?个人主页?:孤寂大仙V
?收录专栏?:C++从小白到高手
?往期回顾?:C++异常
?流水不争,争的是滔滔不
一、智能指针简介二、为什么要用智能指针三、 RAII和智能指针auto_ptrunique_ptrshared_ptrshared_ptr的循环引用与weak_ptr 四、删除器
一、智能指针简介
智能指针是C++标准库中的一个重要概念,主要用于管理动态分配内存的对象。与传统指针不同,智能指针能够自动管理内存的分配和释放,从而减少内存泄漏和其他内存相关错误的风险。C++中主要有三种智能指针:std::unique_ptr、std::shared_ptr和std::weak_ptr。
二、为什么要用智能指针
像前面抛异常的捕获try、catch就非常容易造成内存泄漏。
#include <iostream>#include <stdexcept>void causeMemoryLeak() { int* ptr = new int(42); // 动态分配内存 // 模拟抛出异常 throw std::runtime_error("Something went wrong!"); // 此处如果异常未抛出,应该释放内存 delete ptr;}int main() { try { causeMemoryLeak(); } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cout << "Caught exception: " << e.what() << std::endl; // 这里 ptr 的内存没有被释放,造成内存泄漏 } return 0;}前面的C++异常中聊过,当throw执行时,throw后面的语句将不再被执行。所以当这里抛出runtime_error异常后,导致delete per被跳过。造成了内存泄漏。虽然我们可以通过对代码进行优化,以防止出现这种情况。但是如果用智能指针来对资源进行管理就会非常的方便。
C++98提供了std::auto_ptr
C++11提供了std::unique_ptr 、std::shared_ptr、std::weak_ptr
三、 RAII和智能指针
RAII是Resource Acquisition Is Initialization(资源获取即初始化)的缩写,他是⼀种管理资源的类的设计思想,本质是⼀种利用对象生命周期来管理获取到的动态资源,避免资源泄漏,这里的资源可以是内存、文件指针、网络连接、互斥锁等等。RAII在获取资源时把资源委托给⼀个对象,接着控制对资源的访问,资源在对象的生命周期内始终保持有效,最后在对象析构的时候释放资源,这样保障了资源的正常释放,避免资源泄漏问题。
#include <iostream>#include <memory>class Resource {public: Resource() { std::cout << "Resource acquired." << std::endl; } ~Resource() { std::cout << "Resource released." << std::endl; }};void useResource() { std::unique_ptr<Resource> resPtr(new Resource()); // RAII // 可以在这里使用 resPtr // 当函数结束,resPtr 超出作用域时,Resource 的析构函数会被调用}int main() { try { useResource(); } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << std::endl; } return 0; // 此时 Resource 的内存已经被释放,无需手动 delete}auto_ptr
