C++ Sort函数详解
前言 :sort函数是algorithm库下的一个函数,sort函数是不稳定的,即大小相同的元素在排序后相对顺序可能发生改变,如果某些场景需要保持相同元素间的相对顺序,可使用stable_sort函数,这里不过多介绍。
一、sort函数调用的两种方式
| 方式一(默认) | void sort (RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last); |
|---|---|
| 方式二(自定义) | void sort (RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp); |
默认: 两个参数first,last,将[first, last)区间内元素升序排列。【注意区间为左闭右开】
自定义排序: 需用户指定排序规则Compare comp,将 [first, last)区间内的元素按照用户指定的顺序排列。
二、sort函数使用场景
由于在排序过程中涉及到元素交换等操作,所以sort函数仅支持可随机访问的容器,如数组, string、vector、deque等。
三、sort函数排序原理
sort()并非只是普通的快速排序,除了对普通的快速排序进行优化,它还结合了插入排序和堆排序。根据不同的数量级别以及不同情况,能自动选用合适的排序方法。当数据量较大时采用快速排序,分段递归。一旦分段后的数据量小于某个阀值,为避免递归调用带来过大的额外负荷,便会改用插入排序。而如果递归层次过深,有出现最坏情况的倾向,还会改用堆排序。
所以无论元素初始时为何种状态,sort()的平均排序复杂度为均为O(N*log2(N)) ,具有不错的的性能,在刷算法题时,可以直接使用sort()来对数据进行排序,而不需手动编写排序函数。
四、sort函数使用案例
1.升序排列
sort函数如果不传入第三个参数,则默认是升序排列。
#include<iostream>#include<vector>using namespace std;int main() { // 方式一、使用数组 int a[10] = {9, 6, 3, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, 1, 0}; sort(a, a + 10); // 10为元素个数 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << a[i] << ' ';// 输出排序后数组 cout << endl; // 方式二、使用 vector vector<int> arr = {9, 6, 3, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, 1, 0}; sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); // 10为元素个数 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << arr[i] << ' ';// 输出排序后数组 return 0;}2.降序排列
实现方式1实现降序排列,需传入第三个参数–比较函数,greater<type>(),这里的元素为int 类型,即函数为 greater<int>(); 如果是其他基本数据类型如float、double、long等也是同理。
#include<iostream>#include<vector>using namespace std;int main() { // 方式一、使用数组 int a[10] = {9, 6, 3, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, 1, 0}; sort(a, a + 10, greater<int>()); // 10为元素个数 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << a[i] << ' ';// 输出排序后数组 cout << endl;// 输出 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 // 方式二、使用 vector vector<int> arr = {9, 6, 3, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, 1, 0}; sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), greater<int>()); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << arr[i] << ' ';// 输出排序后数组 return 0;}我们也可以使用自定义的比较函数,函数的返回值为bool类型, 例如
bool cmp(int num1, int num2) { return num1 > num2; // 可以简单理解为 > 降序排列; < 升序排列}#include<iostream>#include<vector>using namespace std;bool cmp(int num1, int num2) { return num1 > num2; // 可以简单理解为 >: 降序排列; < : 升序排列}int main() { // 一、使用数组 int a[10] = {9, 6, 3, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, 1, 0}; sort(a, a + 10, cmp); // 使用自定义排序函数 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << a[i] << ' ';// 输出排序后数组 cout << endl;// 输出 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 // 二、使用 vector vector<int> arr = {9, 6, 3, 8, 5, 2, 7, 4, 1, 0}; sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), cmp); // 使用自定义排序函数 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << arr[i] << ' ';// 输出排序后数组 return 0;}3.结构体排序(自定义比较函数)
要对元素进行排序,前提是元素之间可以进行比较,即谁大谁小。 基本数据类型可直接进行大小比较, 但结构体元素之间的大小关系需要我们自己指定,如果不指定,则结构体之间大小关系就不确定,则不能够排序。
结构体排序案例1: 对学生信息进行排序
学生有姓名,分数两个属性,
struct Student { // 学生结构体 string name; // 学生姓名 int grade; // 学生分数 Student(); // 无参数构造函数 Student(string name, int grade) : name(name), grade(grade) {}; // 有参数构造函数};需求: 对一个班级内的学生成绩进行排序,首先按成绩进行排序降序排列,若成绩相同,则按照姓名字典顺序升序排列。
