值 System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c); //幂运算2^3 2*2*2 = 8 使用工具类操作(Math) double pow = Math.pow(2, 3);//Math.pow(2,3) Alt+Enter System.out.println(pow); //与(and) 或(or) 非(and) boolean a = true; boolean b = false; System.out.println("a&&b"+(b&&a));//逻辑与运算:两个变量为真,结果才为true System.out.println("a||b"+(a||b));//逻辑或运算:两个变量有一个为真,结果才为true System.out.println("!(a&&b)"+(a&&b));//真->假 假->真 //短路运算 c<4为false ,后面c++不执行 int c = 5; boolean d = (c<4)&&(c++<4); System.out.println(d);//false System.out.println(c);//5 /* * A = 0011 1100 * B = 0000 1101 * ------------------ * A&B = 0000 1100 * A|B = 0011 1101 * A^B = 0011 0001 相同为0,不同为1 * ~B = 1111 0010 * * 2*8 = 16 2*2*2*2 * 增加效率!!! * << *2 * << /2 * */ System.out.println(2<<3); int a = 10; int b = 20; a+=b;//a=a+b a-=b;//a=a-b System.out.println(a); //字符串连接符 + ,String ""+()=字符串 System.out.println(""+a+b); System.out.println(a+b+""); //x ? y : z //如果x==true, 则结果为y,否则为z int score = 50; String type = score < 60 ? "不及格":"及格"; System.out.println(type);二、Java流程控制
1.Javadoc
public class Doc { String name; /** * @author kuangshen * @version 1.0 * @since 1.11 */ /** * @author Kuangshen * @param name * @return * @throws Exception */ public String test(String name) throws Exception{ return name; }2.用户交互Scanner
public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个扫描器对象,用于接受键盘数据 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);// new Scanner(System.in)+alt+Enter System.out.println("使用next方式接受:"); //判断用户有没有输入字符串 if(scanner.hasNext()){ //使用Next方式接受 String str = scanner.next(); System.out.println("输入的内容为"+str); } //凡属于Io流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成好习惯用完就关掉 scanner.close(); }} public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个扫描器对象,用于接受键盘数据 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("使用nextLine方式接受:"); if(scanner.hasNextLine()){ //使用Next方式接受 String str = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("输入的内容为"+str); } scanner.close();public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个扫描器对象,用于接受键盘数据 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入数据:"); String str = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("输入的内容为: "+str); scanner.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //从键盘接受数据 int i = 0; float f = 0.0f; System.out.println("请输入整数:"); //如果 .... 那么 if(scanner.hasNextInt()){ i = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("整数数据为:"+i); }else{ System.out.println("输入的不是整数数据!"); } //如果 .... 那么 if(scanner.hasNextFloat()){ f = scanner.nextFloat(); System.out.println("小数数据为:"+i); }else{ System.out.println("输入的不是小数数据!"); } }public static void main(String[] args) { //我们可以输入多个数字,并求和与平均数,每输入一个数字用回车表示 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //和 double sum = 0; //计算输入了多少个数字 int m = 0; //通过循环判断是否还存在输入,并在里面对每一次进行求和和统计 while(scanner.hasNextDouble()){ double x = scanner.nextDouble();//scanner.nextDouble();输入一个数 m=m+1;//m++ sum = sum +x; System.out.println("你输入了第"+m+"个数据,当前的结果sum+"+sum); } System.out.println(m+"个数的和为:"+sum); System.out.println(m+"个数的平均值为:"+(sum/m)); scanner.close(); }3.选择结构
1.if单选择结构
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入内容:"); String s = scanner.nextLine(); //equal:判断字符是否相等 if(s.equals("hellow")){ System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("end"); scanner.close();2.if双选择结构
//双选择结构 public static void main(String[] args) { //考试分数大于60就是及格,小于60分就是不及格 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入成绩:"); int score = scanner.nextInt(); if(score>60){ System.out.println("及格"); }else{ System.out.println("挂了"); } scanner.close(); }3.if多选择结构
public static void main(String[] args) { //多选择结构 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入成绩: "); int score = scanner.nextInt(); if(score==100){ System.out.println("满分"); }else if (score<100&& score>90){ System.out.println("A"); }else if (score<90&& score>80){ System.out.println("B"); }else if (score<80&& score>70){ System.out.println("C"); }else if (score<70&& score>60){ System.out.println("D"); }else if (score<60){ System.out.println("挂了"); }else{ System.out.println("成绩不合法"); } scanner.close(); }4.switch选择结构