auto_ptr是C++98时设计出来的智能指针,他的特点是拷贝时把被拷贝对象的资源的管理权转移给拷贝对象,这是⼀个非常糟糕的设计,因为他会到被拷贝对象悬空,访问报错的问题,C++11设计出新的智能指针后,强烈建议不要使用auto_ptr。其他C++11出来之前很多公司也是明令禁止使用这个智能指针的。
int main(){auto_ptr<int> p1(new int(1));auto_ptr<int> p2(p1);return 0;}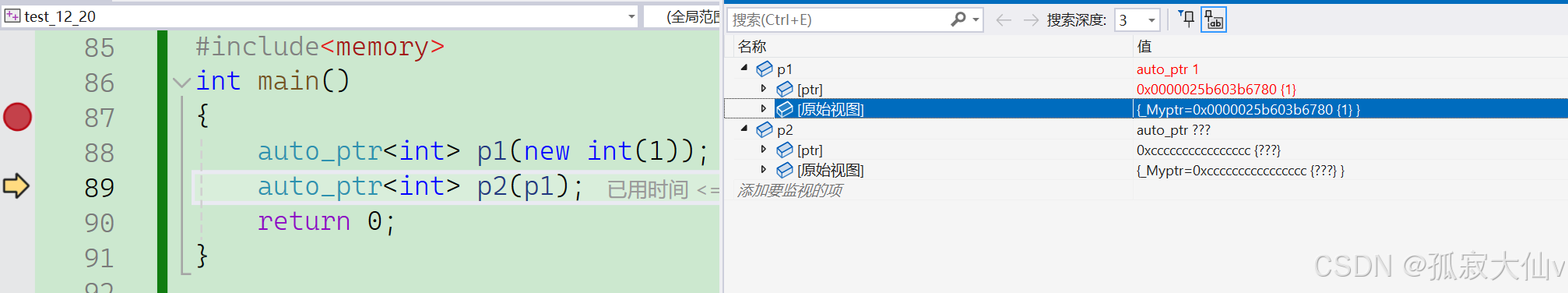

p2拷贝p1,p1的资源管理权给了p2。p1悬空,此时p1是空指针。如果这时访问p1程序就挂了。所以auto_ptr是一个非常糟糕的设计。
auto_ptr的简单模拟实现
namespace hbx{template<class T>class auto_ptr{public://构造auto_ptr(T* ptr):_ptr(ptr){}//拷贝构造auto_ptr(auto_ptr<T>& ap):_ptr(ap._ptr){ap._ptr=nullptr;//指针置为空,管理权转换}//赋值重载auto_ptr<T>& operator=(const auto_ptr<T>& ap){if (this != &ap){if (_ptr){delete _ptr;//释放被赋值对象的资源,这个对象是已经存在的被new出来的。}_ptr = ap._ptr;ap._ptr == nullptr;//赋完值把赋值对象的指针置为空}return *this;}~auto_ptr(){if (_ptr){delete _ptr;}}T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}private:T* _ptr;};}unique_ptr
unique_ptr是C++11设计出来的智能指针,他的名字翻译出来是唯一指针,他的特点的不支持拷贝,只支持移动。如果不需要拷贝的场景就非常建议使用他。不允许左值赋值操作,可以通过move使左值转化为右值。移动后,移动的对象的指针也悬空,要谨慎使用。
int main(){unique_ptr<Date> u1(new Date(1, 1, 1));unique_ptr<Date> u2(move(u1));//不支持拷贝,支持移动。但是也要谨慎使用u1照样悬空。return 0;}跟auto_ptr主要区别是,用unique_ptr那么程序员是知道移动对象是悬空的情况下使用。
unique_ptr的简单模拟实现
namespace hbx{template<class T>class unique_ptr{public://构造unique_ptr(T* ptr):_ptr(ptr){}//析构~unique_ptr(){if (_ptr){delete _ptr;}}//拷贝构造unique_ptr(const unique_ptr<T>& up) = delete;//复制重载unique_ptr<T>& operator=(const unique_ptr<T>& up) = delete;//移动构造unique_ptr(unique_ptr<T>&& up):_ptr(up._ptr){up._ptr = nullptr;}//移动赋值unique_ptr<T>& operator=(unique_ptr<T>&& up){if (_ptr){delete _ptr;}_ptr = up.ptr;up.ptr = nullptr;}T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}private:T* _ptr;};}int main(){hbx::unique_ptr<Date> u1(new Date(1, 1, 1));hbx::unique_ptr<Date> u2(move(u1));return 0;}shared_ptr
