前端
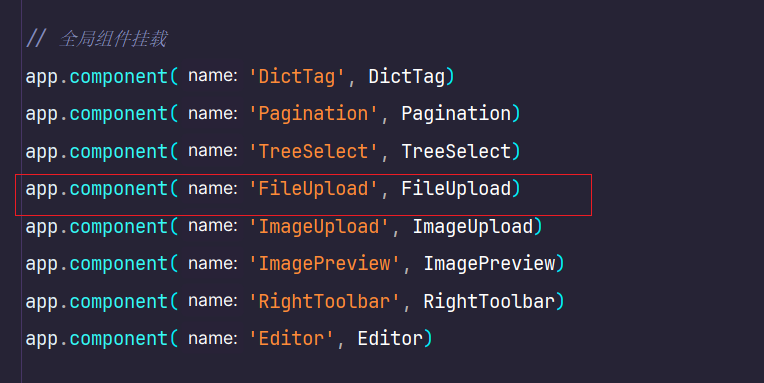
ry的前端文件上传单独写了一个FileUpload.Vue文件。在main.js中进行了全局的注册,可以在页面中直接使用文件上传的组件。全局导入
在main.js中
import 组件名称 from '@/components/FileUpLoad'app.compoent(组件名称) //全局挂载组件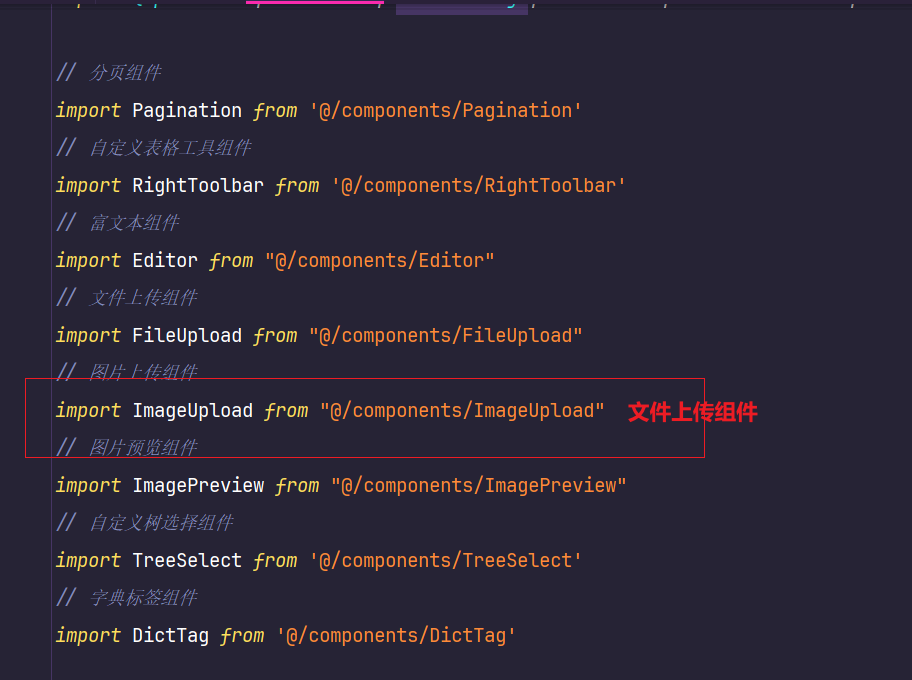
在项目中使用
组件命令 中间有一个-。因为这是两个大写的单词拼接在一起的<el-form-item label="选择文件" prop="file"> <file-upload v-model="fileData"/></el-form-item>对于上传FileUpload组件。
使用element-plus的el-upload组件
<el-upload multiple 允许多个文件上传 :action="uploadFileUrl" 上传的地址 :before-upload="handleBeforeUpload" 在山川之间检查 :file-list="fileList" :limit="limit" :on-error="handleUploadError" :on-exceed="handleExceed" :on-success="handleUploadSuccess" :show-file-list="false" :headers="headers" //请求头 class="upload-file-uploader" ref="fileUpload" //拿到这个fileupload > //展示上传的文件列表 <transition-group class="upload-file-list el-upload-list el-upload-list--text" name="el-fade-in-linear" tag="ul"> <li :key="file.uid" class="el-upload-list__item ele-upload-list__item-content" v-for="(file, index) in fileList"> <el-link :href="`${baseUrl}${file.url}`" :underline="false" target="_blank"> <span class="el-icon-document"> {{file.fileName}}</span> </el-link> <div class="ele-upload-list__item-content-action"> <el-link :underline="false" @click="handleDelete(index)" type="danger">删除</el-link> </div> </li> </transition-group>
上传文件需要携带token。所以需要导入
import { getToken } from "@/utils/auth"; //请求头是键值对的形式const headers = ref({ Authorization: "Bearer " + getToken() });//上传组件绑定:headers="headers"基本的方法包括 上传之前需要校验文件格式和大小、文件数量、成功回调函数、失败回调函数、删除文件、上传结束。
defineProps 是 Vue 3 中的一个组合式 API,用于在组件中定义接收的 props。它允许你声明组件的属性及其类型和默认值,使得组件能够接收父组件传递的数据。具体功能如下:
定义父组件传过来的内容
const props = defineProps({ modelValue: [String, Object, Array], // 数量限制 limit: { type: Number, default: 10, }, // 大小限制(MB) fileSize: { type: Number, default: 100, }, // 文件类型, 例如['png', 'jpg', 'jpeg'] fileType: { type: Array, default: () => ["doc", "xls", "ppt", "txt", "pdf",'mp3'], }, // 是否显示提示 isShowTip: { type: Boolean, default: true }});文件数据
//上传的数据const uploadList = ref([]); //这个是每一次点击上传后的内容const fileList = ref([]); //所有的文件列表上传成功回调函数