public static void main(String[] args) { //case具有穿透性,需要break进行停止 //seitch匹配一个具体的值 char grade = 'A'; switch(grade){ case'A': System.out.println("优秀"); break;//可选 case'B': System.out.println("良好"); break;//可选 case'C': System.out.println("及格"); break;//可选 case'D': System.out.println("挂科"); break;//可选 default: System.out.println("未知"); } }5.循环结构
1.while循环
public static void main(String[] args) { //输出1~100 int i = 0;// System.out.println(i++);// System.out.println(i++);// System.out.println(i++);// System.out.println(i++);// System.out.println(i++);// System.out.println(i++);// System.out.println(i++); while (i<=100){ i++; System.out.println(i); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //死循环 while(true){ //等待客户检查 //定时检查 } } public static void main(String[] args) { //计算1+2+3....100=? int i = 0; int sum = 0; while(i<=100){ sum = sum +i; i++; } System.out.println(sum); }2.do…while
public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; int sum = 0; do{ sum = sum +1; i++; }while(i<=100); System.out.println(sum); } public static void main(String[] args) { //do....while至少执行一次 int a = 0; while(a<0){ System.out.println(a); a++; } System.out.println("==============="); do{ System.out.println(a); }while (a<0); }3.for
public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1;//初始化条件 while(a<=100){//条件判断 System.out.println(a);//循环体 a+=2;//迭代 } System.out.println("while循环结束"); //初始化//条件判断 //迭代 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println(i); } System.out.println("for循环结束!"); //死循环 for (; ;) { } } public static void main(String[] args) { //计算1~100之间奇数和偶数的和 int oddSum = 0; int evenSum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { if(i%2!=0){ oddSum+= i; }else { evenSum+=i; } } System.out.println("奇数和的"+oddSum); System.out.println("偶数和的"+evenSum); } public static void main(String[] args) { //用while或for循环输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出三个 for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { if(i%5==0){ System.out.println(i+"/t"); } if(i%(5*3)==0){//每行 System.out.println(); //System.out.print("/n"); } } //pritntln 输出完全会换行 //print 输出完不会换行 } public static void main(String[] args) { //打印九九乘法表 /* * 1.我们先打印第一列 * 2.固定的1再用一个循环包起来 * 3.去掉重复项 * 4.调整样式 * */ for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) { for (int i = 1; i <= j; i++) { System.out.print(j+"*"+i+"="+j*i+"\t"); } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] number = {10,20,30,40,50}; //遍历数组 for (int x:number){ System.out.println(x); } System.out.println("=============="); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println(number[i]); } }4.break、continue
public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while(i<100){ i++; System.out.println(i); if(i==30){ break; } } System.out.println("1,2,3"); } public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while(i<100){ i++; if(i%10==0){ System.out.println(); continue; } System.out.print(i); System.out.print("\t"); } } 1.break在任何循环语句的主题部分,均可用break控制循环流程。 2.break用于强行退出循环,不执行剩余语句。(break语句也在switch语句中使用) 3.continue语句在循环语句体中,用于终止某次循环过程,即跳出循环体中尚未执行的语句,接着执行下一次是执行循环的判定。训练:打印三角形
public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { for(int j=5;j>=i;j--) { System.out.print(" "); } for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ System.out.print("*"); } for(int j=1;j<i;j++){ System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } }三、Java方法详解
1.方法定义
(1).方法命名规则:首字母小写,后面驼峰规则
(2).形式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名){
方法体;
return 返回值;
}
2.方法调用
值传递