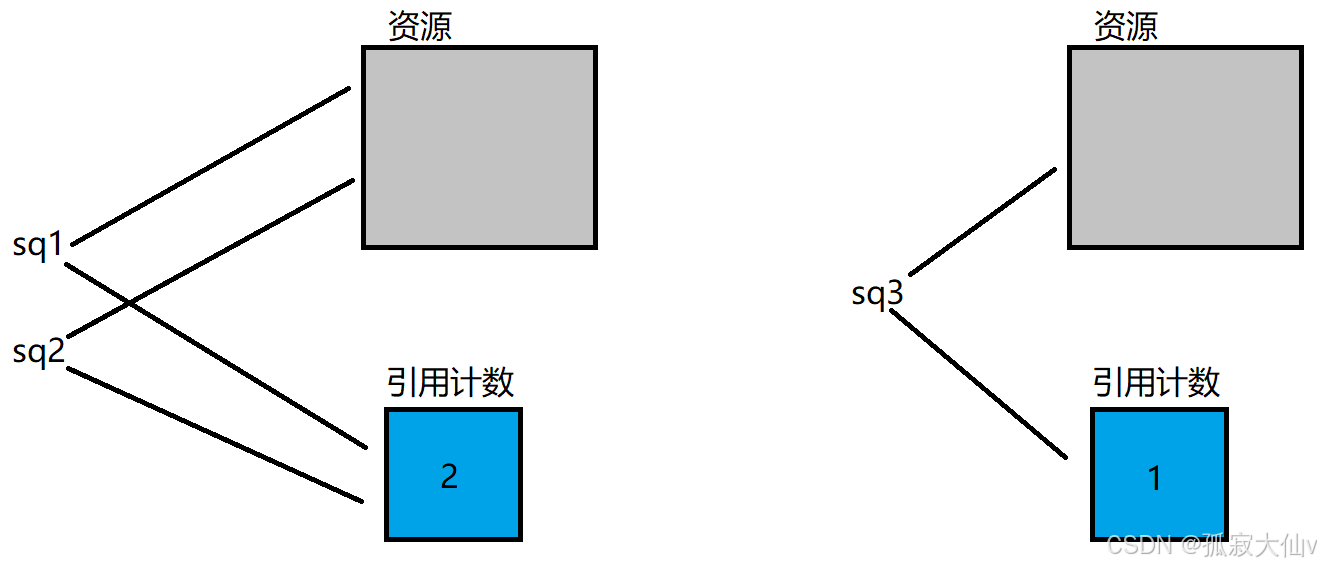
shared_ptr是C++11设计出来的智能指针,他的名字翻译出来是共享指针,他的特点是支持拷贝,也支持移动。如果需要拷贝的场景就需要使用他了。底层是用引用计数的方式实现的。
shared_ptr当复制或则拷贝的时候,引用计数+1,当智能指针析构的时候引用计数-1。如果引用计数为0,那么这块内存就没有资源了就释放它。
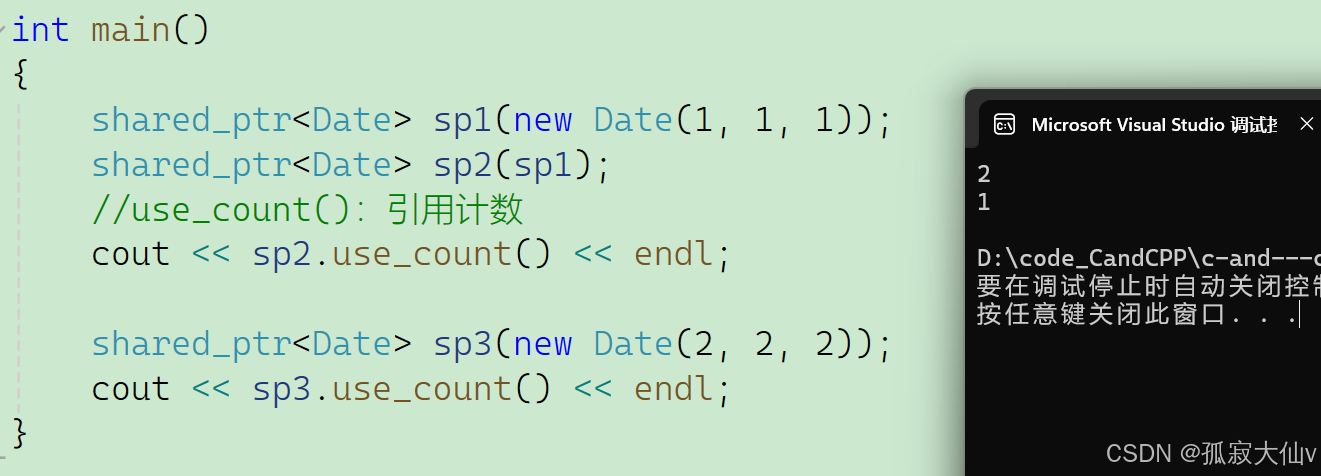
int main(){shared_ptr<Date> sp1(new Date(1, 1, 1));shared_ptr<Date> sp2(sp1);//use_count():引用计数cout << sp2.use_count() << endl;shared_ptr<Date> sp3(new Date(2, 2, 2));cout << sp3.use_count() << endl;}shared_ptr的简单模拟实现
namespace hbx{template<class T>class shared_ptr{public://构造shared_ptr(T* ptr):_ptr(ptr),_pcount(new int(1)){}//析构~shared_ptr(){if (--(*_pcount) == 0){delete _ptr;delete _pcount;}}//拷贝构造shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& ps):_ptr(ps._ptr), _pcount(ps._pcount){++(*_pcount);}//赋值重载shared_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& ps){if (--(*_pcount) == 0){delete _ptr;delete _pcount;}_ptr = ps._ptr;_pcount = ps._pcount;++(*_pcount);}T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}private:T* _ptr;int* _pcount;};}shared_ptr 除了支持用指向资源的指针构造,还支持 make_shared 用初始化资源对象的值直接构造。
#include <iostream>#include <memory>class MyClass {public: MyClass(int num) : data(num) { std::cout << "MyClass constructor called" << std::endl; } void printData() const { std::cout << "Data: " << data << std::endl; }private: int data;};int main() { // 使用make_shared直接初始化资源对象的值来构造shared_ptr std::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr = std::make_shared<MyClass>(10); ptr->printData(); return 0;}shared_ptr 和 unique_ptr 都支持了operator bool的类型转换,如果智能指针对象是⼀个空对象没有管理资源,则返回false,否则返回true,意味着我们可以直接把智能指针对象给if判断是否为空。