自定义排序函数bool cmp(Student s1, Student s2) { // 自定义排序 if (s1.grade != s2.grade) { // 如果学生成绩不相同 return s1.grade > s2.grade; // 则按照成绩降序排列 } return s1.name < s2.name; // 否则按照姓名升序排列}#include<iostream>#include<vector>using namespace std;struct Student { // 学生结构体 string name; // 学生姓名 int grade; // 学生分数 Student(); // 无参数构造函数 Student(string name, int grade) : name(name), grade(grade) {}; // 有参数构造函数};bool cmp(Student s1, Student s2) { // 自定义排序 if (s1.grade != s2.grade) { // 如果学生成绩不同 return s1.grade > s2.grade; // 则按照成绩降序排列 } return s1.name < s2.name; // 否则按照姓名升序排列}int main() { vector<Student> studs; studs.emplace_back("Bob", 80); studs.emplace_back("Ali", 90); studs.emplace_back("Ann", 85); studs.emplace_back("Liming", 90); studs.emplace_back("Trump", 79); studs.emplace_back("Fury", 58); studs.emplace_back("Jam", 62); studs.emplace_back("Lucy", 89); sort(studs.begin(), studs.end(), cmp); // 排序 for (int i = 0; i < studs.size(); i++) { // 输出结果 cout << studs[i].name << "\t" << studs[i].grade << endl; } return 0;}五、自定义comp函数返回true或false作用
bool cmp(int num1, int num2) {// 实现降序排列 return num1 > num2;// num1大于num2时返回true,否则返回false}自定义函数返回值为bool类型
true,则表示num1 与num2应该交换顺序;若返回false, 则num1 与num2 保持原有顺序; 下面举例说明自定义比较函数的执行过程。
对 2, 5, 1, 3, 4 降序排列调用cmp函数时,将5赋值给num1, 2赋值给num2 (注意顺序)5 > 2, 返回true,num1 与 num2需进行交换;即5应该在2的前面数组变为 5, 2, 1, 3, 4第二次 将3赋值给num1, 1赋值给num2,3 > 1, 返回true,num1 与 num2需进行交换;即3应该在1的前面数组变为 5, 2, 3, 1, 4之后经过数次的比较与交换最终排序完成。最终得到 5 4 3 2 1 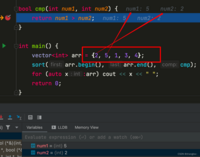
六、补充:匿名函数写法
有时自定义的排序函数比较简单,可以使用匿名函数的形式,这样会使代码更加简洁。
1.语法
在 C++ 中,匿名函数通常被称为 “lambda 表达式”。基本的 lambda 表达式语法如下:
[capture](parameters) -> return_type { function_body }return 语句,编译器可以自动推导返回类型,此时可以省略。function_body:函数体,包含了 lambda 表达式需要执行的代码。 一些细节:
当parameters为空的时候,()可以被省去,当body只有return或返回为void,那么”->return-type“可以被省去。
capture:
[] // 未定义变量.试图在Lambda内使用任何外部变量都是错误的.[x, &y] // x 按值捕获, y 按引用捕获.[&] // 用到的任何外部变量都隐式按引用捕获[=] // 用到的任何外部变量都隐式按值捕获[&, x] // x显式地按值捕获. 其它变量按引用捕获[=, &z] // z按引用捕获. 其它变量按值捕获案例1,简单的 lambda 表达式
auto sum = [](int a, int b) { return a + b; };cout << sum(1, 2); // 输出:3例中,lambda 表达式定义了一个接受两个 int 参数的函数,并返回它们的和。这个 lambda 表达式被赋值给了 sum 变量,然后我们调用 sum(1, 2) 来计算 1 + 2 的结果。
案例2,展示了如何在 lambda 表达式中捕获外部变量:
int factor = 2;auto multiply = [factor](int a) { return a * factor; };cout << multiply(3); // 输出:6例中,lambda 表达式捕获了外部变量 factor,并在函数体中使用它。请注意,因为 factor 是通过值捕获的,所以如果后面修改了 factor 的值,不会影响 multiply 的行为。
2. sort函数使用匿名函数
案例1#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <vector>using namespace std;int main() {vector<int> v(5);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) v[i] = i;// 使用匿名函数, 减少代码量sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int a, int b) { return a > b; // 降序排列}); for (int num : v) cout << num << endl;return 0;}案例2, 对上面学生排序使用匿名函数
#include<iostream>#include<vector>using namespace std;struct Student { // 学生结构体 string name; // 学生姓名 int grade; // 学生分数 Student(); // 无参数构造函数 Student(string name, int grade) : name(name), grade(grade) {}; // 有参数构造函数};int main() { vector<Student> studs; studs.emplace_back("Bob", 80); studs.emplace_back("Ali", 90); studs.emplace_back("Ann", 85); studs.emplace_back("Liming", 90); studs.emplace_back("Trump", 79); studs.emplace_back("Fury", 58); studs.emplace_back("Jam", 62); studs.emplace_back("Lucy", 89); sort(studs.begin(), studs.end(), [](Student s1, Student s2) { if (s1.grade != s2.grade) { // 如果学生成绩不同 return s1.grade > s2.grade; // 则按照成绩降序排列 } return s1.name < s2.name; // 否则按照姓名升序排列 }); for (int i = 0; i < studs.size(); i++) { // 输出结果 cout << studs[i].name << "\t" << studs[i].grade << endl; } return 0;}七、参考文章链接
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/sort/
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41575507/article/details/105936466
胡凡算法笔记