public static void main(String[] args) { //实际参数:实际调用传递的参数 int sum = add(1, 2); System.out.println(sum); } //形式参数,用来定义作用 public static int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; } //方法重载 public static int add(int a,int b,int c){ return a+b+c; }3.方法重载
相同函数名称,形参不同
public static void main(String[] args) { int max = max(10, 20); System.out.println(max); } //比大小 方法重载“名字可以相同,参数类型(个数、类型、排列顺序)不同” public static double max(double a,double b){ double result = 0; if(a == b){ System.out.println("a = b"); return 0;//终止方法 } if(a>b){ result = a; }else { result = b; } return result; } //比大小 public static int max(int a,int b){ int result = 0; if(a == b){ System.out.println("a = b"); return 0;//终止方法 } if(a>b){ result = a; }else { result = b; } return result; }4.命名行传参
5.可变参数
public static void main(String[] args) { //调用可变参数方法 printMax(12.11,21,121,1212,121); printMax(new double[]{1,2,3}); } public static void printMax(double...number){ if(number.length==0){ System.out.println("No argument passed"); return; } double result = number[0]; //排序! for (int i = 1; i <number.length ; i++) { if(number[i]>result){ result = number[i]; } } System.out.println("The max value is"+result); }6.递归
//阶乘 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(f(3)); } public static int f(int n){ if(n==1){ return n; }else { return n*f(n-1); } }四、数组
1.定义与初始化
public class ArrayDemo01 { //变量的类型 变量的名字 = 变量的值; //数组类型 public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums; // 1.定义一个人数组 nums = new int[10]; // 2.创建一个数组 //赋值 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { nums[i] = i; System.out.println("num["+i+"]="+nums[i]); } //求和 //nums.length 数组长度 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { sum = sum + nums[i]; } System.out.println(); System.out.println("数组和为"+sum); }} public static void main(String[] args) { //静态初始化:创建+赋值 int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; System.out.println(a[0]); //动态初始化:包含默认初始化 int[] b = new int[10]; b[0] = 10; b[1] = 11; System.out.println(b[0]); System.out.println(b[1]); System.out.println(b[2]); System.out.println(b[3]); System.out.println(b[4]); System.out.println(b[5]); }3.数组使用
public class ArrayDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; //打印全部数组元素 for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) { System.out.println(array[i]); } System.out.println("============="); //计算机所有元素的和 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) { sum += array[i]; } System.out.println("sum="+sum); System.out.println("=============="); //查找最大的元素 int max = array[0]; for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) { if(array[i]>max){ max = array[i]; } } System.out.println("max="+max); }} public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrays = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};// //JDK1.5 没有下标 arrays.for// for (int array : arrays) {// System.out.println(array);// } int[] revese = revese(arrays); printArray(revese); } //打印数组元素 public static void printArray(int[] arrays) { for (int i = 0; i <arrays.length ; i++) { System.out.print(arrays[i]+""); } } //反转数组 public static int[] revese(int[] arrays){ int[] result = new int[arrays.length]; for (int i = 0,j = arrays.length-1; i <arrays.length; i++,j--) { result[j] = arrays[i]; } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { //[4][2] 面向对象 /* * 1,2 array[0] * 2,3 array[1] * 3,4 array[2] * 4,5 array[3] * */ int[][] array = {{1,2},{2,3},{3,4},{4,5}}; for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <array[i].length ; j++) { System.out.println(+array[i][j]); } } }public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {15,1,1,5,61,561,561,651,561}; //System.out.println(a); //打印数组 // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); printArrray(a); System.out.println(); //数组排序 升序 Arrays.sort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); System.out.println(); //填充 Arrays.fill(a,2,4,0); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } public static void printArrray(int[] a){ for (int i = 0; i <=a.length ; i++) { if(i==0){ System.out.print("["); } if (i==a.length){ System.out.print("]"); }else{ System.out.print(a[i]+","); } } }冒泡排序