#include <iostream>#include <memory>class MyClass {public: MyClass(int num) : data(num) {} void printData() const { std::cout << "Data: " << data << std::endl; }private: int data;};int main() { // shared_ptr使用示例 std::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr1 = std::make_shared<MyClass>(20); if (ptr1) { ptr1->printData(); } else { std::cout << "ptr1 is empty" << std::endl; } std::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr2; if (ptr2) { ptr2->printData(); } else { std::cout << "ptr2 is empty" << std::endl; } // unique_ptr使用示例 std::unique_ptr<MyClass> uptr1 = std::make_unique<MyClass>(30); if (uptr1) { uptr1->printData(); } else { std::cout << "uptr1 is empty" << std::endl; } std::unique_ptr<MyClass> uptr2; if (uptr2) { uptr2->printData(); } else { std::cout << "uptr2 is empty" << std::endl; } return 0;}shared_ptr 和 unique_ptr 都得构造函数都使用explicit 修饰,防止普通指针隐式类型转换成智能指针对象。
#include <iostream>#include <memory>class MyClass {public: MyClass(int num) : data(num) {} void printData() const { std::cout << "Data: " << data << std::endl; }private: int data;};int main() { // shared_ptr使用示例 std::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr1 = std::make_shared<MyClass>(20); if (ptr1) { ptr1->printData(); } else { std::cout << "ptr1 is empty" << std::endl; } std::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr2; if (ptr2) { ptr2->printData(); } else { std::cout << "ptr2 is empty" << std::endl; } // unique_ptr使用示例 std::unique_ptr<MyClass> uptr1 = std::make_unique<MyClass>(30); if (uptr1) { uptr1->printData(); } else { std::cout << "uptr1 is empty" << std::endl; } std::unique_ptr<MyClass> uptr2; if (uptr2) { uptr2->printData(); } else { std::cout << "uptr2 is empty" << std::endl; } return 0;}shared_ptr的循环引用与weak_ptr