function handleUploadSuccess(res, file) { if (res.code ==200) { //将后端返回的数据赋值给uploadlist数组 uploadList.value.push({ fileName: res.data.fileName, url: res.data.url }); uploadedSuccessfully(); } else { number.value--; proxy.$modal.closeLoading(); proxy.$modal.msgError(res.msg); proxy.$refs.fileUpload.handleRemove(file); uploadedSuccessfully(); }}function uploadedSuccessfully() { if (number.value > 0 && uploadList.value.length === number.value) { //fileList 加上uploadlist fileList.value = fileList.value.concat(uploadList.value); //将filelist床穿给父组件 emit("update:modelValue", fileList.value); proxy.$modal.closeLoading(); uploadList.value = []; number.value = 0; }}v-model的语法糖使用。
emit 向父组件传递消息在 Vue 3 中,`v-model` 语法糖用于实现双向数据绑定,默认情况下,它实际上是通过发出 `update:modelValue` 事件与父组件进行通信的。### 工作原理1. **v-model 绑定**: - 当你在父组件中使用 `v-model="fileData"` 时,Vue 会自动将其转换为 `:modelValue="fileData"` 和 `@update:modelValue="value => fileData = value"` 的组合。2. **子组件的 emit**: - 在子组件中,调用 `emit("update:modelValue", fileList.value);` 会发出 `update:modelValue` 事件,并将当前的 `fileList.value` 作为新值传递。3. **父组件接收更新**: - 父组件通过 `@update:modelValue` 监听这个事件,接收到的值会自动更新到 `fileData` 中,实现双向绑定。### 总结因此,使用 `v-model` 使得父组件能够方便地接收子组件通过 `emit("update:modelValue", ...)` 发送的数据更新,从而实现了更简洁的状态管理和组件通信。watch(() => props.modelValue, val => { if (Array.isArray(val) && val.length) { fileList.value = val.map(item => { return { fileName: item.fileName || item, url: item.url || item, // uid: item.uid || new Date().getTime() uid: item.uid || new Date().getTime() }; }); } else { fileList.value = []; }}, { deep: true, immediate: true });这段代码使用 Vue 3 的 `watch` API 来监视 `props.modelValue` 的变化,并根据这个变化更新 `fileList`。具体来说,它的功能如下:### 代码分析1. **监视 `props.modelValue`**: ```javascript watch(() => props.modelValue, val => { ... }, { deep: true, immediate: true });() => props.modelValue:这是一个计算属性,用于获取 modelValue 的值。val:当 modelValue 发生变化时,这个回调函数将被调用,val 是新的值。 判断类型和内容:
if (Array.isArray(val) && val.length) { ... } else { fileList.value = []; }val 是否是一个数组且非空。如果是,执行下一步;否则,将 fileList.value 设置为空数组。 映射 fileList:
fileList.value = val.map(item => { ... });map 方法遍历 val 数组,将每个元素转换为一个对象,包含 fileName、url 和 uid。如果 item 没有提供 fileName 或 url,则使用 item 本身。 选项:
{ deep: true }:如果 modelValue 是一个嵌套对象,深度监视将确保任何内部属性的变化也会触发回调。{ immediate: true }:在组件初始挂载时立即调用回调,以便在初始渲染时更新 fileList。 总结
这段代码的主要作用是确保当 modelValue 更新时,fileList 也会随之更新,从而保持两个数据状态的一致性。如果 modelValue 是一个有效的数组,fileList 将根据其内容进行填充;如果不是,fileList 将被清空。这种方式适用于处理上传文件列表或类似的场景。