import java.util.Arrays;public class ArrayDemo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1,222,45,564,64,4654,564,16,54,6,5,14}; int[] poposort = poposort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(poposort)); } /*冒泡排序 *1.比较相邻元素,如果第1个数比第二个数大,交换他们的位置 *2.每一次比较,都会产生一个最大的,或者最小的数字 *3.下一次排序可以少一次排序! *4.以此循环,直到结束 * */ public static int[] poposort(int[] array){ //临时变量 int temp=0; //外层循环,判断走了多少次 for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) { boolean flag = false;//通过Flag标志位减少无意义的比较。 //内层循环,比较判断两个数,第一个数比第二的数大,则交换位置 for (int j = 0; j <array.length-1-i; j++) { if(array[j+1]<array[j]){ temp=array[j]; array[j]=array[j+1]; array[j+1]=temp; flag = true; } } if (flag==false){ break; } } return array; }}4.二维数组与稀疏数组使用
public static void main(String[] args) { //1.创建一个二维数组11*11 0:没有棋子 1:黑棋 2:白棋 int[][] array1 = new int[11][11]; array1[1][2] = 1; array1[2][3] = 2; //输出原始数据 System.out.println("输出原始数据"); for (int[] ints : array1) { for (int anInt : ints) { System.out.print(anInt+"\t"); } System.out.println(); } //转换为稀疏数组保存 //获得有效值的个数 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i <11 ; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <11 ; j++) { if(array1[i][j]!=0){ sum++; } } } System.out.println("有效值的个数:"+sum); //创建一个稀疏数组 int[][] array2 = new int[sum+1][3]; array2[0][0] = 11; array2[0][1] = 11; array2[0][2] = sum; //遍历二维数组,将非零值存放在稀疏数组中 int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i <array1.length ; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <array1[i].length; j++) { if (array1[i][j] != 0) { count++; array2[count][0] = i; array2[count][1] = j; array2[count][2] = array1[i][j]; } } } //输出稀疏数组 System.out.println("稀疏数组"); for (int i = 0; i <array2.length ; i++) { System.out.println(array2[i][0]+"\t"+array2[i][1]+"\t"+array2[i][2]+"\t"); } System.out.println("==============="); System.out.println("还原"); //1.读取稀疏数组 int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]]; //2.给其中元素还原他的值 for (int i = 1; i <array2.length ; i++) { array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2]; } //3.打印 for (int[] ints : array3) { for (int anInt : ints) { System.out.print(anInt+"\t"); } System.out.println(); } }二维数组底层逻辑图:
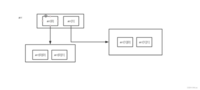
五、面向对象编程(OPP)
1.理解及定义



2.方法定义及调用
/
* 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(){
* //方法体
* return 返回值;
* }
* /
import java.io.IOException;//Demo类public class Demo01 { //main方法 public static void main(String[] args) { } /* * 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(){ * //方法体 * return 返回值; * } * */ //return 结束方法,返回一个结果 public String sayhellow(){ return"Hellow"; } public void print(){ return; } public int max(int a,int b){ return a > b?a:b;//三元运算符 } //数组下标越界:Arrayindexoutofbounds public void readFile(String file)throws IOException { }}调用方法
public static void main(String[] args) { //调用静态方法直接用 类.方法(); Student.say(); //调用非静态方法 // 1.实例化 对象类型 对象名 = 对象值; // 2.对象.方法 Student student = new Student(); student.play(); //或者 new Student().play() } //和类一起加载的 public void a( ){ b(); } //实例化之后才存在 public void b( ){ a(); } //带static不可以调用不带的}实际参数要对应形式参数的类型
public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //实际参数要对应形式参数的类型 int add = Demo03.add(3, 2);//实际参数 System.out.println(add); } public static int add(int a,int b){//形式参数 return a+b; }}值传递
public class Demo04 { //值传递 public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1; System.out.println(a);//a:1 Demo04.chage(a); System.out.println(a);//a:1 } //返回值为空 public static void chage(int a){ a = 10; }}3.类与对象的关系
引用传递