weak_ptr是C++11设计出来的智能指针,他的名字翻译出来是弱指针,他完全不同于上面的智能指针,他不支持RAII,也就意味着不能用它直接管理资源,weak_ptr的产生本质是要解决shared_ptr的⼀个循环引用导致内存泄漏的问题
hared_ptr大多数情况下管理资源非常合适,支持RAII,也支持拷贝。但是在循环引用的场景下会导致资源没得到释放内存泄漏,所以我们要认识循环引用的场景和资源没释放的原因,并且学会使用weak_ptr解决这种问题。
右边的节点什么时候释放呢,左边节点中的_next管着呢,_next析构后,右边的节点就释放了。_next什么时候析构呢,_next是左边节点的的成员,左边节点释放,_next就析构了。左边节点什么时候释放呢,左边节点由右边节点中的_prev管着呢,_prev析构后,左边的节点就释放了。_prev什么时候析构呢,_prev是右边节点的成员,右边节点释放,_prev就析构了。• 至此逻辑上成功形成回旋镖似的循环引用,谁都不会释放就形成了循环引用,导致内存泄漏
• 把ListNode结构体中的_next和_prev改成weak_ptr,weak_ptr绑定到shared_ptr时不会增加它的引用计数,_next和_prev不参与资源释放管理逻辑,就成功打破了循环引用,解决了这里的问题
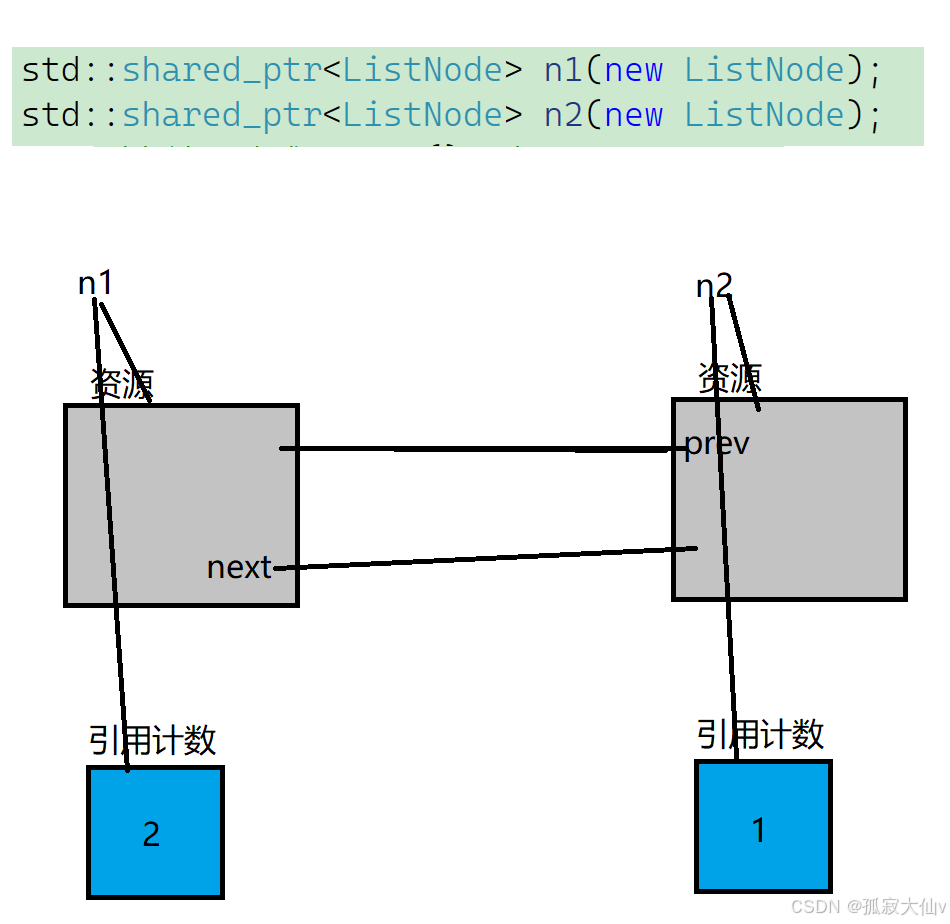
struct ListNode{int _data;std::shared_ptr<ListNode> _next;std::shared_ptr<ListNode> _prev;// 这里改成weak_ptr,当n1->_next = n2;绑定shared_ptr时// 不增加n2的引用计数,不参与资源释放的管理,就不会形成循环引用了/*std::weak_ptr<ListNode> _next;std::weak_ptr<ListNode> _prev;*/~ListNode(){cout << "~ListNode()" << endl;}};int main(){// 循环引用 -- 内存泄露std::shared_ptr<ListNode> n1(new ListNode);std::shared_ptr<ListNode> n2(new ListNode);cout << n1.use_count() << endl;cout << n2.use_count() << endl;n1->_next = n2;n2->_prev = n1;cout << n1.use_count() << endl;cout << n2.use_count() << endl;// weak_ptr不支持管理资源,不支持RAII// weak_ptr是专⻔绑定shared_ptr,不增加他的引用计数,作为⼀些场景的辅助管理//std::weak_ptr<ListNode> wp(new ListNode);return 0;}weak_ptr不支持RAII,也不支持访问资源,所以我们看文档发现weak_ptr构造时不支持绑定到资源,只支绑定到shared_ptr,绑定到shared_ptr时,不增加shared_ptr的引用计数,那么就可以解决上述的循环引用问题。
weak_ptr也没有重载operator*和operator->等,因为他不参与资源管理,那么如果它绑定的shared_ptr已经释放了资源,那么他去访问资源就是很危险的。weak_ptr支持expired检查指向的资源是否过期,use_count也可获取shared_ptr的引用计数,weak_ptr想访问资源时,可以调用lock返回⼀个管理资源的shared_ptr,如果资源已经被释放,返回的shared_ptr是⼀个空对象,如果资源没有释放,则通过返回的shared_ptr访问资源是安全的。
当weak_ptr的expired函数返回值为 0(在 C++ 中,0 通常代表false)时,这意味着weak_ptr所关联shared_ptr仍然有效,即对应的对象尚未被销毁。打印出来引用计数是2,weak_pt不增加计数但是不代表不指向计数。

weak_ptr所关联的share_ptr过期了

调用lock返回⼀个管理资源的shared_ptr,如果资源已经被释放,返回的shared_ptr是⼀个空对象,如果资源没有释放,则通过返回的shared_ptr访问资源是安全的。

四、删除器
智能指针析构时默认是进行delete释放资源,这也就意味着如果不是new出来的资源,交给智能指针管理,析构时就会崩溃。智能指针支持在构造时给⼀个删除器,所谓删除器本质就是⼀个可调用对象,这个可调用对象中实现你想要的释放资源的方式,当构造智能指针时,给了定制的删除器,在智能指针析构时就会调用删除器去释放资源。
因为new[]经常使用,所以为了简洁⼀点,unique_ptr和shared_ptr都特化了⼀份[]的版本,管理new []的资源。
unique_ptr<Date[]> up1(newDate[5]);shared_ptr<Date[]> sp1(new Date[5]); 定制删除器还有lambda版本和仿函数版本
在shared_ptr下建议使用lambda版本
class Fclose{public: void operator()(FILE* ptr) { cout << "fclose:" << ptr << endl; fclose(ptr); }};template<class T>void DeleteArrayFunc(T* ptr){ delete[] ptr;}int main(){std::shared_ptr<Date> sp1(new Date);std::shared_ptr<Date[]> sp2(new Date[10]);//lambda版本 bit::shared_ptr<Date> sp3(new Date[10], [](Date* ptr) {delete[] ptr; }); //仿函数版本 std::shared_ptr<Date> sp4(new Date[5], DeleteArrayFunc<Date>);//文件操作//lambda版本shared_ptr<FILE> sp6(fopen("Test.cpp", "r"), [](FILE* ptr) {fclose(ptr);});//仿函数版本std::shared_ptr<FILE> sp5(fopen("Test.cpp", "r"), Fclose()); }在unique_ptr下建议使用仿函数版本
class Fclose{public: void operator()(FILE* ptr) { cout << "fclose:" << ptr << endl; fclose(ptr); }};std::unique_ptr<Date> up1(new Date);std::unique_ptr<Date[]> up2(new Date[10]);//lambda版本auto fcloseFunc = [](FILE* ptr) {fclose(ptr); };std::unique_ptr<FILE, decltype(fcloseFunc)> up4(fopen("Test.cpp", "r"), fcloseFunc);//仿函数版本std::unique_ptr<FILE, Fclose> up3(fopen("Test.cpp", "r"));