//对象、内存public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); System.out.println(person.name);//null Demo05.change(person); System.out.println(person.name);//qinyan } public static void change(Person person){ //person是一个对象:指向的--->Person person = new Person();这是一个具体的人,可以改变属性! person.name= "qinyan"; }}//定义一个Person,有一个属性:nameclass Person{ String name;//NULL}package com.oop.demo01;public class Student { //静态方法 public static void say(){ System.out.println("学生说话了"); } //非静态方法 public void play(){ System.out.println("学生wan了"); }}4.创建和初始化对象
构造器
* 构造器:* 1.与类名相同* 2.没有返回值*作用:* 1.new 的本质在调用构造方法* 2.初始化对象的值** 注意:一旦定义了有参构造,若想用无参构造,无参构造必须显示!!!,否则无意义*this.当前类 = 定义参数//java---->classpublic class Person { //Person类中存在一个空的Person方法 //一个类即使什么也不写,也会存在一个方法 //显示构造器 String name; int age; //实例化初始值 //1.使用new关键字必须有构造器 //2.用来初始化值 public Person(){//无参构造 this.name = "QINyan"; } //有参构造:一旦定义了有参构造,无参构造必须显示,否则无意义 public Person(String name){//无参构造 this.name = "QINyan"; } //alt+insert 生成构造器!!!! public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; }}/** public static void main(String[] args) { //Person类中存在一个默认的空的Person方法 Person person = new Person(); System.out.println(person.name); } //学生类public class Student { //属性:字段 String name;//默认null int age; //方法 public void study(){ System.out.println(this.name+"学习"); } 测试: public static void main(String[] args) { //类:抽象的,实例化 //类实例化后会返回一个自己的对象! //student对象就是一个Student类的具体实例! //不同的对象有相同的属性,可以给对象的属性赋不同的值 Student student = new Student(); Student student1 = new Student(); student.name = "james"; student.age = 2; System.out.println(student.name); System.out.println(student.age); student1.name = "curruy"; student1.age = 1; System.out.println(student1.name); System.out.println(student1.age); } }构造器底层原理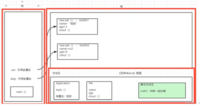
public class Pet { public String name; public int age; //无参构造 public void shout(){ System.out.println("哇哇哇哇"); }}/** Pet dog = new Pet(); dog.name = "qqq"; dog.age = 1; dog.shout(); System.out.println(dog.age); System.out.println(dog.name); Pet cat = new Pet();* */5.opp三大特性-封装
1.提高程序的安全性,保护数据2.隐藏代码的实现细节3.统一接口4.系统可维护增加了
//类 private:私有public class Student { private String name; private int id; private int age; private char sex; //提供一些可以操作这个属性的方法! //提供一些publicd的get,set方法 //alt +insert Fn //get 获得这个数据 public String getName() { return name; } //set 给这个数据设值 public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public char getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(char sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { if(age>120||age<0){//不合法 this.age = 3; }else { this.age = age; } this.age = age; }}测试: Student s1 = new Student(); System.out.println("\t\t学生信息情况表"); s1.setName("秦严"); System.out.println(s1.getName()); s1.setAge(18); System.out.println(s1.getAge()); s1.setSex('w'); System.out.println(s1.getSex()); s1.setId(2020304621); System.out.println(s1.getId()); 6.opp三大特性-继承
1.person、student、teacher
//person 人 基类:父类//java中所有的类默认直接或者间接继承Objectpublic class Person {//extend Object protected String name = "Kg"; public Person() { System.out.println("无参构造Person"); } //只能用public,不能用private,私有的不能被继承 public void print(){ System.out.println("person"); }}/** //继承用public 或者不加修饰符 int money = 1000_000; public void say(){ System.out.println("哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈"); } //如果用private 可以构建一个get,set方法由子类来调用 private int money1 = 1444; public int getMoney1() { return money1; } public void setMoney1(int money1) { this.money1 = money1; }* *///学生 is person 派生类:子类//子类继承父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法public class Student extends Person { //ctrl + H 展开继承树 private String name = "Qy"; public Student() { //隐藏代码,调用了父类的无参构造 super();//调用父类的构造器必须在子类构造器的第一行 System.out.println("无参构造Student"); } public void print(){ System.out.println("student"); } public void test1(){ print(); this.print(); super.print(); } public void test(String name){ System.out.println(name);//方法参数中的 System.out.println(this.name);//子类中的 System.out.println(super.name);//父类 Person中的 }}/*1.* Student student = new Student(); student.say(); 2.* Student student = new Student(); System.out.println("===============1"); student.test("秦严"); System.out.println("===============2"); student.test1();* *///老师 is person 派生类:子类public class Teacher extends Person {}2.A-B
public class A extends B{ //重写 @Override @Override //注解:由功能的注释 public void test() { super.test(); System.out.println("A=>test"); }}/*import com.oop.demo05.A;import com.oop.demo05.B;import com.oop.demo05.Student;//静态方法:方法的调用只和左边,调用的数据有关//非静态方法:重写* public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(); a.test();//A //父类的引用指向子类 B b = new A();//子类继承父类,并重写了父类的方法 b.test();//B }* */public class B { //重写都是方法的重写与属性无关 public void test(){ System.out.println("B=>test"); }}注意:
1. java中所有的类默认直接或者间接继承Object 2.JAVA中类只有单继承,没有多继承! 一个儿子只能有一个爸爸,但是一个爸爸可以有多个儿子! 3.Super-this(P,T,S):super注意点:
super调用父类的构造方法,必须在构造方法的第一个super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中!super和 this不能同时调用构造方法!this注意点:
superVSthis:
1.代表的对象不同:
*** this: 本身调用者这个对象
*** super: 代表父类对象的应用
2.前提
*** this:没有继承也可以使用
*** super:只能在继承条件才可以使用
3.构造方法
*** this();本类的构造
*** super():父类的构造
方法重写(A,B)
子类继承父类,并重写了父类的方法
重写:需要有继承关系,子类重写父类
*** 1.方法名必须相同
*** 2.参数列表必须相同
*** 3.修饰符:范围可以扩大但不能缩小:public>protected>Default>private
*** 4.抛出的异常:范围可以缩小但不能扩大:classNotFoundException–>Exception(大)
重写,子类的方法和父类必须一致:方法体不同
为什么要重写:
***1. 父类的功能,子类不一定需要,或者不一定能满足!
***2.ALT+Insert(Fn):override
7.三大特性-多态
1.定义
2.instanceof(类型转换)引用类型
多态注意事项
1.static 方法 属于类 它不属于实例 2.final 常量 3.private 方法:public class Person { public void run(){ System.out.println("run"); }}/** 1. public void run(){ System.out.println("run!!!!!"); }** */public class Student extends Person { public void go(){ System.out.println("go"); } }/*多态注意事项* 1.多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态* 2.子类父类,有联系,类型转换异常! ClassCastException!* 3.存在条件:继承关系,方法需要重写,父类引用指向子类对象!Father f1 = new Son* 4.以下不能重写:* 1.static 方法 属于类 它不属于实例* 2.final 常量* 3.private 方法:**1. @Override public void run() { System.out.println("son"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("吃"); } * * * public static void main(String[] args) { //一个对象的实际类型是确定的 //new Student(); //new Person(); //可以指向引用类型就不确定了:父类的引用指向子类 // Student 能调用的方法都是自己的或者调用父类的 Student s1 = new Student(); // Person 父类型 指向子类,不可以调用子类独有的方法 Person s2 = new Student(); Object s3 = new Student(); s2.run(); s1.run();//子类重写了父类的方法,执行子类的方法 //s2.eat();不能执行 对象能执行那些方法主要看左边类型,和右边关系不大 ((Student)s2).eat();//可以强转后执行 } * *2. * public static void main(String[] args) { //Object>String //Object>Person>Teacher //Object>Person>Student //System.out.println(X instanceof Y);//是否能编译通过取决于具有父子关系 //System.out.println(X instanceof Y);//true或者false取决于引用对象X指向的类型是不是Y的子类型 Object object = new Student(); System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);//flase System.out.println(object instanceof String);//flase System.out.println("======================="); Person person = new Student(); System.out.println( person instanceof Student);//true System.out.println( person instanceof Person);//true System.out.println( person instanceof Teacher);//false System.out.println( person instanceof Object);//true //System.out.println( person instanceof String);//编译报错 System.out.println("======================="); Student student = new Student(); System.out.println( student instanceof Student);//true System.out.println( student instanceof Person);//true System.out.println( student instanceof Object);//true // System.out.println( student instanceof Teacher);//编译报错 //System.out.println( person instanceof String);//编译报错* */public class Teacher extends Person {}/** public static void main(String[] args) { //类型之间的转换 父 子(高转低 强制转换 低转高 自动转换) //父类引用指向子类对象 //student将这个对象类型强制转换成Student类型,就可以使用Student类型的方法了 Person person = new Student(); ((Student)person).go(); //子类转换为父类可能丢失一些自己本来的方法 Student student = new Student(); Person person1 = student; }** */8.Static关键字、抽象类,接口
1.Static关键字
public class Person { { System.out.println("匿名代码块"); } static { System.out.println("静态代码块"); } public Person() { System.out.println("构造方法"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); System.out.println("============="); Person person1 = new Person(); //静态代码块只执行一次 }}public class Student { //静态属性 private static int age;//静态变量 多线程 private int score;//非静态变量 //静态方法 public void run(){ } public static void go(){ } public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student(); System.out.println(Student.age); //System.out.println(Student.score);类只能调用静态变量 System.out.println(s1.score); System.out.println(s1.age); Student.go(); go(); //Student.run(); 不可以编译 s1.run(); }}//静态导入包import static java.lang.Math.random;import static java.lang.Math.PI;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(random()); System.out.println(PI); //类被final定义,无法继承 }}2.抽象类
抽象类的所有方法 继承他的子类 都必须实现的方法 除非也是抽象类public abstract class A extends Actionpublic class A extends Action { @Override public void something() { }}// abstract 抽象类: extends 单继承 (接口可以多继承)插排public abstract class Action { //约束 不实现 //abstract 抽象方法 只有方法名字,没有方法实现 public abstract void something(); //1.不能new这个抽象类,只能靠子类实现它:约束 //2.抽象类可以写普通方法,普通方法不能有抽象类}3.接口
声明:interface
作用:
1.约束
2.定义一些方法,让不同的人实现
3.public static final
4.public abstract
5.接口不能实例化,接口不能构造方法
6.inplements可以实现多个接口
7.必须重写接口中的方法
public interface TimeService { void time();}// interface 是关键字,接口都需要有实现类public interface UserService { //常量 public abstract final int age = 99; //接口中的所有定义都是抽象的 public abstract public abstract void add(String name); void delete(String name); void update(String name); void query(String name);}//抽象类extends//类 实现接口 implements 接口//实现接口中的类 就要重写接口中的方法//接口可以实现多继承public class UserServiceImp implements UserService,TimeService { @Override public void add(String name) { } @Override public void delete(String name) { } @Override public void update(String name) { } @Override public void query(String name) { } @Override public void time() { }}9.内部类
public class Outer { private int id = 11; public void out(){ System.out.println("外部类"); } public class inner{ public void out(){ System.out.println("内部类"); } //获得外部类的私有属性 public void GetId(){ System.out.println(id); } }}//一个java中只有一个public类,可以有多个class类class a{ public static void main(String[] args) { }}/** public static void main(String[] args) { Outer outer = new Outer(); //通过外部类实例化内部类 Outer.inner inner = outer.new inner(); inner.GetId(); }* */public class Outer { private int id = 11; public void out(){ System.out.println("外部类"); } public class inner{ public void out(){ System.out.println("内部类"); } //获得外部类的私有属性 public void GetId(){ System.out.println(id); } }}//一个java中只有一个public类,可以有多个class类class a{ public static void main(String[] args) { }}/** public static void main(String[] args) { Outer outer = new Outer(); //通过外部类实例化内部类 Outer.inner inner = outer.new inner(); inner.GetId(); }* */六、异常机制
1.异常定义

2.异常结构体
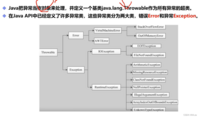
1.Error与Exception

Ctrl Alt T:自动生成抛出异常
3.异常处理机制与自定义异常


public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 0; int b = 1; try {//try监控区域 if(a==0){//throw throws throw new ArithmeticException();//主动抛出异常 } System.out.println(b/a); } catch (ArithmeticException e) {//catch 异常捕获 e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("程序出现异常,被除数不为0"); }finally {//处理善后工作 System.out.println("final"); } //可以不要finall,在 假设 IO 资源 关闭 //捕获多个异常 从小到大 try { new Test().a1(); } catch (RuntimeException e) { System.out.println("出现异常1"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("出现异常2"); } catch (Throwable e) { System.out.println("出现异常3"); } } public void a1(){ b1(); } public void b1(){ a1(); }}public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Test1().tset(10,0); } public void tset(int a,int b){ if(b==0){ throw new ArithmeticException();//主动抛出异常,一般用在方法中 } System.out.println(a/b); }}实际应用中的经验总结:
